Notes For All Chapters Geography Class 8
People are a nation’s greatest resource. It is their ability and knowledge which turns them into the resource.
The way in which people are spread across the earth’s surface is known as a pattern of population distribution.
Nearly 90 percent of the world’s population lives in about 10% of the land surface.
High altitude areas, tropical deserts, high mountains and areas of equatorial forests are sparsely populated. Whereas South and Southeast Asia, Europe and northeastern North America are densely populated.
The number of people living in a unit area of the earth’s surface is called density of population.
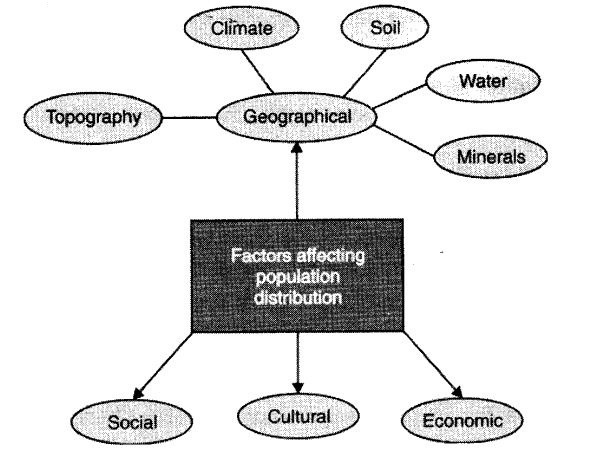
Topography, climate, soil, water, minerals, social, cultural and economic conditions are the important factors that affect the distribution of the population.
Change in the number of people during a specific time is known as population change. The important causes of population change are birth rate, death rate, and migration.
The difference between the birth rate and death rate is known as the growth rate of the population.
Rate of population growth varies across the world.
Population composition refers to the structure of the population. From population composition, we mean the number of males and females, age group they belong to, education level, occupational distribution, income level, social status, etc.
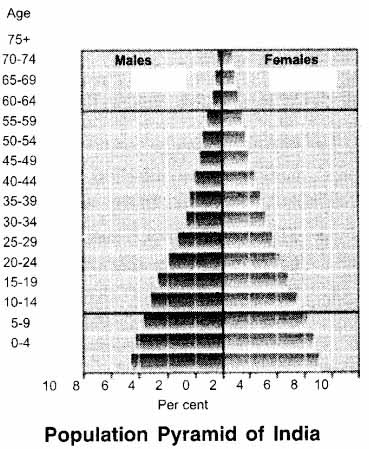
A population pyramid, also called the age and sex pyramid, helps us to understand the composition of population in any country.
Human beings are the most important resource of a nation. They are significant because had they not utilised their brains, the other resources of nature would not have found any utility. In other words, human resource is the ultimate resource.
The way in which people are spread across the earth’s surface is known as the pattern of population distribution. Some areas are very crowded (high density) while some are less crowded (low density). Population density depends on the climate conditions and topography of the place, like few people live in high latitude areas, tropical deserts, mountainous terrains, and forest areas, whereas a large number of people reside in plains.
The density of population is defined as the average number of people living in a unit area of the earth’s surface. The density of a particular region is calculated by dividing the population of the region by its area.
Topography, favourable climate, fertility of soils, availability of fresh water, minerals are major geographical factors affecting population density of a region. People prefer to live on plains more than mountains or plateaus and they live more in moderate climates than extreme hot or cold. From the agriculture point of view, fertile lands are preferred. Areas with mineral deposits are more populated.
Some social factors that boost the density of population in a region are better housing, education and health facilities.
Places with cultural or historical significance are usually populated.
Employment opportunities are another attraction for large chunks of population.
The term population change refers to change in the population with respect to time. The population of the world is never stable; the number of births and deaths affect its change.
With better health facilities due to development in medical science, now the number of deaths is lower than before.
Birth rate is a statistic that measures the number of live births per 1000 people. Death rate is a statistic that measures the number of deaths per 1000 people.
When we talk of the population of a particular region, country or continent, and not the whole world, then along with birth and death rate, another factor affecting population change is migration. Migration refers to the movement of people from one area to another.
Since births and deaths are natural causes of population change, the difference between the birth and death rate is called the natural death rate.
People leaving a country are called emigrants and the phenomenon is called emigration. People arriving in a country’are called immigrants and the phenomenon is called immigration. People usually migrate from less developed areas to more developed ones, in search for better employment opportunities, among other facilities.
The pattern of population change is different for different parts of the world.
The structure of the population with various respects Age like age, sex, literacy, occupations, health facilities, 75+ economic condition, etc is called population composition.
A population pyramid is a pictorial way to describe 55-59 the population composition. An age-sex pyramid of India is shown in the figure.
The shape of population pyramid of a country is indicative of a lot of information about the country.
The size towards the bottom may be used to 20-24 estimate the birth rate, while the size towards the top to estimate the death rate.
The youngsters (ages 0-15) and senior citizens (aged 65 above) are said to fall under the “dependent” group.
They are considered to be economically inactive; they depend on the working class for their living. The middle age group constitutes the working class.
A population pyramid in which the base is broad and the top part is narrow means that although a large amount of births take place, not all grow up to be adults and old; it means many die before reaching these ages. This indicates a large death rate and Kenya shows such a pyramid. This means a high population growth rate.
In countries like India, the death rate is decreasing, so the pyramid is broad in the younger age groups, and the size of the pyramid decreases steadily.
Human Resources: Human beings who are healthy, educated, and mentally strong can prove to be useful for a country or community and are treated as resources themselves, called human resources.
Population: The total number of people living in a particular region is said to be the population of that particular region.
The pattern of Population Distribution: The way in which people are spread across the earth’s surface is known as the pattern of population distribution.
Population Density: The average number of people living in a unit area of a particular region, calculated by dividing the total population of the region by the total area of that region, is called the population density of that region.
Population Change: The change in the population, when described over a certain length of time, is called population change.
Birth Rate: Birth rate is a statistic that measures the number of live births per 1000 people.
Death Rate: Death rate is a statistic that measures the number of deaths per 1000 people.
Life Expectancy: Life expectancy is the number of years that an average person can expect to live, calculated according to existing data for the particular region.
Migration: Migration refers to the movement of people from one area to another.
Natural Death Rate: The difference between the birth and death rate is called a natural death rate.
Emigrants/Emigration: People leaving a country are called emigrants and the phenomenon is called emigration.
Immigrants/Immigration: People arriving in a country are called immigrants and the phenomenon is called immigration.
Population Composition: The structure of the population with various respects like age, sex, literacy, occupations, health facilities, economic condition, etc is called population composition.
Population Pyramid: A population pyramid is a pictorial way to describe the population composition.

Leave a Reply