Notes For All Chapters – Science Curiosity Class 8
The Amazing World of Solutes, Solvents, and Solutions
1. Mixtures: Uniform and Non-uniform
- When sugar or salt dissolves in water → a uniform mixture is formed (solution).
- When chalk powder, sand, or sawdust is mixed with water → a non-uniform mixture is formed.
- Uniform mixtures = Solutions (components not seen separately).
- Non-uniform mixtures = Components remain separate and visible.
2. Solute, Solvent, and Solution
1. Solute: The substance that dissolves (smaller quantity).
2.Solvent: The substance in which solute dissolves (larger quantity).
3. Solution: Uniform mixture of solute and solvent.
- Example: Salt in water → Salt = solute, Water = solvent.
- Example: Sugar syrup (Gulab Jamun chashni) → Sugar = solute, Water = solvent.
- Example: Air → Nitrogen (largest amount) = solvent, Oxygen, Carbon dioxide, Argon = solutes.
3. How Much Solute Can Dissolve in Solvent?
- At first, solute dissolves completely.
- After a stage, no more solute dissolves → saturation point reached.
Types of Solutions
- Unsaturated Solution → More solute can dissolve at that temperature.
- Saturated Solution → No more solute can dissolve at that temperature.
- Concentrated Solution → Contains large amount of solute.
- Dilute Solution → Contains small amount of solute.
Solubility
- Maximum solute that dissolves in a fixed amount of solvent at a particular temperature.
4. Effect of Temperature on Solubility (Solids in Liquids)
- Generally, solubility increases with temperature.
- Example: Baking soda dissolves more in hot water than in cold water.
- A solution saturated at lower temperature may become unsaturated if heated.
5. Solubility of Gases in Liquids
- Many gases dissolve in water (e.g., oxygen).
- Dissolved oxygen is necessary for aquatic life.
Effect of Temperature:
- As temperature increases → solubility of gases decreases.
- Cold water dissolves more oxygen → supports aquatic life.
- Warm water → less oxygen dissolved → harmful for aquatic life.
6. Floating and Sinking in Water
- Some objects float (oil, husk), some sink (rice, sand).
- Common belief: lighter objects float, heavier objects sink.
- Actual reason → depends on density of the substance.
7. Density
- Definition: Mass per unit volume.
- Formula:
- Units:
- SI unit → kg/m³.
- Common units → g/mL, g/cm³.
Relative Density
- Comparison with water:
- No unit. Example: Aluminium has relative density = 2.7 (2.7 times denser than water).
8. Measuring Mass
- Measured using a balance (digital or traditional).
- Mass = quantity of matter.
Note: Mass ≠ Weight.
- Mass → amount of matter (kg, g).
- Weight → force of gravity on object (Newton, N).
9. Measuring Volume
For liquids: Measured using a measuring cylinder (5 mL, 10 mL, 50 mL, 100 mL etc.).
- Read volume at bottom of meniscus (curved surface).
- For coloured liquids → read at top of meniscus.
For regular solids (cuboid, box, dice):Volume=l×w×h
For irregular solids (stone, key):
- Use water displacement method in a measuring cylinder.
- Volume of water displaced = Volume of object.
10. Density Calculation
- Once mass and volume are known → Density = Mass ÷ Volume.
- Example: Mass = 16.4 g, Volume = 5 cm³ → Density = 3.28 g/cm³.
11. Effect of Temperature on Density
- Heating → particles spread apart → volume increases → density decreases.
- Cooling → particles come closer → volume decreases → density increases.
- Example: Hot air rises because it is less dense. (Hot air balloon principle).
12. Effect of Pressure on Density
- Gases: Increase in pressure → particles come closer → density increases.
- Liquids and Solids: Hardly affected by pressure because particles are already close.
13. Why Does Ice Float on Water?
- Water has highest density at 4°C.
- When water freezes at 0°C → it expands → occupies more volume → density decreases.
- Ice becomes lighter than water → floats.
- Floating ice keeps water below it warm enough for aquatic life to survive.
14. Examples and Applications
- Egg in water: Egg sinks in normal water, but floats if salt is added (water becomes denser).
- Oil packets: 1 L oil weighs less than 1 kg → oil is less dense than water.
- Bamboo rafts: Bamboo is hollow and light → floats easily.
- Earth’s layers: Density increases from crust to inner core.
15. Snapshots (Summary Points)
- Solution = Uniform mixture.
- Solute = Dissolving substance.
- Solvent = Medium in which solute dissolves.
- Saturated solution = Cannot dissolve more solute.
- Unsaturated solution = Can dissolve more solute.
- Solubility of solids ↑ with temperature.
- Solubility of gases ↓ with temperature.
- Density = Mass ÷ Volume.
- Density ↓ when temperature ↑.
- Pressure affects gases most.
- Ice floats on water because it is less dense.
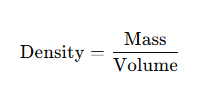
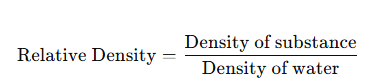

Helpful and good notes ☺️
Best thank you
these notes are very effecient but these are some small i want some big notes
👏🏻👍🏻