Solutions For All Chapters – Science Class 8
Light: Mirrors and Lenses
Keep the curiosity alive
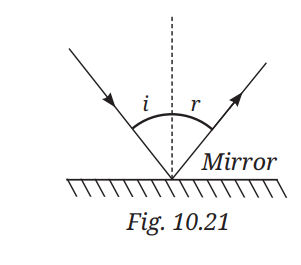
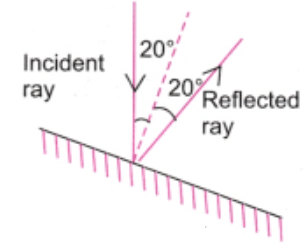
1. A light ray is incident on a mirror and gets reflected by it (Fig. 10.21). The angle made by the incident ray with the normal to the mirror is 40°. What is the angle made by the reflected ray with the mirror?
(i) 40° (ii) 50° (iii) 45° (iv) 60°
Answer:- (ii) 50°
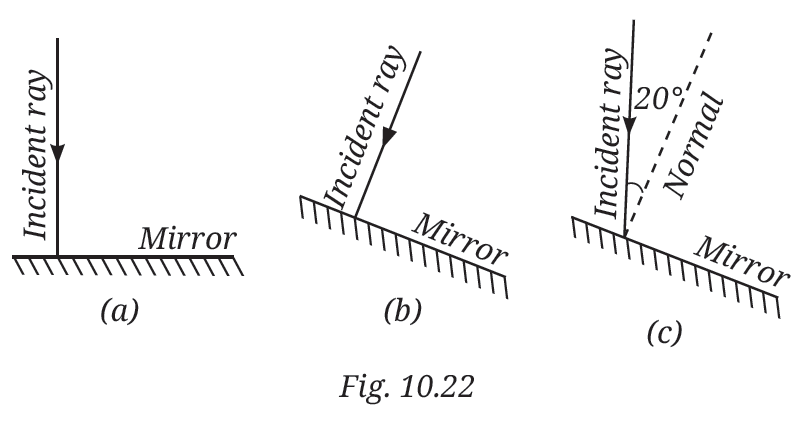
2. Fig. 10.22 shows three different situations where a light ray falls on a mirror:
(i) The light ray falls along the normal.
(ii) The mirror is tilted, but the light ray still falls along the normal to the tilted surface.
(iii) The mirror is tilted, and the light ray falls at an angle of 20° from the normal.
Draw the reflected ray in each case (Use a ruler and protractor for accurate drawing).
What is the angle of reflection in each case?
(i) The light ray falls along the normal.
Answer:–
Angle of incidence = 0°
Angle of reflection = 0°
The ray retraces its path. It reflects straight back along the same line.
(ii) The mirror is tilted, but the light ray still falls along the normal to the tilted surface.
Answer:–
Even though the mirror is tilted, the ray is still perpendicular to the surface.
Angle of incidence = 0°
Angle of reflection = 0°
The ray again retraces its path — the tilt doesn’t affect the reflection if the ray is normal to the surface.
(iii) The mirror is tilted, and the light ray falls at an angle of 20° from the normal.
Answer:–
Angle of incidence = 20°
By the law of reflection:
Angle of reflection = 20°
The reflected ray will make a 20° angle with the normal, on the opposite side.
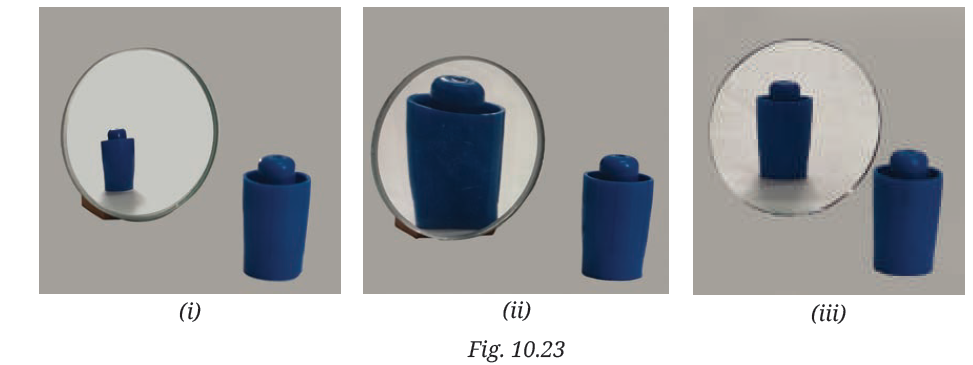
3. In Fig. 10.23, the cap of a sketch pen is placed in front of three types of mirrors.
Match each image with the correct mirror.
Answer:-
| Image | Mirror Type |
|---|---|
| i | Convex Mirror |
| ii | Concave Mirror |
| iii | Plane Mirror |
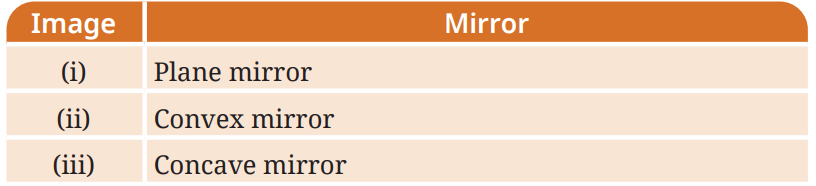
4. In Fig. 10.24 the cap of a sketch pen is placed behind a convex lens, a concave lens, and a flat transparent glass piece – all at the same distance.
Match each image with the correct type of lens or glass.
Answer:-
| Image | Lens / Glass Type |
|---|---|
| i | Convex Lens |
| ii | Concave Lens |
| iii | Flat Transparent Glass Piece |
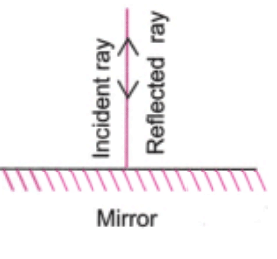
5. When the light is incident along the normal on the mirror,which of the following statements is true:
(i) Angle of incidence is 90°
(ii) Angle of incidence is 0°
(iii) Angle of reflection is 90°
(iv) No reflection of light takes place in this case
Answer:- (ii) Angle of incidence is 0°
When light hits a surface at a 90° angle (perpendicular), it is considered to be incident normally.
Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection: In reflection, the angle of the reflected light is always equal to the angle of the incident light. Since the light is hitting the mirror normally (at a 0° angle), the reflected light will also be at a 0° angle.
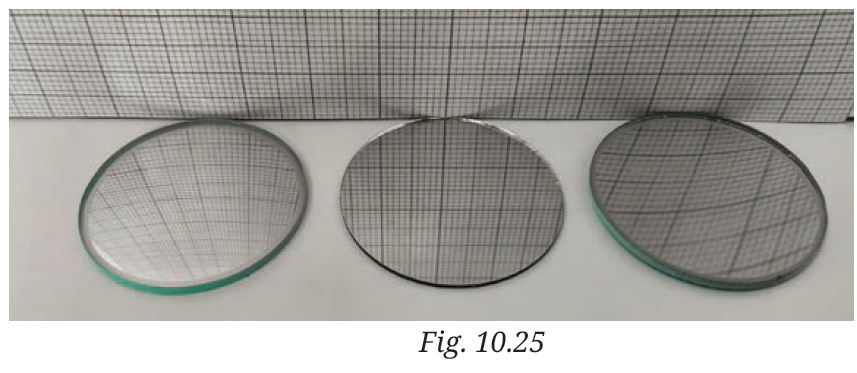
6. Three mirrors-plane, concave and convex are placed in Fig. 10.25. On the basis of the images of the graph sheet formed in the mirrors, identify the mirrors and write their names above the mirrors.
Answer:
(i) Left Mirror: Convex Mirror
(ii) Middle Mirror: Plane Mirror
(iii) Right Mirror: Concave Mirror
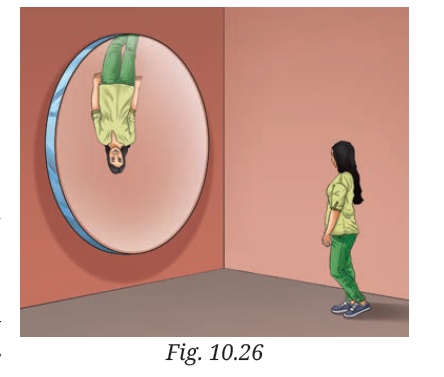
7. In a museum, a woman walks towards a large convex mirror (Fig. 10.26). She will see that:
(i) her erect image keeps decreasing in size.
(ii) her inverted image keeps decreasing in size.
(iii) her inverted image keeps increasing in size and eventually it becomes erect and magnified.
(iv) her erect image keeps increasing in size.
Answer: (iv) her erect image keeps increasing in size.
8. Hold a magnifying glass over text and identify the distance where you can see the text bigger than they are written. Now move it away from the text. What do you notice? Which type of lens is a magnifying glass?
Answer: When you hold a magnifying glass over some text, you can see the letters appear bigger when the glass is held at the right distance. This distance is close to the object but not too close. As you move the magnifying glass away, the text becomes blurred and smaller.
This happens because a magnifying glass is a convex lens, which is thicker in the middle and converges light rays. It forms an enlarged, erect image of the object when it is placed close to the lens.
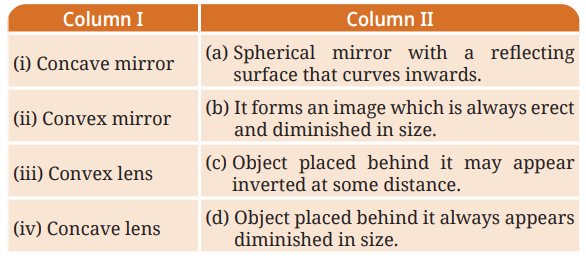
9. Match the entries in Column I with those in Column II
Answer:-
| Column I | Column II |
|---|---|
| (i) Concave mirror | (a) Spherical mirror with a reflecting surface that curves inwards. |
| (ii) Convex mirror | (b) It forms an image which is always erect and diminished in size. |
| (iii) Convex lens | (c) Object placed behind it may appear inverted at some distance. |
| (iv) Concave lens | (d) Object placed behind it always appears diminished in size. |
10. The following question is based on Assertion/Reason.
Assertion: Convex mirrors are preferred for observing the traffic behind us.
Reason: Convex mirrors provide a significantly larger view area than plane mirrors.
Choose the correct option:
(i) Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
(ii) Both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not the correct explanation for Assertion.
(iii) Assertion is correct but Reason is incorrect.
(iv) Both Assertion and Reason are incorrect.
Answer:- (i) Both Assertion and Reason are correct and Reason is the correct explanation for Assertion.
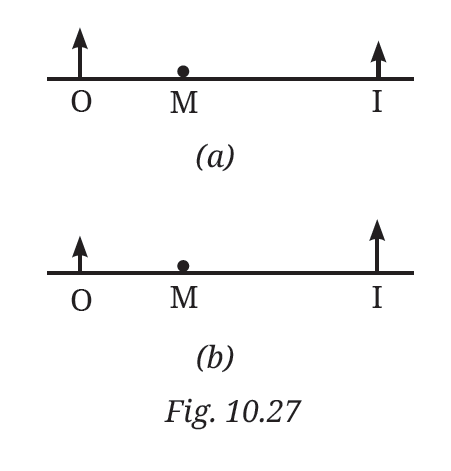
11. In Fig. 10.27, note that O stands for object, M for mirror, and I for image.
Which of the following statements is true?
(i) Figure (a) indicates a plane mirror and Figure (b) indicates a concave mirror.
(ii) Figure (a) indicates a convex mirror and Figure (b) indicates a concave mirror.
(iii) Figure (a) indicates a concave mirror and Figure (b) indicates a convex mirror.
(iv) Figure (a) indicates a plane mirror and Figure (b) indicates a convex mirror.
Answer:- (ii) Figure (a) indicates a convex mirror and Figure (b) indicates a concave mirror.
12. Place a pencil behind a transparent glass tumbler (Fig. 10.28a). Now fill the tumbler halfway with water (Fig. 10.28b). How does the pencil appear when viewed through the water? Explain why its shape appears changed.
Answer:- When you place a pencil behind a transparent glass tumbler (Fig. 10.28a) and then fill the tumbler halfway with water (Fig. 10.28b), the pencil appears bent or distorted when viewed through the water. This happens because light rays bend as they pass from the air into the water due to refraction. Refraction occurs when light changes speed while traveling from one medium (air) to another (water) with a different density, causing the light rays to change direction. This bending of light makes the part of the pencil in the water appear to be at a different angle than the part in the air, giving the illusion that the pencil’s shape has changed.




Leave a Reply