Solutions For All Chapters – Science Class 8
The Invisible Living World: Beyond Our Naked Eye
Keep the curiosity alive
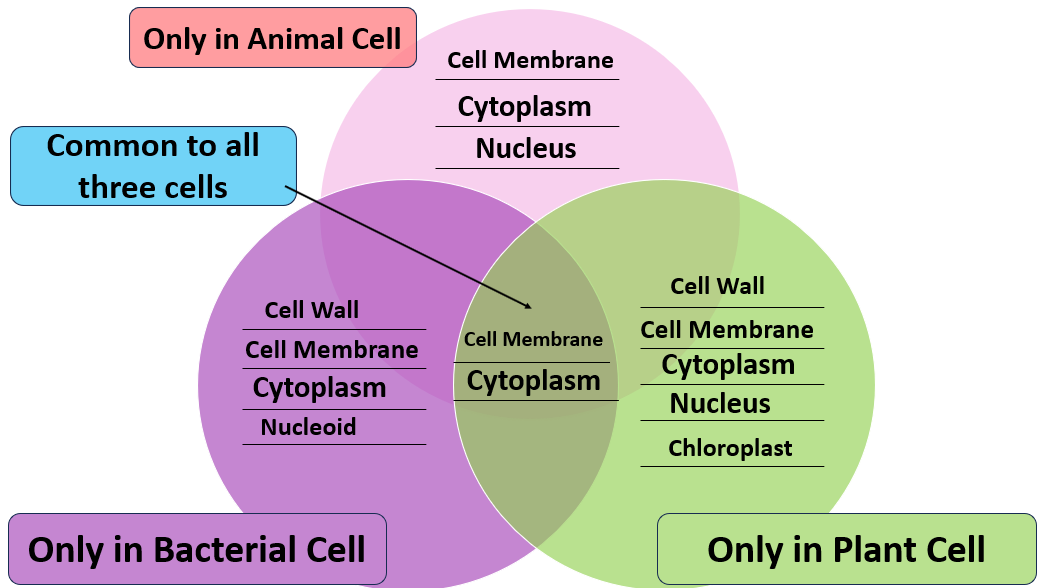
1. Various parts of a cell are given below.Write them in the appropriate places in the following diagram.
Nucleus Cytoplasm
Chloroplast Cell wall
Cell membrane Nucleoid
Answer :-
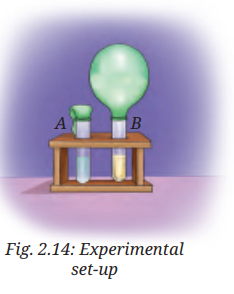
2. Aanandi took two test tubes and marked them A and B. She put two spoonfuls of sugar solution in each of the test tubes. In test tube B, she added a spoonful of yeast. Then she attached two incompletely inflated balloons to the mouth of each test tube. She kept the set-up in a warm place, away from sunlight.
(i) What do you predict will happen after 3-4 days? She observed that the balloon attached to testtube B was inflated. What can be a possible explanation for this?
(a) Water evaporated in test tube B and filled the balloon with the water vapour.
(b) The warm atmosphere expanded the air inside the test tube B, which inflated the balloon.
(c) Yeast produced a gas inside the test tube B which inflated the balloon.
(d) Sugar reacted with warm air, which produced gas, eventually inflating the balloon.
Answer :- The correct answer is (c) Yeast produced a gas inside the test tube B which inflated the balloon. This happens because yeast, a type of microorganism, ferments the sugar solution and releases carbon dioxide gas, which fills and inflates the balloon.
(ii) She took another test tube, 1/4 filled with lime water. She removed the balloon from test tube B in such a manner that the gas inside the balloon did not escape. She attached the balloon to the test tube with lime water and shook it well. What do you think she wants to find out?
Answer :- Aanandi wants to find out if the gas produced by yeast in test tube B contains carbon dioxide. When the balloon is attached to the test tube with lime water and shaken, the lime water will turn milky if carbon dioxide is present, as it reacts with lime water to form calcium carbonate.
3. A farmer was planting wheat crops in his field. He added nitrogen-rich fertiliser to the soil to get a good yield of crops. In the neighbouring field, another farmer was growing bean crops, but she preferred not to add nitrogen fertiliser to get healthy crops. Can you think of the reasons?
Answer :- The farmer growing bean crops did not need to add nitrogen-rich fertilizer because bean plants, like other legumes, have a special relationship with Rhizobium bacteria. These bacteria live in root nodules of the bean plants and can trap nitrogen from the air, converting it into a form that the plants can use to grow healthy. This natural process helps maintain soil fertility, reducing the need for additional nitrogen fertilizers.
4. Snehal dug two pits, A and B, in her garden. In pit A, she put fruit and vegetable peels and mixed it with dried leaves. In pit B, she dumped the same kind of waste without mixing it with dried leaves. She covered both the pits with soil and observed after 3 weeks. What is she trying to test?
Answer :- Snehal is trying to test how mixing dried leaves with fruit and vegetable peels affects the decomposition process. She wants to see if the combination in pit A, which includes dried leaves, helps microorganisms break down the waste into manure faster or more effectively compared to pit B, where only the peels are used without dried leaves. This experiment shows the role of microorganisms and the right conditions, like adding dry material, in making nutrient-rich manure.
5. Identify the following microorganisms:
(i) I live in every kind of environment, and inside your gut
Answer:- Bacteria
(ii) I make bread and cakes soft and fluffy.
Answer:- Yeast
(iii) I live in the roots of pulse crops and provide nutrients for their growth.
Answer:- Rhizobium
6. Devise an experiment to test that microorganisms need optimal temperature, air, and moisture for their growth.
Answer:- To test that microorganisms need optimal temperature, air, and moisture for their growth, you can follow this experiment:
Materials needed: 4 small containers, bread slices, water, plastic wrap, a warm place (e.g., near a heater), a cool place (e.g., refrigerator), and a notebook.
Steps:
- Take four bread slices and label the containers as A, B, C, and D.
- For container A (control), sprinkle a little water on the bread, cover it loosely with plastic wrap to allow air, and keep it at room temperature.
- For container B, sprinkle water on the bread, seal it tightly with plastic wrap to block air, and keep it at room temperature.
- For container C, do not add water to the bread, cover it loosely with plastic wrap, and keep it at room temperature.
- For container D, sprinkle water on the bread, cover it loosely with plastic wrap, and place it in a refrigerator.
- Observe all containers after 3-5 days and note any growth of mold or microorganisms.
Observations:
- Container A should show mold growth because it has optimal moisture, air, and room temperature.
- Container B may show little or no growth due to lack of air.
- Container C may show little or no growth due to lack of moisture.
- Container D may show little or no growth due to low temperature.
Conclusion: This experiment shows that microorganisms need the right balance of moisture, air, and temperature to grow, with room temperature being more optimal than a cold environment.
7. Take 2 slices of bread. Place one slice in a plate near the sink. Place the other slice in the refrigerator. Compare after three days. Note your observations. Give reasons for your observations
Answer:- Observations:
- After three days, the bread slice placed near the sink likely shows mold growth, appearing fuzzy or discolored (e.g., green, white, or black).
- The bread slice in the refrigerator likely shows little or no mold growth, remaining mostly unchanged.
Reasons:
- The bread near the sink is in a warm, moist environment with air, which are ideal conditions for microorganisms like mold to grow. The sink area may also have more spores from the air or water splashes.
- The refrigerator provides a cold temperature, which slows down or stops the growth of microorganisms because they need warmth to thrive. The lack of optimal temperature limits their activity on the bread slice kept there.
8. A student observes that when curd is left out for a day, it becomes more sour. What can be two possible explanations for this observation?
Answer:- Two possible explanations for the curd becoming more sour when left out for a day are:
1. The Lactobacillus bacteria in the curd continue to feed on the lactose (sugar in milk) and produce more lactic acid, which increases the sourness over time.
2. The warm temperature outside the refrigerator helps the bacteria grow and ferment the curd faster, leading to more lactic acid production and a stronger sour taste.
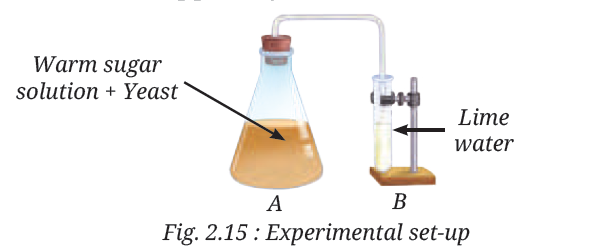
9. Observe the set-up given in Fig. 2.15 and answer the following questions.
(i) What happens to the sugar solution in flask A?
Answer:- In flask A, the sugar solution with yeast undergoes fermentation. The yeast breaks down the sugar into alcohol and carbon dioxide gas, causing bubbles to form in the solution.
(ii) What do you observe in test tube B after four hours? Why do you think this happened?
Answer:- In test tube B, after four hours, the lime water turns milky or cloudy. This happens because the carbon dioxide gas produced by the yeast in flask A passes into the lime water, reacting with it to form calcium carbonate, which makes it appear milky.
(iii) What would happen if yeast was not added in flask A?
Answer:- If yeast was not added in flask A, there would be no fermentation, and no carbon dioxide gas would be produced. As a result, the lime water in test tube B would remain clear, with no change observed.

Leave a Reply