Solutions For All Chapters – Science Class 8
Exploring Forces
Keep the curiosity alive
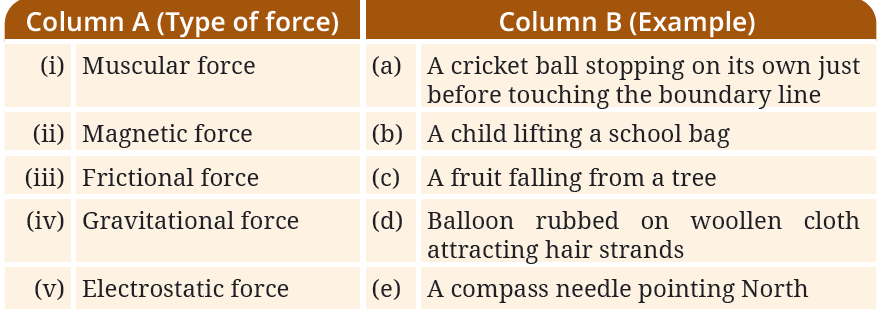
1. Match items in Column A with the items in Column B.
Answer:-
| Column A (Type of force) | Column B (Example) |
|---|---|
| (i) Muscular force | (b) A child lifting a school bag |
| (ii) Magnetic force | (e) A compass needle pointing North |
| (iii) Frictional force | (a) A cricket ball stopping on its own |
| (iv) Gravitational force | (c) A fruit falling from a tree |
| (v) Electrostatic force | (d) Balloon attracting hair strands |
2. State whether the following statements are True or False.
(i) A force is always required to change the speed of motion of an object.
Answer: True
(ii) Due to friction, the speed of the ball rolling on a flat ground increases.
Answer: False
(iii) There is no force between two charged objects placed at a small distance apart.
Answer: False
3. Two balloons rubbed with a woollen cloth are brought near each other. What would happen and why?
Answer: When two balloons rubbed with a woollen cloth are brought near each other, they will move away from each other, meaning they will repel each other.
Why: When balloons are rubbed with a woollen cloth, they gain electrical charges, becoming charged objects. Both balloons get the same type of charge (either both positive or both negative). Since like charges repel each other, the balloons push away from one another due to the electrostatic force, which is a force that acts between charged objects even when they are not touching.
4. When you drop a coin in a glass of water, it sinks, but when you place a bigger wooden block in water, it floats. Explain.
Answer:- When you drop a coin in a glass of water, it sinks because the gravitational force acting on the coin (its weight) is greater than the buoyant force (upthrust) applied by water.
On the other hand, when you place a bigger wooden block in water, it floats because the buoyant force acting on the block is equal to or greater than the weight of the block.
This happens because the wooden block is less dense than water, and water applies an upward force (called buoyant force) which balances its weight, making it float.
So, whether an object sinks or floats depends on the balance between gravitational force and buoyant force.
5. If a ball is thrown upwards, it slows down, stops momentarily, and then falls back to the ground. Name the forces acting on the ball and specify their directions
(i) During its upward motion
Answer:- The gravitational force acts downwards (towards the Earth). The ball moves upwards, but due to the downward force of gravity, its speed decreases.
(ii) During its downward motion
Answer:- The gravitational force still acts downwards. This force increases the speed of the ball as it falls back to the ground.
(iii) At its topmost position
Answer:- The gravitational force continues to act downwards. The ball stops momentarily, meaning its speed becomes zero for an instant before starting to fall down.
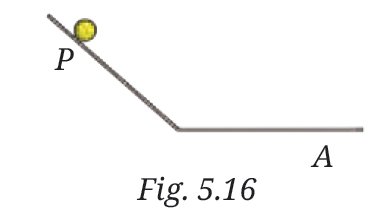
6. A ball is released from the point P and moves along an inclined plane and then along a horizontal surface as shown in the Fig. 5.16. It comes to stop at the point A on the horizontal surface. Think of a way so that when the ball is released from the same point P, it stops (i) before the point A (ii) after crossing the point A.
Answer:-
(i) To make the ball stop before point A: Place a rough surface on the horizontal path (between P and A).
This increases friction, which will slow down the ball faster and make it stop before point A.
(ii) To make the ball stop after crossing point A:Place a smooth surface or reduce the friction on the path from P to A.
This allows the ball to keep rolling longer because there is less friction, so it stops after point A.
7. Why do we sometimes slip on smooth surfaces like ice or polished floors? Explain.
Answer: – We sometimes slip on smooth surfaces like ice or polished floors because of the reduced force of friction between our shoes and the surface. Friction is the force that helps us walk by providing grip between our feet and the ground. On smooth surfaces, there are fewer irregularities for the shoes to lock onto, so the friction is very low. This makes it easier for our feet to slide instead of staying in place, causing us to slip. For example, ice is extremely smooth and slippery, and polished floors also have a low friction due to their shiny, even surface, making it hard to maintain balance.
8.Is any force being applied to an object in a non-uniform motion?
Answer:- Yes, a force is being applied to an object in non-uniform motion.This is because non-uniform motion means the object’s speed or direction is changing, and a force is always required to cause such changes. Therefore, the presence of non-uniform motion indicates that a force is acting on the object.
9. The weight of an object on the Moon becomes one-sixth of its weight on the Earth. What causes this change? Does the mass of the object also become one-sixth of its mass on the Earth?
Answer:- The weight of an object on the Moon becomes one-sixth of its weight on the Earth because weight is the gravitational force with which a planet pulls an object, and the Moon has a much weaker gravitational force than the Earth. This weaker gravity is due to the Moon’s smaller size and mass compared to the Earth, causing it to pull objects with less force. The mass of the object, however, does not change. Mass is the amount of matter in an object and remains the same everywhere, whether on Earth or the Moon. Only the weight changes due to the difference in gravitational force.
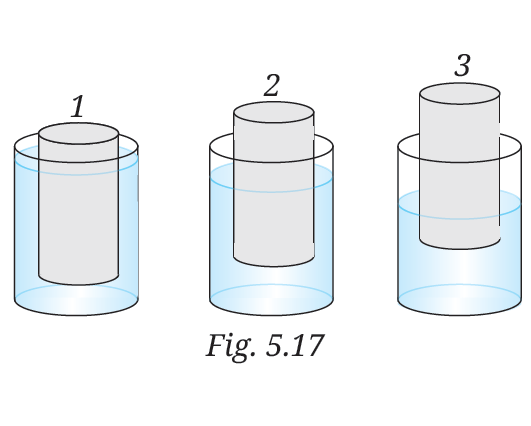
10. Three objects 1, 2, and 3 of the same size and shape but made of different materials are placed in the water.They dip to different depths as shown in Fig. 5.17. If the weights of the three objects 1, 2, and 3 are w1 ,w2 and w3, respectively, then
(i) w1=w2=w3
(ii)w1>w2>w3
(iii)w2>w3>w1
(iv)w3>w1>w2
Answer:- (ii) w1>w2>w3

I agree with 🙋🏻♂️👍🏻
nice new books and easy to understand