Solutions For All Chapters – Science Class 8
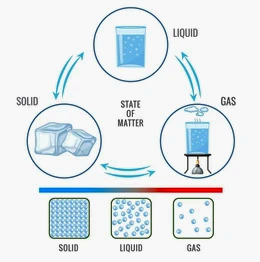
Particulate Nature of Matter
Keep the curiosity alive
1. Choose the correct option.
The primary difference between solids and liquids is that the constituent particles are:
(i) closely packed in solids, while they are stationary in liquids.
(ii) far apart in solids and have fixed position in liquids.
(iii) always moving in solids and have fixed position in liquids.
(iv) closely packed in solids and move past each other in liquids.
Answer:- (iv) closely packed in solids and move past each other in liquids.
2. Which of the following statements are true? Correct the false statements.
(i) Melting ice into water is an example of the transformation of a solid into a liquid.
Answer: True
(ii) Melting process involves a decrease in interparticle attractions during the transformation.
Answer: True
(iii) Solids have a fixed shape and a fixed volume.
Answer: True
(iv) The interparticle interactions in solids are very strong, and the interparticle spaces are very small.
Answer: True
(v) When we heat camphor in one corner of a room, the fragrance reaches all corners of the room.
Answer: True
(vi) On heating, we are adding energy to the camphor, and the energy is released as a smell.
Answer: False
Correction for (vi): On heating, we add energy to the camphor, which causes its particles to move faster and turn into a gas, spreading the fragrance throughout the room.
3. Choose the correct answer with justification. If we could remove all the constituent particles from a chair, what would happen?
(i) Nothing will change.
(ii) The chair will weigh less due to lost particles.
(iii) Nothing of the chair will remain.
Answer: (iii) Nothing of the chair will remain.
JUSTIFICATION:- Everything is made up of tiny particles. If all the particles that make up the chair are removed, then there will be nothing left. The chair would completely vanish because its entire structure is formed by those particles.
4. Why do gases mix easily, while solids do not?
Answer: Gases mix easily because their particles are far apart, have very weak interparticle attractions, and move freely in all directions. This allows gas particles to spread and mix with other gases quickly, like when smoke or fragrance fills a room. Solids, however, do not mix easily because their particles are closely packed, held together by strong interparticle attractions, and can only vibrate in fixed positions. This prevents solid particles from moving and mixing with other substances.
5. When spilled on the table, milk in a glass tumbler, flows and spreads out, but the glass tumbler stays in the same shape. Justify this statement.
Answer: Milk, a liquid, flows and spreads out when spilled on the table because its particles are loosely packed and have weaker interparticle attractions, allowing them to move past each other and take the shape of the surface they are on. The document explains that liquids have no fixed shape but a fixed volume, which is why milk spreads out. The glass tumbler, a solid, stays in the same shape because its particles are tightly packed with strong interparticle attractions, keeping them in fixed positions. This gives solids a definite shape and volume, so the tumbler does not change shape when milk is spilled.
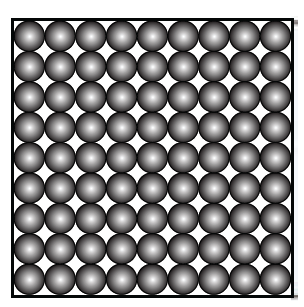
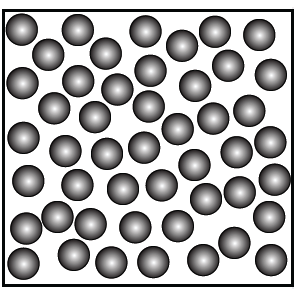
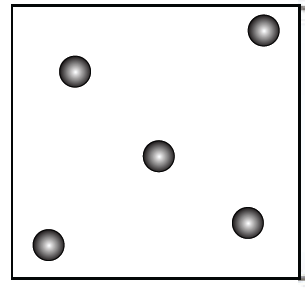
6. Represent diagrammatically the changes in the arrangement of particles as ice melts and transforms into water vapour.
Answer:
7. Draw a picture representing particles present in the following:
(i) Aluminium foil
(ii) Glycerin
(iii) Methane gas
Answer:
(i) Aluminium foil
(ii) Glycerin
(iii) Methane gas
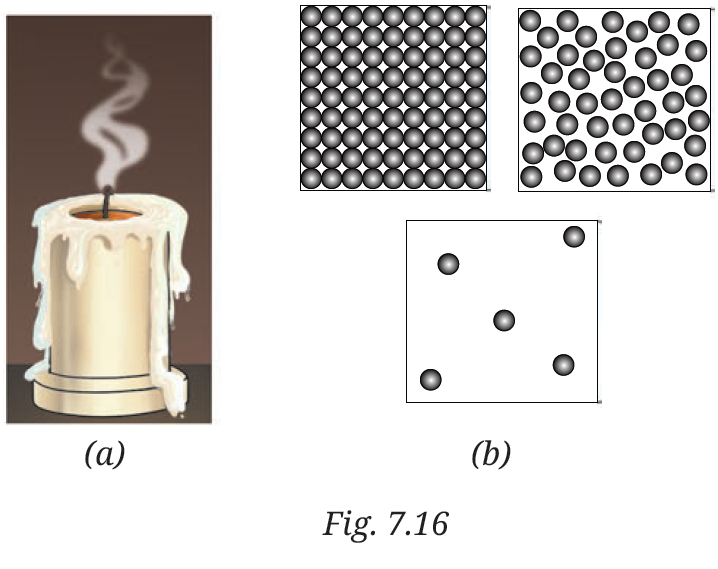
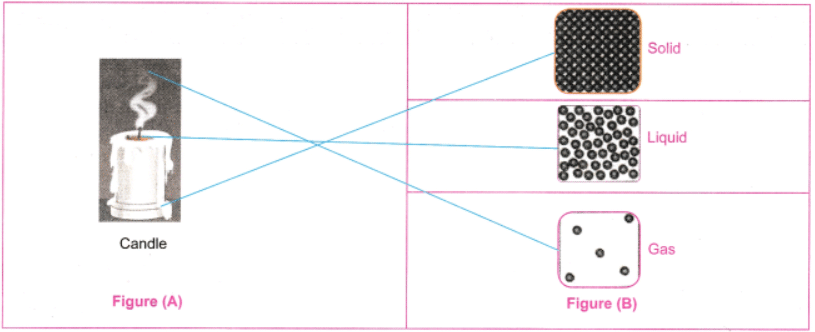
8. Observe Fig. 7.16a which shows the image of a candle that was just extinguished after burning for some time. Identify the different states of wax in the figure and match them with Fig. 7.16b showing the arrangement of particles.
Answer:
1. Solid wax (at base): Rigid, unmelted portion—matches tightly packed particles.
2.Liquid wax (melted pool): Flowing around wick—matches loosely arranged particles with movement.
3. Gaseous wax (vapour/smoke): Rising as fumes—matches widely spaced, freely moving particles.
The figure shows transitions: solid to liquid (melting) and liquid to gas (evaporation), with particle arrangements changing from fixed to mobile.
9. Why does the water in the ocean taste salty, even though the salt is not visible? Explain.
Answer: Ocean water tastes salty because it contains dissolved salts like sodium chloride. The salt is broken into tiny particles and mixes completely with water. These particles are too small to be seen with our eyes, but they are still present and give the salty taste.
10. Grains of rice and rice flour take the shape of the container when placed in different jars. Are they solids or liquids? Explain.
Answer: Grains of rice and rice flour are solids. They take the shape of the container when placed in different jars because, as solids, they consist of closely packed particles with strong interparticle attractions. However, unlike typical solids with a fixed shape, loose particles like rice grains and flour can shift and settle to fill the container’s shape due to gravity and the space between the particles. Their volume remains definite, and they do not flow like liquids, confirming they are solids.

This app is very useful for exams . the notes are very easy to understand and the MCQ test help to revise the chapter
This app and website provide short, clear, and easy-to-understand answers.
Thank you for sending me the question answer of particulate nature of matter for my exam which is written in clear and easy language
Thank you