Solutions For All Chapters – Science Class 8
The Amazing World of Solutes, Solvents, and Solutions
Keep the curiosity alive
1. State whether the statements given below are True [T] or False [F]. Correct the false statement(s).
(i) Oxygen gas is more soluble in hot water rather than in cold water.
→ False [F]
Correct Statement:- Oxygen gas is more soluble in cold water than in hot water.
(ii) A mixture of sand and water is a solution.
→ False [F]
Correct Statement:- A mixture of sand and water is a non-uniform mixture, not a solution.
(iii) The amount of space occupied by any object is called its mass
→ False [F]
Correct Statement:- The amount of space occupied by an object is called its volume.
(iv) An unsaturated solution has more solute dissolved than a saturated solution.
→ False [F]
Correct Statement:- An unsaturated solution has less solute than a saturated solution.
(v) The mixture of different gases in the atmosphere is also a solution.
→ True [T]
2. Fill in the blanks.
(i) The volume of a solid can be measured by the method of displacement,
where the solid is submerged in water and the rise in water level is measured.
(ii) The maximum amount of solute dissolved in solvent at a particular temperature
is called solubility at that temperature.
(iii) Generally, the density decreases with increase in temperature.
(iv) The solution in which glucose has completely dissolved in water,
and no more glucose can dissolve at a given temperature, is called a saturated
solution of glucose.
3. You pour oil into a glass containing some water. The oil floats on top. What does this tell you?
(i) Oil is denser than water
(ii) Water is denser than oil
(iii) Oil and water have the same density
(iv) Oil dissolves in water
Answer: (ii) Water is denser than oil
4. A stone sculpture weighs 225 g and has a volume of 90 cm³ .Calculate its density and predict whether it will float or sink in water.
Answer:
Density Calculation: The formula for density is: Density = Mass / Volume
Given:
- Mass of the stone sculpture = 225 g
- Volume = 90 cm³
Density = 225 g / 90 cm³ = 2.5 g/cm³
5. Which one of the following is the most appropriate statement, and why are the other statements not appropriate?
(i) A saturated solution can still dissolve more solute at a given temperature.
(ii) An unsaturated solution has dissolved the maximum amount of solute possible at a given temperature.
(iii) No more solute can be dissolved into the saturated solution at that temperature.
(iv) A saturated solution forms only at high temperatures.
Answer: – Most Appropriate Statement:
(iii) No more solute can be dissolved into the saturated solution at that temperature.
Why is this statement appropriate?
A saturated solution is one where the maximum amount of solute has been dissolved, and no more can dissolve at that temperature.
Why are the other statements not appropriate?
(i) Correct: A saturated solution cannot dissolve more solute at a given temperature.
(ii) Correct: An unsaturated solution can still dissolve more solute, not the maximum amount.
(iv) Correct: Saturated solutions can form at any temperature, not only at high temperatures.
6. You have a bottle with a volume of 2 litres. You pour 500 mL of water into it. How much more water can the bottle hold?
Answer: The bottle has a volume of 2 litres, which is 2000 mL
(since 1 litre = 1000 mL).
You pour 500 mL of water into it.
Amount of water the bottle can still hold = 2000 mL – 500 mL = 1500 mL.
The bottle can hold 1500 mL more water.
7. An object has a mass of 400 g and a volume of 40 cm³. What is its density?
Answer: The formula for density is:
Density = Mass / Volume
Given:
- Mass = 400 g
- Volume = 40 cm³
Density = 400 g / 40 cm³ = 10 g/cm³
8. Analyse Fig. 9.25a and 9.25b. Why does the unpeeled orange float, while the peeled one sinks? Explain.
Answer: In Fig. 9.25a, the unpeeled orange floats because its peel contains tiny air pockets. These air pockets increase the volume of the orange without adding much mass, making the orange less dense than water. As a result, it floats.
In Fig. 9.25b, the peeled orange sinks because removing the peel reduces its volume but the mass remains almost the same. This makes the peeled orange denser than water, so it sinks.
9. Object A has a mass of 200 g and a volume of 40 cm³. Object B has a mass of 240 g and a volume of 60 cm³. Which object is denser?
Answer:
The formula for density is: Density = Mass / Volume
For Object A:
- Mass = 200 g
- Volume = 40 cm³
- Density = 200 g / 40 cm³ = 5 g/cm³
For Object B:
- Mass = 240 g
- Volume = 60 cm³
- Density = 240 g / 60 cm³ = 4 g/cm³
Since 5 g/cm³ (Object A) is greater than 4 g/cm³ (Object B), Object A is denser.
10. Reema has a piece of modeling clay that weighs 120 g. She first moulds it into a compact cube that has a volume of 60 cm³ . Later, she flattens it into a thin sheet. Predict what will happen to its density.
Answer: Reema’s piece of modeling clay has a mass of 120 g and a volume of 60 cm³. When she moulds it into a cube, the density is:
Density = Mass / Volume = 120 g / 60 cm³ = 2 g/cm³
Later, when she flattens it into a thin sheet, the mass and volume stay the same, only the shape changes. Since density depends on mass and volume, and both remain unchanged, the density will also remain unchanged.
11. A block of iron has a mass of 600 g and a density of 7.9 g/cm³. What is its volume?
Answer: To find the volume of the iron block, we use the formula:
Density = Mass / Volume. Rearrange it to solve for volume:
Volume =Mass / Density. Given:
- Mass = 600 g
- Density = 7.9 g/cm³
Calculation:
- Volume = 600 g / 7.9 g/cm³ ≈ 75.95 cm³ (rounded to two decimal places).
The volume of the iron block is approximately 75.95 cm³.
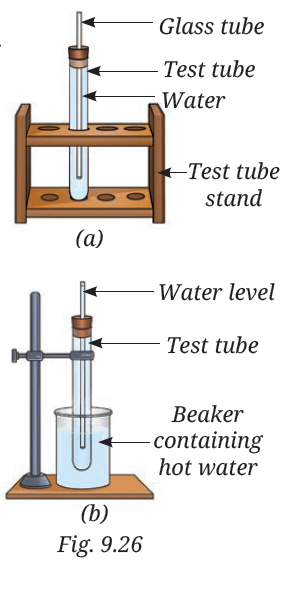
12. You are provided with an experimental setup as shown in Fig. 9.26a and 9.26b. On keeping the test tube (Fig 9.26b) in a beaker containing hot water (~70 °C), the water level in the glass tube rises. How does it affect the density?
Answer:- When the test tube is kept in a beaker containing hot water (~70 °C) as shown in Fig. 9.26b, the water level in the glass tube rises. This happens because the temperature of the water in the test tube increases. According to the concept of density (Density = Mass/Volume), when the temperature rises, the particles of the water expand and the volume increases, while the mass remains the same. As a result, the density of the water decreases. This decrease in density causes the water to rise in the glass tube due to the expansion and the principle of buoyancy.


best website to study