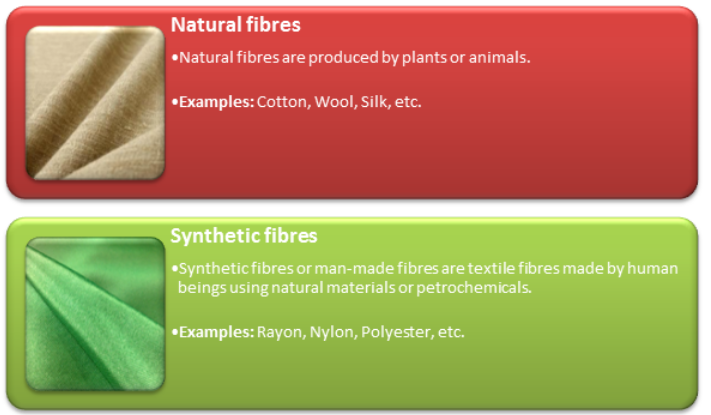
Fabrics are made by weaving fibres (or threads) obtained from natural or artificial sources. They can be of two types:
What are Synthetic Fibres?
What is a synthetic fibre made up of?
A synthetic fibre, as well as plastic, is made up of a chain of small units (called Monomers) which combine to form polymers.
Monomers: A monomer is a single molecule that can bond with other identical molecules to form polymers through a process called Polymerization.
Polymers: Polymer is a Greek word in which ‘poly’ means ‘many’ and ‘mer’ means units. Hence, polymers are large molecule made up of several molecules (or monomers) linked together.
Example of Polymers:
All synthetic fibres, such as Rayon and Nylon, are polymers.
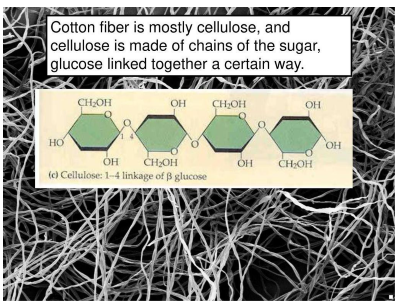
Polymers are also found in Nature. ‘Cotton’ is a polymer called ‘Cellulose’. ‘Cellulose’ is made up of a number of single units (or monomers) called ‘Glucose’.
Polymerization Reaction: The process of linking small monomers together to form polymers is called Polymerization.
Types of Synthetic Fibres
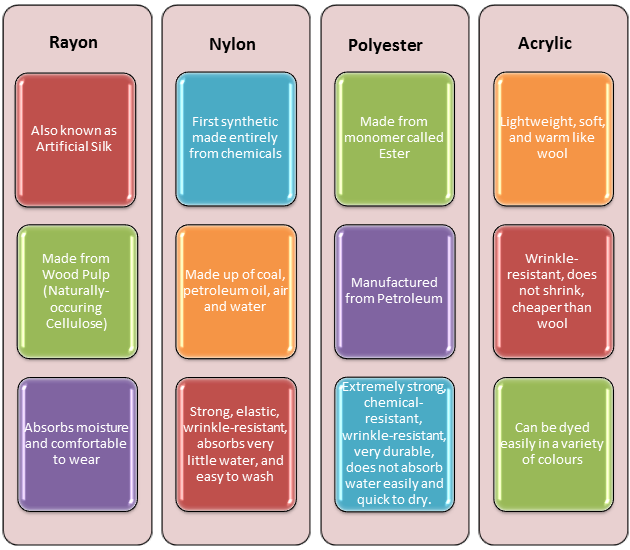
Rayon

Rayon is a versatile fibre and can imitate the feel and texture of silk, wool, cotton and linen with drape and slipperiness akin to nylon.
Why Rayon is called artificial silk?
Rayon resembles silk in appearance, texture and shine. Hence, it is also known as Artificial Silk.
Silk fibre was discovered in China and made from silkworms. It had a beautiful texture and was very costly. By the end of the 19th century, scientists managed to make an artificial silk-like fibre made by treating wood pulp chemically.
Uses of Rayon
This man-made fibre uses natural material (wood pulp) and can be woven like silk fibre. It is cheaper than silk and can be dyed in a variety of colours. It can be:
1. Make apparels like suits, slacks, jackets etc.
2. Make automobile tyre cords (because of its strength)
3. Mixed with cotton to make bedsheets and bedspreads
4. Mixed with wool to make carpets and blankets
5. Used to make other home furnishings, such as curtains and tablecloths
Nylon
Nylon is the first synthetic fibre to be prepared without using any natural raw materials (materials produced by plants and animals).
Which properties make Nylon suitable for:
Making Ropes used for Rock Climbing: Strong fibre, Lightweight, Weather Resistant
Making Fishing Nets: Strong, Elastic, Water Resistant
Making Tents: Strong, Light, Does Not Absorb Much Water, Dries Quickly
Uses of Nylon
Developed in 1931, this thermoplastic silky material is strong, elastic, light, lustrous and easy to wash. A nylon thread is, in fact, stronger than a steel wire. Hence, it is used to:
1. Make clothes (including socks)
2. Make parachutes as well as ropes for rock climbing
3. Make ropes, toothbrushes, and car seat belts etc.
4. Make tents, curtains, and sleeping bags
Polyester
Polyester fibre does not get wrinkled easily. Hence, a fabric made from this fibre is easy to wash and does not need to be ironed – which makes it suitable for dress material.
Polyester is made up of two words – ‘poly’ which means many, and ‘ester’ which is a chemical.
Esters are chemicals which give fruits their smell.
Name some types of Polyester fibres.
Some popular polyester fibres are:
Terylene (often known by brand name Dacron) which can be drawn into a very fine fibre and can be woven like any other yarn.
Polyethylene terephthalate (P.E.T.) is used for making wires, films, bottles, utensils and other products.
What are blended fibres? Give some examples.
Blended fibres are formed by mixing natural and synthetic fibres. Polyester is often used in blended fibres. For Example,
Polywool is made by mixing polyester and wool.
Polycot is made my mixing polyester and cotton.
Terrycot is made by mixing Terylene and cotton.
Uses of Polyester
Since polyester is strong, wrinkle-resistant and water-resistant, it has several uses. It can be used to:
Make a variety of textiles (including sarees, curtains, dress materials etc.) and can be blended with natural fibres (like cotton and wool)
Make films, magnetic recording tapes, etc (as Mylar)
Make sails of sailboats
Make water hoses for firefighting purposes
Acrylic
Acrylic is a strong, lightweight and warm synthetic fibre that resembles wool. It is available in a number of colours and is more durable and affordable than natural wool.
Acrylic fibre, fabric, plastic or paint are all made from acrylic acid. The word ‘acrylic’ means ‘containing acryl (or acrolein)’ Acrolein is the sharp and bitter liquid in onions and has its roots in two Latin words – ‘acer’ which means ‘sharp’, and ‘olere’ which means ‘to smell’.
Why storage of acrylic clothes is easier than woollen clothes?
Woollen clothes need naphthalene balls to protect them from attack by insects. Acrylic is synthetic wool and is hence, resistant to the action of moths and insects.
Uses of Acrylic Fibre
Acrylic can mimic wool as well as cotton at times and is hypoallergenic in nature. It means that people who have sensitive skin can wear it easily. Some acrylic fibres are very resilient – more than other natural or synthetic fibres. It can be used to:
Make woollen clothes like hats, scarves, gloves, sweaters, blankets, and other home-furnishing fabrics.
Make fake fur used for making toys and fur accessories.
Make garments for babies (as the fabric is machine-washable).
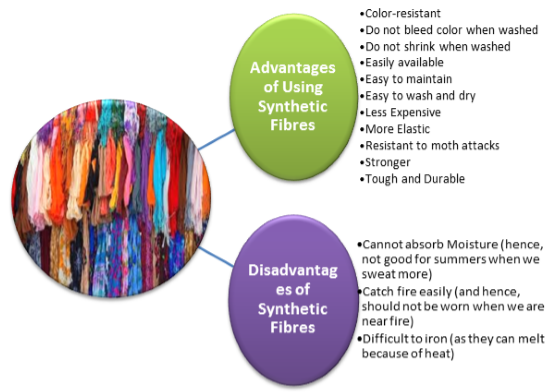
Characteristics of Synthetic Fibres
What are synthetic fibres made up of?
All the synthetic fibres are manufactured by processing raw materials of petroleum origin in a number of ways. The raw materials of petroleum origin are called Petrochemicals.
Why should we not wear synthetic clothes in the kitchen?
Synthetic fibres melt on heating. If the clothes catch fire, the fabric made up of synthetic fibres will melt and stick to one’s body. Hence, it is recommended that one should not wear synthetic clothes while working in the kitchen or laboratory.
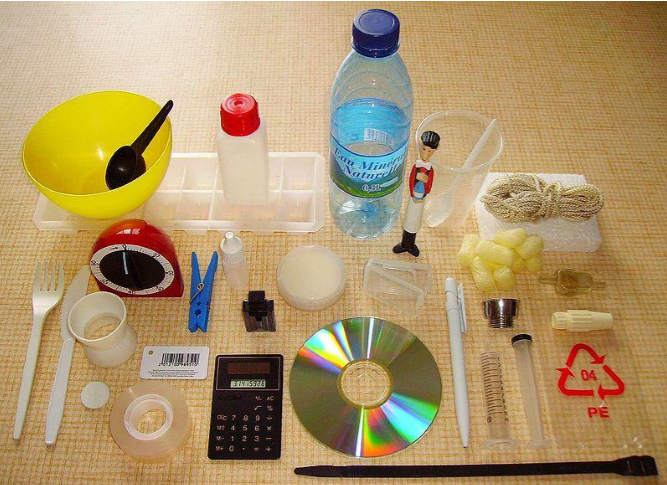
Plastics
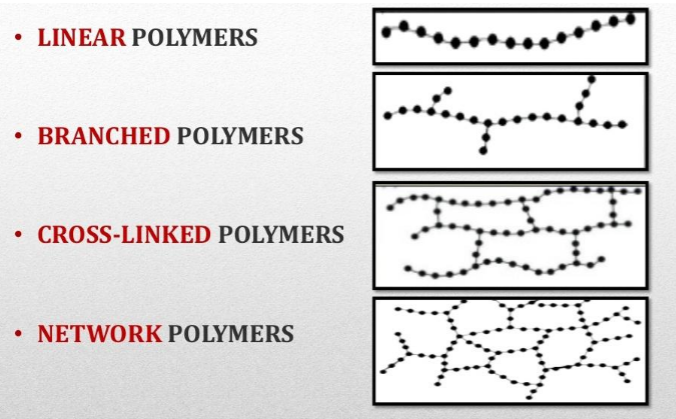
Plastic is a polymer (like the synthetic fibre) which can be moulded into different shapes. The word ‘plastic’ originates from the Greek word ‘plastikos’ which means ‘that can be moulded or shaped’. Plastic polymers can have different types of arrangement of monomers:
Plastic can be recycled and used. It can also be melted, rolled into sheets, made into wires, and coloured.
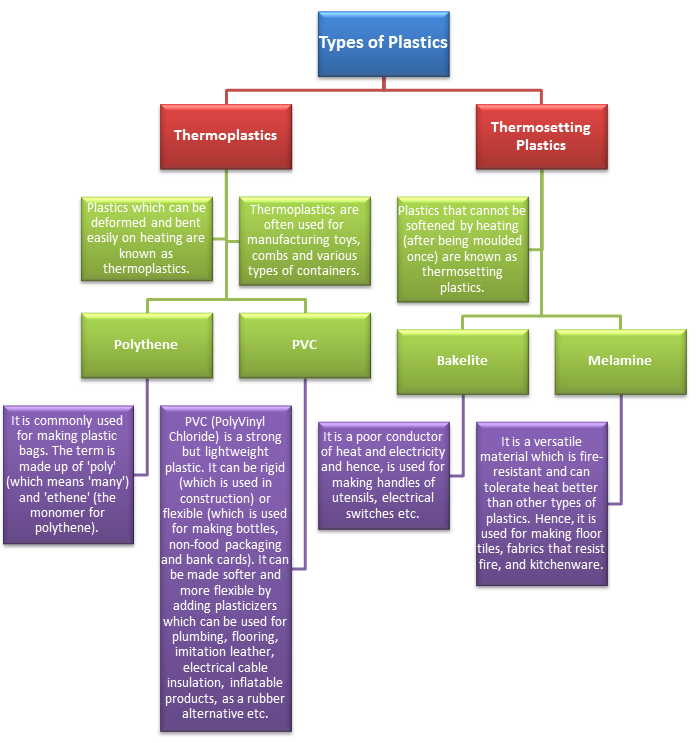
Some popular types of plastics are:
Plastics as Materials of Choice
| Advantages of Plastic | |||||
| Lightweight | Lower price | Good strength | Easy handling | Not-reactive(does not rust like iron when exposed to water and air, and doesnot corrode easily) | Poor conductor of heat and electricity |
Give Reasons Why:
Buckets are made of plastic these days.
Plastic buckets are strong, lightweight, and do not rust.
Bakelite plastic is used to make electrical switches.
Bakelite is a poor conductor of heat and electricity. Hence, they would not give anyone an electric shock when someone touches the switch.
Melamine is used to make crockery.
Melamine is unbreakable, fire resistant, and tolerates heat better than plastics. Hence, it can be used to make crockery that can hold hot liquids or dishes served in it.
Plastics are used in cars, aircraft and spacecraft.
Plastics are strong, durable, lightweight, and corrosion-resistant.
Chemicals are stored in plastic bottles.
Plastic bottles are lightweight, unbreakable, corrosion-resistant, and are resistant to the action of chemicals. Hence, they are suitable for storing chemicals.
Which plastic is used to make:
Non-stick coating on Cookware: Teflon
Insulation covering on Wires: PVC
Polythene Bags: Polythene
Flame-resistant Uniforms: Melamine
Special uses of Plastic
Besides being used in packaging for food and non-food items and several daily-used items (such as furniture, electrical switches, slippers etc.), plastic also has special uses such as:
1. Used in the healthcare industry for packaging of tablets, syringes, doctor’s gloves, a number of medical instruments, and threads for stitching wounds.
2. Used to make cookware used in microwave ovens
3. Used as a non-stick coating on cookware (made of a special plastic called Teflon is used on which oil and water do not stick)
4. Used to make the fire-resistant uniform for firefighters (made of Melamine)
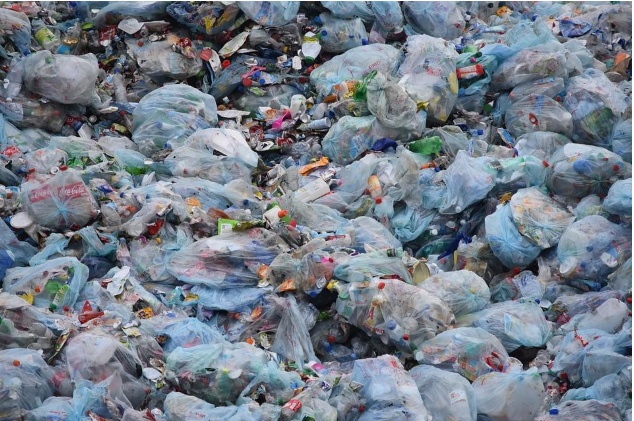
Plastics and the Environment
Plastic is a threat to the environment as it is non-biodegradable. Its disposal is a big problem.
Biodegradable: Material which gets decomposed through natural processes (such as bacterial action) is called Biodegradable.
Non-biodegradable: Material which cannot be easily decomposed by natural processes is called Non-biodegradable.
How do plastics cause environmental pollution?
Plastics cause pollution as they:
1. are non-biodegradable, and
2. release toxic fumes when burnt (and hence, cause air pollution).
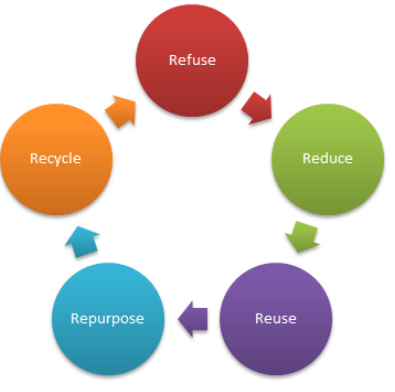
5 Rs to Minimize the Environmental Damage caused by Plastic
Refuse: Do not buy things we do not need.
Reduce: Minimize the use of plastics in our daily lives.
Reuse: Reuse the items we already instead of throwing them away.
Repurpose: If we are not using something, alter or change to use it in a different way.
Recycle: Some plastic waste can be sorted and made into other things in recycling factories. This helps us to reduce our carbon footprint.
How can we minimize pollution caused by plastics at home?
We should use jute, cotton, or paper bags instead of plastics. We also need to minimize the use of plastic in our daily lives (such as using a steel lunch box instead of a plastic one). Also, we should not throw plastics on the road or in the water bodies.





Leave a Reply