Issue and Redemption of Debentures
Notes For All Chapters Accountancy Class 12
Topic 1: Introduction, Issue of Debentures and Various Cases from The Point of View of Redemption
1. Meaning of Debenture It means a document of companies indebtedness issued under the seal of the company and containing a contract for the repayment of the principal sum at a specified date with interest at a fixed rate.
2. Definition of Debenture According to Section 2(30) of the Companies Act, 2013 ‘Debenture includes debenture stock, bonds and any other instrument of the company evidencing a debt, whether constituting a charge on the assets of the company or not.’
3. Rond Bond is also an instrument of acknowledgement of debt. Bond is similar to debenture in terms of contents and texture. However, bonds can be issued without pre-determined rate of interest.
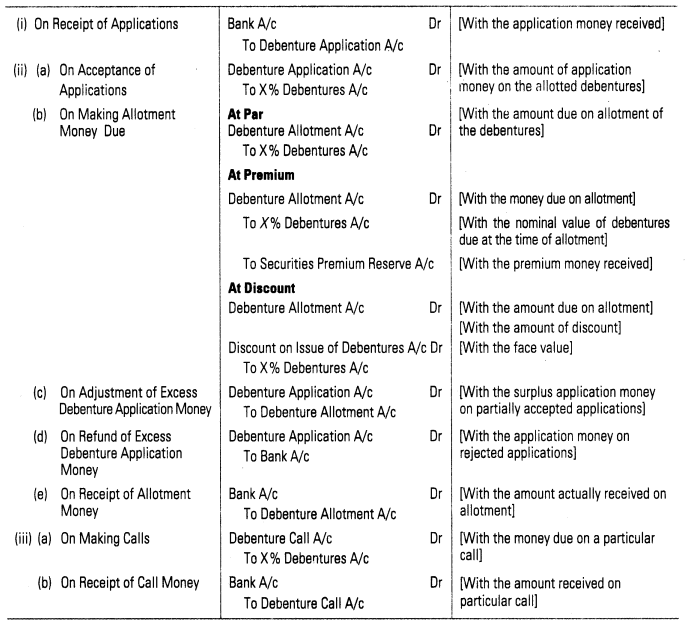
4. Issue of Debentures for Cash Debentures, like shares, issued for cash, may be issued
(i) at par (ii) at premium or (iii) at discount
(i) Issue of Debentures at Par Debentures are said to be issued at par when the issue price and face value of the debentures is same.
(ii) Issue of Debentures at a Premium Debentures are said to be issued at premium when the issue price is more than the face value.
(iii) Issue of Debentures at a Discount Debentures are said to be issued at discount when they are issued at a price below its nominal or face value.
5. Accounting Entries for Issue of Debentures for Cash
6. Issue of Debentures for Consideration other than Cash When debentures are issued to vendors against purchase of assets or against purchase of business, it is termed as issue of debentures for consideration other than cash. In this case, consideration for issue of debentures is not cash but the assets or business. Debentures in this instance can also be issued at par, premium or discount.
Following journal entries will be passed in this case:
(i) On Purchase of Assets or Business
(a) When assets are purchased
Sundry Assets A/c Dr
To Vendor’s A/c Dr
(b) When business is purchased
Sundry Assets A/c Dr
To Sundry Liabilities A/c To
Vendor’s A/c *To Capital Reserve A/c
(ii) On Issue of Debentures
(a) When debentures are issued at par
Vendor’s A/c Dr
To X% Debentures A/c
(b) When debentures are issued at premium
Vendor’s A/c Dr
To X% Debentures A/c To Securities Premium Reserve A/c
(c) When debentures are issued at discount
Vendor’s A/c Dr
Discount on Issue of Debentures A/c Dr
To X% Debentures A/c
(i) Purchase consideration is the amount paid by the purchasing company for purchasing of assets/business from another enterprise.
(ii) If the purchase consideration is greater than the value of the net assets acquired, the difference is debited to goodwill account.
(iii) If the amount of purchase consideration is lower than the value of net assets acquired, the difference is credited to capital reserve account.
(iv) Either of the two i.e. capital reserve or goodwill will come.
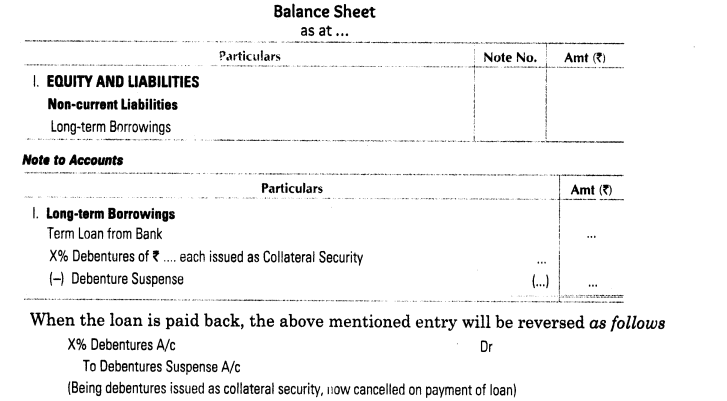
7. Issue of Debentures as Collateral Security When a company takes a loan, it may provide primary security on its assets. However, the lending institution may insist on some more assets as secondary or collateral security. In such a situation, the company may issue debentures to the lender as secondary or collateral security, such an issue of debentures is known as ‘debentures issued as collateral security’.
If the company fails to repay the loan along with the interest and the primary security is insufficient to repay the loan, only in that case the lender is free to use the debentures as collateral security. The lender may either present such debentures for redemption or sell them in the open market.
Debentures issued as collateral security can be dealt in two ways
(i) First Method (Without Passing Journal Entry) In this method, no journal entry is passed in the books for issue of debentures as collateral security.
However, the fact of debentures issued as collateral security is disclosed by way of information below debentures, which are shown as long-term borrowings under non-current liabilities or as short-term borrowings under current liabilities.
(ii) Second Method (With Journal Entry) Debentures issued as collateral security may be recorded in the books of accounts.
Following journal entry will be passed for issue of debentures as collateral security: Debenture Suspense A/c Dr [This appears on assets side]
To X% Debentures A/c [This appears on liabilities side]
When the loan is paid the above entry is cancelled by passing its reverse entry. In balance sheet, debentures issued as collateral security must be shown separately from other debentures.
Disclosure of Debenture Issued as Collateral Security in the Balance Sheet As debenture issued as collateral security is related to the loan of the company, therefore, it is shown in the note in which the loan secured by debenture is shown.
8. Interest on Debentures Interest on debentures is calculated at a fixed rate on its face value and is usually payable half yearly. Debenture interest is a charge on profit and it is not an appropriation of profit. Hence, interest on debentures is payable even if the company suffers a loss, i.e. does not earn profit.
According to Income Tax Act 1961, a company paying interest on debentures is required to deduct income tax at the prescribed rate from the gross amount of debenture interest before any payment is made to debenture holders, it is called Tax Deducted at Source (TDS).
Entries for interest on debentures are as follows
(i) When interest is due
Debentures Interest A/c Dr [With gross interest]
To Debentureholders’ A/c [With net interest]
To Income Tax Payable A/c [With income tax deducted]
(ii) When interest is paid
Debentureholders’ A/c Dr [With interest]
To Bank or Cash A/c
(iii) On payment of income tax to government Income Tax Payable A/c Dr
To Bank A/c
(iv) On transfer of interest on debentures to profit and loss account Statement of Profit and Loss Dr [With the amount of interest]
To Debenture Interest A/c

Leave a Reply