Notes For All Chapters Biology Class 12 CBSE
1. Humans are sexually reproducing and viviparous organisms. There are remarkable differences between the reproductive events and systems in male and female.
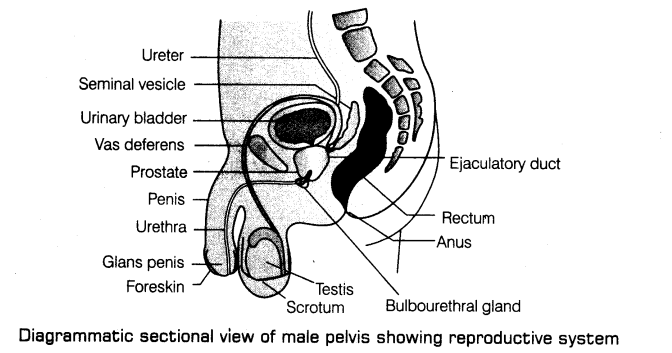
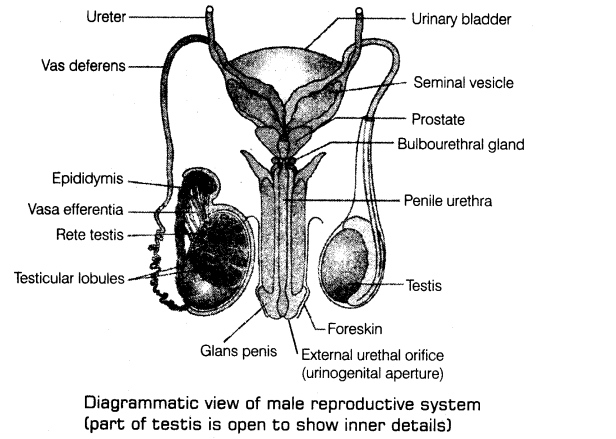
2. Male reproductive system includes a pair of testes, accessory ducts, glands and the external genitalia.
(i) Testes are located outside the abdominal cavity within a pouch called scrotum.
Scrotum maintains the low temperature of the testes (2-2.5°C lower than the normal body temperature) required for spermatogenesis.
(a) Each testis is oval-shape (length 4-5 cm and width 2-3 cm) and covered by a dense covering called tunica albuginea.
(b) Internally it is divided into about 250 compartments known as testicular lobules.
(c) Each lobule contains 1-3 highly coiled (structural and functional units of testis) called seminiferous tubules in which sperms are produced.
(d) Seminiferous tubule is lined on its inside by two types of cells called male germ cells (spermatogonia) and Sertoli cells.
(e) Male germ cells undergo meiotic divisions finally leading to sperm formation.
(f) Sertoli cells provide nutrition to the germ cells.
(g) Interstitial spaces are present in outside regions of seminiferous tubules which contain small blood vessels and interstitial cells or Leydig cells.
(h) Leydig cells synthesise and secrete the testicular hormones called androgens.
(ii) Male accessory ducts include rete testis, vasa efferentia, epididymis and vas deferens.
(a) The intratesticular duct system starts with tubuli recti, which are short, straight end segments of the seminiferous tubules. These tubules connect the seminiferous tubules to the highly anastomosing, cuboidal epithelium-lined channels called rete testis.
(b) From rete testis, 10-25 fine tubules arise called vasa efferentia that leave the testis and open into the epididymis.
(c) Epididymis leads to vas deferens that ascends to the abdomen and loops over the urinary bladder.
Diagrammatic sectional view of male pelvis showing reproductive system
Diagrammatic view of male reproductive system [part of testis is open to show inner details)
Urinary bladder receives a duct from the seminal vesicle to form ejaculatory duct that runs through the prostate and opens into urethra.
(e) Urethra receives the ducts of prostate gland and the bulbourethral gland (Cowper’s glands) a little ahead and runs through the penis to its external opening called urethral meatus.
(iii) The accessory glands of male reproductive system include
(a) A pair of seminal vesicles, a prostate gland and a pair of bulbourethral glands (Cowper’s glands).
(b) The secretion of all these glands is called seminal plasma.
(c) Seminal plasma contains fructose, calcium and some enzymes. It is to provide nutrition to the spermatozoa, while travelling through female reproductive tract.
(d) Seminal plasma along with sperms is called semen.
(e) Secretion of bulbourethral glands also helps in the lubrication of the penis.
(iv) External genitalia is the penis. It is made up of special erectile tissue that helps in erection of the penis. The enlarged tip of the penis is called glans penis. It is covered by a loose fold of skin called foreskin or prepuce.
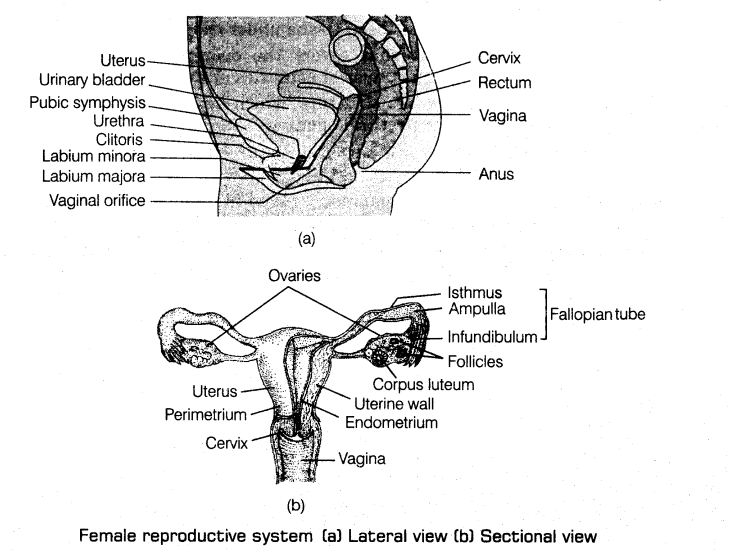
3. Female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries, secondary sex organs, external genitalia and mammary glands.
(i) Ovaries are primary female sex organs which produce female gametes called ova and secrete the female sex hormones.
(a) These are located one on each side of the lower abdomen.
(b) It is almond-shaped, 2-4 cm in length, 1.5 cm in width.
(c) It is connected to the pelvic wall and uterus by ligaments.
(d) Each ovary is covered by a thin epithelium which encloses the ovarian stroma.
(e) Stroma is divided into two regions, i.e. peripheral cortex and inner medulla.
(ii) The female accessory ducts constitute oviducts (Fallopian tubes), uterus and vagina.
(iii) Each Fallopian tube is about 10-12 cm long and extends from the periphery of each ovary to the uterus.
(a) The part of oviduct closer to the ovary is funnel-shaped infundibulum.
(b) The edges of infundibulum possess finger-like projections called fimbriae, which help in collection of the ovum after ovulation.
(c) Infundibulum leads to a wider part of the oviduct called ampulla.
(d) Isthmus is the last part of the oviduct, which has a narrow lumen and it joins the uterus.
(iv) Uterus or womb is a pear-shaped muscular organ. It is attached to the pelvic wall and supported by ligaments.
(a) Wall of the uterus has three layers of tissue.
(b) Perimetrium is the outermost thin membranous layer, myometrium is the middle thick layer of smooth muscles and endometrium is the innermost glandular layer which lines the uterine cavity.
(c) Uterus opens into the vagina through a narrow cervix, its cavity is called cervical canal, which along with vagina forms birth canal.
(d) Endometrium layer undergoes cyclic changes during menstrual cycle.
(e) Smooth muscles in myometrium contract during parturition to deliver the baby.
(v) Vagina is a muscular tube-like structure that opens to the outside. It receives spermatozoa during insemination and serve as birth canal.
(vi) Female external genitalia include mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris and hymen.
(a) Mons pubis is a cushion of fatty tissue covered by skin and pubic hair.
(b) Labia majora are fleshy folds of tissue which extend down from the mons pubis and surround the vaginal opening.
(c) Labia minora are paired folds of tissue under the labia majora.
(d) Hymen is a membrane that covers the opening of vagina partially. It gets ruptured during vigorous physical activities or during the first coitus.
(e) Clitoris is a tiny finger-like structure, which lies at the upper junction of the two labia minora above the urethral opening.
(vii) Mammary glands (breasts) are paired structures that contain glandular tissue and variable amount of fat.
(a) Glandular tissue of each mammary gland is divided into 15-20 mammary lobes containing the cluster of cells called alveoli.
(b) The cells of alveoli secrete milk, which is stored in the cavities (lumen) of alveoli.
(c) Alveoli open into mammary tubules. The tubules of each lobe join to form a mammary duct.
(d) Several mammary ducts join to form a wider mammary ampulla, which is connected to lactiferous duct through which milk is sucked out.

Leave a Reply