Notes For All Chapters Biology Class 12
Reproduction:
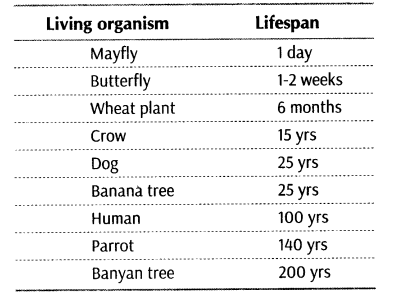
1. The period between birth and natural death of an organism is called its lifespan. It can vary from less than a day to more than 400 yrs.
Whatever be the lifespan, death of every individual organism is a certainty,
i. e. no individual is immortal, except single-celled organisms.
Lifespan of some organisms are given in the following table:
2. Reproduction is a biological process of continuity of a race in which the grown up individuals give rise to off springs similar to them.
It performs the following functions:
(i) Enables continuity of the species.
(ii) Maintains life on the earth.
(iii) Creates variations among population.
The mechanism to produce offsprings shows large variations, depending on organisms habitat, its internal physiology and several other factors.
Based on the participation of one or two organisms, reproduction can be of following two types:
(i) Asexual reproduction
(ii) Sexual reproduction
3. Asexual reproduction A single parent is capable of producing offsprings. Thus, the offsprings are genetically and morphologically identical to one another and to their parent. These are often referred to as clone. The unit of reproduction is commonly formed from the somatic cells of the parent. Meiosis does not occur in asexual reproduction.
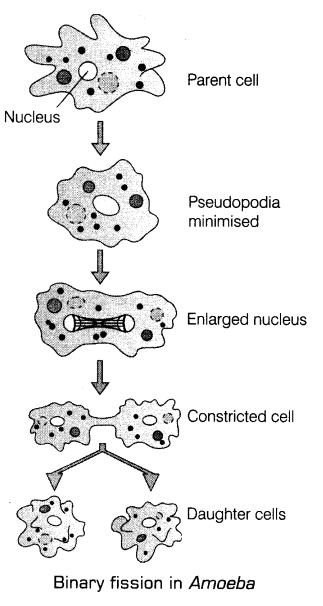
Asexual reproduction is common among single-celled organisms and in plants and animals with simple organisations. Cell division in itself is a mode of reproduction in protists, e.g. bacteria and monerans, e.g. Amoeba (the parent cell divide into two to give rise to new individuals).
Types of asexual reproduction are as given below:
I. Fission can be further classified as:
(i) Binary fission The body of an individual divides into two equal halves.
It can be following types:
(a) Simple binary fission When division occurs in any plane but it is always right angle to the elongated dividing nucleus, e.g. Amoeba.
(b) Longitudinal binary fission When division occurs along the longitudinal axis, e.g. Euglena, Vorticella.
(c) Oblique binary fission When division occurs at an angle to the transverse axis, e.g. Ceratium, Gonyaulax.
(d) Transverse binary fission When division occurs along the transverse axis of the individual, e.g. Paramecium, diatoms, bacteria, Planaria.
(ii) Multiple fission The division of the parent body into many daughter organisms, e.g. Amoeba,
Plasmodium, Monocystis (all Protozoa).
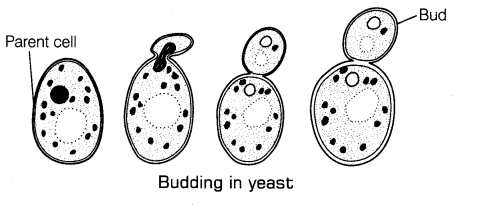
II. Budding, (torulation) an outgrowth or bud develops, grows, constricts at the base and separates from the parent body, e.g. yeast and Hydra. The complex budded condition is called torala stage.
III. Sporulation occurs by tiny, single-celled, thin-walled spores that are extremely resistant to environmental extremes. The spores form new individuals. It commonly occurs in Monera, Protista, Fungi and Algae.
Spores formed can be of following main types:
IV. Fragmentation occurs by breaking of the parent body into two or more parts, each of which grows to form an independent individual, e.g. algae like Spirogyra and bryophytes such as Marchantia, Riccia.
V. Regeneration is a type of asexual reproduction in which the missing part of the organism is repaired by the proliferation of cells, e.g. Hydra, planaria and sponges.
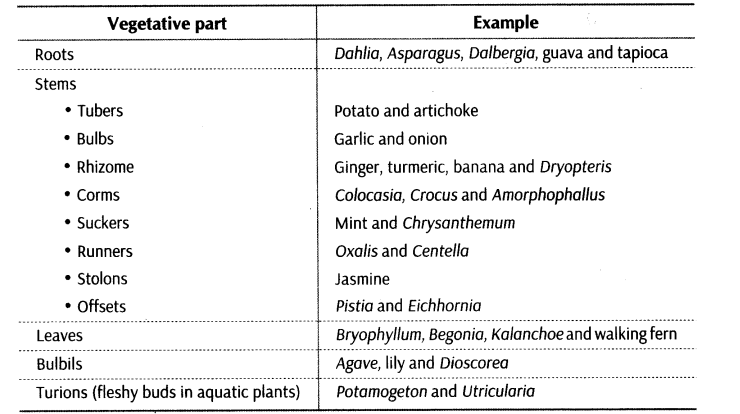
VI. Vegetative propagation is the formation of a new plants from vegetative parts like root, stem, leaf, etc., naturally, e.g. water hyacinth (scourage of the water bodies or Terror of Bengal) propagates very quickly by vegetative mode and drains out dissolved 02 from water bodies. Some artificial methods of vegetative propagation are also developed by the farmers like cutting, layering, grafting, etc.
Some examples of natural method of vegetative propagation are:
The units of vegetative propagation such as runner, rhizome, sucker, tuber, offset, bulb all have capability to give rise to new offsprings. These structures are known as vegetative propagules.


Leave a Reply