Notes For All Chapters Chemistry Class 12 CBSE
1. Amines are the derivatives of ammonia in which one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by alkyl groups.
2. Amines are classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary according as one, two or three hydrogen
atoms in the ammonia molecule have been substituted by alkyl groups.
3. Preparation of amines:
(i) By reduction of nitro compounds.
(ii) An alkyl or benzyl halide on reaction with an ethanolic solution of ammonia undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction in which the halogen atom is replaced by an amino (-NH2) group.
(iii) By reduction of nitriles.
(iv) By reduction of amides.
(v) By Ghbriel phthalimide synthesis: For primary alkyl amines only, not for aromatic amines.
(vi) By Hoffmann bromide degradation reaction:
4. All the three classes of aliphatic amines (1°, 2°and 3°) form H-bonds with water. As a result, lower aliphatic amines are soluble in water.
5. Some important reactions of amines
(i) Amines are basic in nature they react with acid to form salt.
(ii) Aliphatic and aromatic primary and secondary amines react with acid chlorides, anhydrides and esters by nucleophilic substitution reaction. This reaction is known as acylation.
(iii) Aliphatic and aromatic primary amines on heating with chloroform and ethanolic potassium hydroxide form isocyanides or carbylamines which are foul smelling substances. Secondary and tertiary amines
do not show this reaction. This reaction is known as carbylamine reaction or isocyanide test and is used as a test for primary amines.
(iv) CH6H5SO2Cl is also called Hinsberg’s reagent and reacts with primary and secondary amines to form sulphonamides. Tertiary amines do not react with benzene sulphonyl chloride.
6. Diazonium salt have the general formula RN2+ X–, where R stands for an aryl group and X– ion maybe Cl”, Br, HSO2–, BF4–, etc.
7. Primary aliphatic amines form highly unstable alkyl diazonium salts which decomposes to give alcohols with the evolution of N2. Primary aromatic amines form arene diazonium salts which are stable for a short time in solution at low temperature (273 -278 K).
8. Arenediazonium ion is resonance stabilized.
9. Benzene diazonium chloride is prepared by the reaction of aniline with nitrous acid at 273 – 278 K. This conversion of primary aromatic amines into diazonium salt is known as diazotisation.
10. Chemical properties:
(i) Diazonium group being a very good leaving group, is substituted by other groups such as Cl–, Br–, I–, CN– and OH–.
(ii) The Cl–, Br– and CN– nucleophiles can easily . be introduced in the benzene ring in the presence of Cu (I) ion. This reaction is called Sandmeyer reaction.
(iii) The reaction in which chlorine or bromine is introduced in the benzene ring by treating the diazonium salt solution with corresponding halogen acid in the presence of copper powder is called Gatterman reaction.
11. Importance of diazonium salts: They are very good intermediates for the introduction of -F, -Cl, -Br, -I, -CN, -OH, -NO2 groups into the aromatic ring.
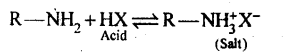

Leave a Reply