Notes For All Chapters Chemistry Class 12 CBSE
1. Carbohydrates is a class of compounds that include polyhydric aldehydes and ketones and large number of other polymeric molecules that yield these on hydrolysis, e.g., sugars, glycogen, cellulose, starch, etc.
2. Depending upon their behaviour on hydrolysis, carbohydrates are further divided into three types: Monosaccharides (e.g., glucose, fructose etc.), disaccharides (e.g., sucrose, maltose etc.) and polysaccharides (e.g., starch, cellulose, etc.)
3. Another classification of carbohydrates is as sugars and non sugars. Sugars are sweet in taste, crystalline, soluble in water, mainly include mono and oligosaccharides. Non Sugars are tasteless, amorphous, water insoluble and mainly include polysaccharides.
4. Carbohydrates can also be classified as reducing and non reducing sugars. Reducing sugars respond to Tollens’ and Fehling solution test. All monosaccharides, aldoses and ketoses,fall in this category. Some other oligosaccharides also may be reducing. All polysaccharides are non reducing (starch, cellulose, glycogen etc). Sucrose is a disaccharide and non reducing sugar.
5. The molecular formula of glucose is C6H12O6. It is prepared by boiling sucrose with dil HCl or dil H2SO4 in alcoholic solution or by the hydrolysis of starch with dil H2SO4 at 393 K under pressure.
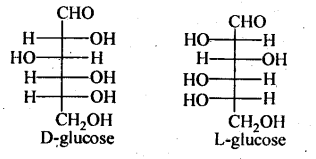
6.The Fisher projection for D-and L-glucose are shown below:
7. A pair of stereoisomeric ring forms of any sugar differing in configuration only at carbon 1 (the anomeric carbon) are called anomers.
8. The spontaneous change that takes place in specific rotation of an optically active sugar when dissolved in water is known as mutarotation.
9. The cyclic structure of glucose was proposed by R. D. Haworth. The six-membered cyclic structure of glucose is called as pyranose structure (α or β).
10. The hydrolysis of sucrose brings about a change in the sign of rotation, from dextro (+) to laevo (-). Such a change is known as inversion of sugar.
11. Starch/Amylum (C6H10O5)n is a polymer of D-glucose and consists of two components amylose and amylopectin. Natural starch consists of approximately 15 – 20% of amylose and 80 -85% of amylopectin.
12. Cellulose (C6H10O5)n is a linear polymer of β-D-glucose in which the β-D- glucose units are joined by β-D-glucosidic linkage.
13. Proteins are the most abundant biomolecules of the living system. They are required for growth and maintenance of body. All proteins are polymers of α-amino acids.
14. The amino acidsare the compounds containing at least one amino (-NH2) and one carboxyl
(-COOH)ftactional group. The amino acids are classified as α , β , γ, δ and so on depending upon the position of the two functional groups in the alkyl chain.
15. There are 20 different amino acids, each with a different – R group, commonly found, in the proteins of living things. The human body can synthesis 10 out of the 20 amino acids found in
the proteins. These are called non-essential amino acids, e.g., glycine, alanine, aspartic acid, glutamic acid, etc.
16. Certain amino acids are required for proper health and growth in human beings. But the human body is unable to synthesize them. These must be supplied to body through food and are called essential amino acids, e.g., valine, leucine, phenylalanine, etc.
17. Denaturation refers to the loss of a biological activity of a protein brought about by changes in its secondary and tertiary structure due to heat, pH change, presence of salts, etc.
18. Enzymes are naturally occurring simple or conjugated proteins that catalyse biological reactions.
19. Vitamins are substances necessary to maintain normal health, growth and nutrition. They cannot
be synthesized by organisms mid thus have to be supplied in the diet. Vitamins A, D, E and K are fat soluble whereas vitamins B and C are water soluble.
20. Nucleic acids are polymers of complex repeating units called nucleotides. There are two types of nucleic acids: DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid).
21. Nucleic acids play two important functions replication and protein synthesis.
22. A nucleotide consists of three parts:
(a) A five carbon atom sugar unit, which is either ribose and deoxyribose.
(b) A nitrogen containing heterocyclic base, and
(c) A phosphate group.
23. The nitrogen containing bases in nucleotides belong to the following two classes:
(i) Purines: The bases derived from purines are adenine (A) and guanine (G).
(ii) Pyrimidines: The bases derived from pyrimidines are cytosine (C), thymine (T) and uracil (U).
24. A mutation is a chemical change in DNA molecule that could lead to synthesis of proteins with an altered amino acid sequence. The changes in a DNA molecule can happen spontaneously or may be caused by radiation, chemical agents or viruses.

Leave a Reply