Notes For All Chapters Chemistry Class 12 CBSE
1. Chemical kinetics is the branch of chemistry which deals with the study of rates (or fastness) of chemical reactions, the factors affecting it and the mechanism by which the reactions proceed.
2. Rate of reaction is the change in concentration of reactants or products per unit time.
For a general reaction, A+B –> C
The rate of reaction
The negative sign indicates that the concentration is decreasing with time.
Unit for reaction rate is mol L-1s-1.
3. The rate of reaction is not a constant quantity (except for zero order reactions). It decreases as the reaction proceeds in the forward direction.
4. A rate law expresses a mathematical relationship between the reaction rate and the molar concentration of one or more reactants.
Where m and n are determined experimentally and represent the order of reaction with respect to A and B respectively, m + n represents the overall order of reaction.
5. Rate constant is the rate of reaction when the concentration of each of reacting species is unity. It is represented by ‘k’ It is also called specific reaction rate or velocity constant of reaction.
6. Order of reaction is defined as the sum of the exponents to which the concentration terms are raised in the rate equation (or rate law) of the reaction. It can be fraction, zero or any whole number.
7. Modularity of reaction is defined as the number of reacting particles (atoms or molecules or any other species), which collides simultaneously to bring about the chemical change.
It is a theoretical concept. Its value is always a whole number. It is never more than three. It cannot be zero.
8. First order reaction: A reaction is said to be first order if its reaction rate is determined by the variation of one concentration term only.
9. The integrated rate equation expresses the concentration of reactants as a function of time.
10. The integrated rate equation for a first order reaction is given as
11. Second order reaction: The reaction in which sum of powers of concentration terms in rate law equation is two.
12. Zero order reaction: Those reactions in which rate of reaction does not change with concentration of the reactants.
Rate law for such a reaction is expressed as. Rate = k [A]°[B]°
13. Half life period: It is the time required for the initial concentration of the reactant to be reduced to half its value.
14. It has been found that for a chemical reaction with rise in temperature by 10 °C, the rate constant gets nearly doubled.
15. The temperature coefficient of a reaction is the ratio of the rate constants of the reaction at two temperatures differing from one another by 10°C. The two temperatures usually taken are 35 °C and 25 °C.
16. The variation of rate constants with temperature can be represented by the Arrhenius equation,
K=Ae-Ea/Rt
where A is a constant known as frequency factor, and Ea is-called the energy of activation.
From the above equation, the rate constants at two different temperatures are related as
17. There are two important theories of reaction rates:
(i) Collision theory and,
(ii) Transition state theory.
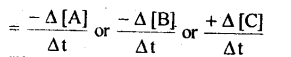
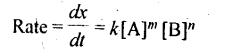

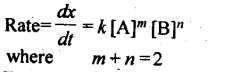
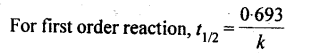
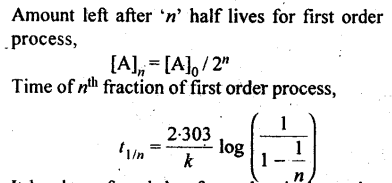
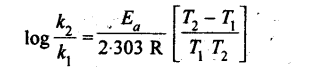

umm…ok okk
so nice