Notes For All Chapters Chemistry Class 12 CBSE
1. Coordination compounds contain a central atom (or cation) which is coordinated to a suitable number of anions or neutral molecules and usually retain their identity in solution as well as in solid state. These may be a positively charged, negatively charged or a neutral species,
[Co(NH3)6]3+, [NiCl4]2-, [Ni(CO)4] etc.
2. In 1893, Werner proposed a theory to explain the structure and bonding in coordination compounds:
(a) In coordination compounds, metals show two types of valencies : Primary valency and secondary valency.
(b) Primary valencies are ionisable.
(c) Secondary valencies are not ionisable.
(d) This theory was successful to very limited extent and could not explain many aspects of coordination compounds.
3. In modern formulations, such spatial , arrangements are called coordination polyhedra.
The species within the square bracket are coordination entities or complexes and the ions outside the square brackets are called counter ions.
4. The compounds which have the same molecular formula but differ in their structural arrangements are known as isomers.
5. The types of isomerism shown by coordination compounds are :
(a) Geometrical (or cis-trans) isomerism: Two coordination compounds are said to be geometrical isomers, when they differ in the arrangement of their ligands in space. When two identical ligands occupy adjacent position, the isomer is called ‘cis-form’ and when they arranged opposite to one another, the isomer is called ‘trans-form’.
(b) Optical isomerism shown by the chiral molecule, i.e., the molecules which do not have plane of symmetry e.g., [Cr(ox)3]3-.
(c) Linkage isomerism occurs in complexes when an ambidentate ligand is present in the coordination sphere, e.g., [CO(NH3)5N02]2+ and [Co(NH3)5(-ONO)]2+.
(d) Coordination isomerism occurs in those complexes which are made of cationic and anionic coordination entities due to the interchange of ligands between the cation and anion entities, e.g., [CO(NH3)6] [Cr(CN)6] and [Co(CN)6] [Cr(NH3)6].
(e) Ionisation isomerism, is due to the exchange of ions in coordination sphere of metal ion and the ions outside the coordination sphere. These two isomers give different ions in aqueous solution, e.g,
[Co(NH3)5Br]2+ S042- and [Co(NH3)5(S04)]+ Br–
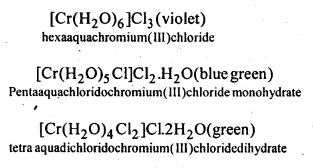
(f) Solvate or hydrate isomerism occurs when water is a part of coordination entity or is outside it, e.g., CrCl3-6H20 has three isomers.
6. Magnetic properties:
(i) Inner orbital (low spin) complexes are those complexes in which hybrid orbitals of metal are formed by hybridisation of (n-1) d, ns and np-orbitals, e.g., [Fe(CN)6]4-, [CO(NH3)6]3+, [Cr(NH3)6]3+, [Fe(CN)6]2+, [Fe(H20)6]2+, [(MnCCN)6]3-, etc.
(ii) Outer orbital (high spin) complexes are those comp lexes in which the hybrid orbitals of metal are formed by hybridisation ns, np and nd-vacant orbitals, e.g., [MnF6]3-, [FeF6]3-, [Ni(NH3)6]2+,[Ni(H20)6]2+, etc.
7. Assumptions of Crystal Field Theory:
(a) The ligands are assumed to be point charges.
(b) The interaction between the point charges and the electrons of the central metal are electrostatic in nature.
(c) The 5d-orbitals in an isolated gaseous metal ion have the same energy, i.e., they are degenerate.
8. The stability of a coordination compound [MLn] is measured in terms, of its stability constant
For overall reaction,
9. Drawbacks of Crystal Field Splitting:
(a) From the assumption that ligands are point charges, it follows that anionic ligands should exert greatest splitting effect. But anionic ligands actually are found at the low end of the spectro chemical series.
(b) It does not take into account for the covalent character of bonding between the ligand and the central atom.
10. Bonding in metal carbonyls: In metal carbonyl, the metal carbon (M – C) bond possesses both the σ- and π-bond character.
11. Importance and applications of coordination compounds:
(a) In many quantitative and qualitative chemical analysis.
(b) In extraction processes of metals, like silver and gold.
(c) Purification of metals like Ni can be achieved through formation and subsequent decomposition of their coordination compounds.
(d) In biological systems the pigment responsible for photosynthesis is chlorophyll, is a coordination compound of magnesium. Haemoglobin, coordination compound, of Fe, acts as a oxygen carrier.
(e) Case of chelate therapy in medicinal chemistry.
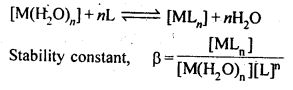

Leave a Reply