Notes For All Chapters Chemistry Class 12 CBSE
1. Electrochemistry is the branch of chemistry which deals with the relationship between electrical energy and chemical energy and inter-conversion of one form into another.
2. An electrochemical cell consists of two metallic electrodes dipped in electrolytic solutions. The cells are of two types:
(a) Electrolytic cells (b) Galvanic cells
3. A galvanic cell consists of two half cells. Each half cell contains an electrolytic solution and a metallic electrode.The electrode at which- oxidation takes place is called an anode and the electrode at which reduction takes place is called the cathode. The half-cells are separated from each other by means of a porous pot or a salt bridge.
4. The passage of current from one electrode to the other indicates the existence of potential difference between them. This difference of potential which causes current to flow from the electrode of higher negative potential is called the electromotive force (emf).
5. Electrical energy = Emf (volts) x Quantity of electricity (coulombs)
6. The potential of SHE is assigned an arbitrary value of zero. E° = 0 V. It is used as a reference electrode for measuring the standard electrode potentials. .
7. When the elements are arranged in order of their standard electrode potentials, a series known as electrochemical series is obtained.
8. Standard emf of a cell,
E0cell =E0cathode – E0node = E0Riglit – E0Left
9. ΔG° = -nFE0cell
If E0cell is positive, ΔG° would be negative and reaction would be spontaneous. If E0cell is
negative, ΔG° would be positive and the reaction would be non-spontaneous.
10. A species with higher standard reduction potential has greater tendency to accept electrons to undergo reduction or vice versa.
11. The potential of an electrode in contact with its ions in solution varies with the concentration of the ion. Thus, for a redox reaction,
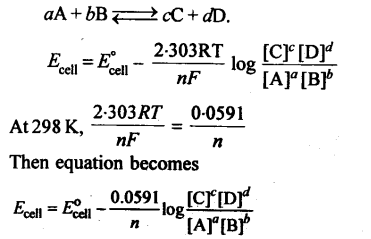
12. For an electrochemical cell for which the overall reaction is
13. The equilibrium constant, Aofcell can be relate to standard emf of cell
14. Resistance is the measure of obstruction to the flow of current.
where S = specific resistance or resistivity. Unit of R is ohm.
15. Resistivity is defined as the resistance of a conductor of 1cm length and having an area of cross-section equal to 1cm2.
unit of resistivity is ohm-cm
16. Conductance is reciprocal of resistance, i. e.,
Unit of conductance is ohm-1 or mho or Siemen(S).
17. Specific conductance Λsp is reciprocal of specific resistance.
Specific conductance is thus defined as the conductance of a solution taken in a cell whose electrodes are at unit distance apart from each other and each having an area equal to 1 cm2. Unit of specific conductance is ohm-1 cm-1 or S cm-1.
18. Molar conductance (Λm) is defined as the conductance of the volume of solution which contains one mole of the solute and is placed between two parallel electrodes which are one centimetre apart and having sufficient area to hold the whole of the solution.
Unit of molar conductance is Ω-1 cm2 mol-1 or S cm2 mol-1
19.
where C = concentration of solution in moles per litre (or Molarity).
20. The electrical conductance through metals decreases with increase in temperature.
21. The electrolytic conductance increases with increase of temperature.
22. Effect of Dilution on
(а) Equivalent conductance: The value of equivalent conductance increase with dilution and attains a maximum value at infinite dilution.
(b) Specific conductance: The value of specific conductance decreases with dilution as the number of current carrying particles i.e., ions present per cm3 of solution decreases on dilution.
(c) Molar conductance: The value of molar conductance increases with dilution and finally attains a maximum value at infinite dilution.
23. Variation of molar conductance with concentration:
(a) Strong electrolytes:
(b) Weak electrolytes:
24. According to Kohlrausch law of independent migration of ions, the limiting molar conductivity of an electrolyte can be expressed as the sum of the contributions of the cation and the anion of the electrolyte.
where v+, v– are the number of cat ions and anions per unit formula of the electrolyte respectively; λ0+, and λ0– are the limiting molar conductivities of the cation and anion respectively.
25. Faraday’s laws of electrolysis:
(a) First law: The amount of a substance deposited or liberated at an electrode is directly proportional to the quantity of electricity passed through the electrolyte. Mathematically,
where m = mass of substance deposited or liberated.
Mass of substance A deposited or liberated Mass of substance B deposited or liberated current in amperes t = time in seconds, and Z = constant called electrochemical equivalent.
(b) Second law: When the same quantity of electricity is passed through solutions of different electrolytes, the weight of different substances deposited or liberated at the respective electrodes are proportional to their chemical equivalent weights.
26.
27. The charge on one mole of electrons is approximately equal to 96500 coulombs. This quantity of electricity is called Faraday constant (F).
28. A battery consists of two or more galvanic cells connected in series. There are two kinds of batteries:
(a) Primary batteries: In primary batteries, when the reactants have been converted into
products, no more electricity is produced. The cell reaction cannot be reversed and the battery becomes dead.
(b) Secondary batteries: In secondary batteries (or cells), the cell reaction can be reversed by passing electricity through the battery (charging). It means that the battery can be used again and again through a large number of discharging and charging cycles.
29. The most common example of secondary battery is the lead storage battery.
30. Electrical cells that are discharged to convert the energy from the combustion of fuels (hydrogen, carbon monoxide, methane, etc.) directly into the electrical energy are called fuel cells.
31. The corrosion of metals is an electrochemical process. It occurs in presence of water and oxygen.
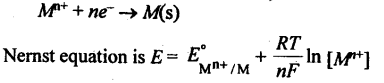
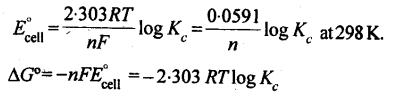
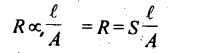
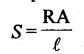
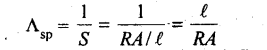
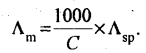

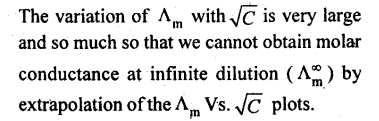



Leave a Reply