Notes For All Chapters Chemistry Class 12 CBSE
1. Haloalkanes are classified as fluoro, chloro, bromo or iodo compounds according to the type of halogen present and as mono-, di- tri-, tetra- haloalkanes, etc., according to the one, two, three, four, etc., halogen atoms respectively present in their molecule.
2. Alkyl halides are further classified as primary (1°), secondary (2°) and tertiary (3°) according to the halogen atom attached to primary, secondary and tertiary carbon atoms, respectively.
3. Due to electronegativity difference between the carbon and the halogen, the shared pair of electron lies closer to the halogen atom. As a result, the halogen carries a small negative charge, while the carbon carries a small positive charge. Consequently, C-X bond is a polar covalent bond.
4. Methods of Preparation of Haloalkabes: Haloalkanes can be prepared from displacement of alcoholic group in alkyl alcohol by halogen acid, PCl5 or PCl3. Haloalkanes can also be prepared by addition of halogen acids or halogens on alkene and alkyne. Alkyl halides can also be prepared by free radical halogenation of alkane.
5. Methods of preparation of Haloarenes. Haloarenes can be prepared by side chain halogenation or nuclear halogenation of aromatic hydrocarbons.
6. From diazonium salts:
(i) By Sandmeyer reaction:
(ii) By Gattermann reaction:
7. Chemical reactions of haloalkanes
(a) Nucleophilic substitution reactions:
(i) C-X bond in alkyl halide is more polar due to electron repelling nature of alkyl group (-) and thus readily undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction. These are of two types:
(1) SN1(Substitution, nucleophilic, unimolecuiar): In such type of reactions, rate = k [RX], i.e., rate, is independent of concentration of nucleophile and occurs in two steps. Such reactions are favoured by polar solvents.
(2) SN2(Substitution, nucleophilic, bimolecular): In such type of reactions, rate = k [RX] [ Nu ]–, i.e., rate of reaction depends on concentration of nucleophile and take place in one step.
(ii) A SN2 reaction proceeds with complete stereochemical inversion while a SN1 reaction proceeds with racemisation.
(b) Elimination reaction: When a haloalkane with β-halogen atom is heated with alcoholic solution of potassium hydroxide, there is elimination of hydrogen atom from α-carbon and a halogen atom from the a-carbon atom. An alkene is formed as a product, also called β-elimination.
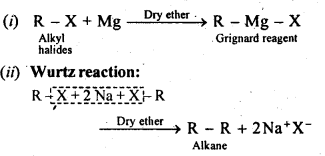
(c) Reaction with metals:
8. Aryl halides are extremely less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction due to following reasons:
(a) In haloarenes, the lone pair of electrons on the halogen atom are delocalized on the benzene ring due to resonance.
(b) In haloalkanes, the halogen atom is attached to sp3-hybridized carbon while in haloarenes the halogen atom is attached to sp2– hybridized carbon.
9. Electrophilic substitution reaction: Haloarenes undergo the usual electrophilic substitution reactions of the benzene ring such as halogenation, nitration, sulphonation and Friedel crafts reactions. Halogen atom is slightly deactivating and o, p-directing.
10. Trichloromethane (Chloroform):
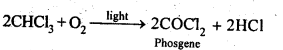
The major use of chloroform today is in the production of the freon refrigerant R-22. Chloroform is stored in closed dark coloured bottles completely filled so that air is kept out Because it is slowly oxidised by air in the presence of light to an extremely poisonous gas, carbonyl chloride (Phosgene).
11. Freons are the chlorofluorocarbons compounds of methane and ethane. They are extremely stable, unreactive, norttoxic, noncorrosive and easily liquefiable gases. Freon-12 (CCl2F2) is most common freons in industrial use.

Leave a Reply