Notes For All Chapters Chemistry Class 12 CBSE
1. A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or 9.
more chemically non-reacting substances.
The components of a solution generally cannot be separated by filtration, settling or centrifuging.
2. A solution may be classified as solid, liquid or a gaseous solution.
3. Solubility is defined as the amount of solute in a saturated solution per 100g of a solvent.
4. The solubility of a gas in a liquid depends upon
(a) the nature of the gas and the nature of the liquid,
(b) the temperature of the system, and
(c) the pressure of the gas.
5. The effect of pressure on the solubility of a gas in a liquid is governed by Henry’s Law. It states that the solubility of a gas in a liquid at a given temperature in directly proportional to the partial pressure of the gas Mathematically, P = KHX where P is the partial pressure of the gas; and X is the mole fraction of the gas in the solution and KH is Henry’s Law constant.
6. The vapour pressure of a liquid is the pressure exerted by its vapour when it is in dynamic equilibrium with its liquid, in a closed container.
7. According to Raoults Law, the vapour pressure of a solution containing a non-volatile solute is directly proportional to the mole fraction of the solvent ( XA). The proportionality constant being the vapour pressure of the pure solvent, i.e., P× XA or P = P° XA.
8. A solution which obeys Raoult’s Law at all concentrations and temperatures is known as an ideal solution.
9. Characteristics of an ideal solution:
(a) ∆sol V = 0, i.e., there is no change in volume when an ideal solution is formed.
(b) ∆sol H= 0; i.e., heat is neither evolved nor absorbed during the formation of an ideal solution.
10. (a) The solution shows positive deviation from Raoult’s Law if its vapour pressure is higher than that predicted by Raoult’s Law.
(b) The solution shows negative deviation if its vapour pressure is lower than that predicted by Raoult’s Law.
11. Colligative properties of solutions are those properties which depend only upon the number of solute particles in the solution and not on their nature. Such properties are
(a) Relative lowering in vapour pressure,
(b) Elevation of boiling point,
(c) Depression of freezing point and
(d) Osmotic pressure.
12.
Thus, according to Raoult’s Law, the relative lowering of vapour pressure of a solution is equal to the mole fraction of the solute.
13. For a dilute solution, the elevation in boiling point is found to be proportional to the molality of the
where ∆Tb is the elevation in boiling point, ‘m’ is the molality and Kb is the Molal elevation constant
14. The depression in freezing point (∆Tf) is proportional to the molality of the solution.
where Kf is molal depression constant (freezing point depression constant).
15. The spontaneous flow of solvent molecules from a dilute solution into a concentrated solution when the two are separated by a perfect sernipermeable membrane is called osmosis.
16. Osmotic pressure (π) is the pressure which must be applied to the solution side (more concentrated solution) to just prevent the passage of pure solvent into it through a sernipermeable membrane.
Mathematically, π = CRT= nB/V- RT
where n is the osmotic pressure of the solution,
C is the concentration of solution
nB is the number of moles of solute,
V is the volume of the solution in litres,
R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature on the Kelvin scale.
17. Isotonic solutions are those solutions which have the same osmotic pressure. Also they have same molar concentration.
For isotonic solutions, π1 = π2 Also, C1 = C2
18. Van’t Hoff factor, ‘ i’ is used to express the extent of association or dissociation of solutes in solution. It is die ratio of the normal and observed molar masses of the solute, i. e.,
19. In case of association, observed molar mass being more than the normal, the factor ‘T has a value less than one. But in case of dissociation, the van’t Hoff factor is more than one because the observed molar mass has a less value.
20. In case of solutes which do not undergo any association or dissociation in a solvent, the Vant Hoff factor, ‘i’, will be equal to one because the observed and normal molar masses will be same.
21. Inclusion of van’t Hoff factor, ‘F, modifies the equations for colligative properties as follows:
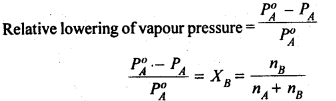



Leave a Reply