Notes For All Chapters Physics Class 12 CBSE
1. Electric Charge Charge is the property associated with matter due to which it produces and experiences electric and magnetic effect.
2. Conductors and Insulators Those substances which readily allow the passage of electricity through them are called conductors, e.g. metals, the earth and those substances which offer high resistance to the passage of electricity are called insulators, e.g. plastic rod and nylon.
3. Transference of electrons is the cause of frictional electricity.
4. Additivity of Charges Charges are scalars and they add up like real numbers. It means if a system consists of n charges q1, q2, q3 , … ,qn, then total charge of the system will be q1 +q2 + … +qn.
5. Conservation of Charge The total charge of an isolated system is always conserved, i.e. initial and final charge of the system will be same.
6. Quantisation of Charge Charge exists in discrete amount rather than continuous value and hence, quantised.
Mathematically, charge on an object, q=±ne
where, n is an integer and e is electronic charge. When any physical quantity exists in discrete packets rather than in continuous amount, the quantity is said to be quantised. Hence, charge is quantised.
7. Units of Charge
(i) SI unit coulomb (C)
(ii) CGS system
(a) electrostatic unit, esu of charge or stat-coulomb (stat-C)
(b) electromagnetic unit, emu of charge or ab-C (ab-coulomb)
1 ab-C = 10 C, 1 C = 3 x 109 stat-C
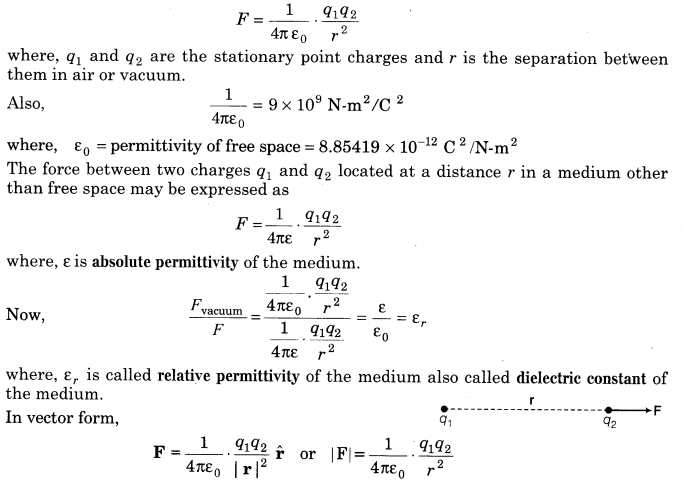
8. Coulomb’s Law It states that the electrostatic force of interaction or repulsion acting between two stationary point charges is given by
9. Electrostatic forces (Coulombian forces) are conservative forces.
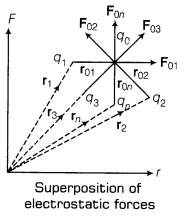
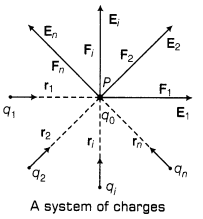
10. Principle of Superposition of Electrostatic Forces This principle states that the net electric force experienced by a given charge particle q0 due to a system of charged particles is equal to the vector sum of the forces exerted on it due to all the other charged particles of the system.
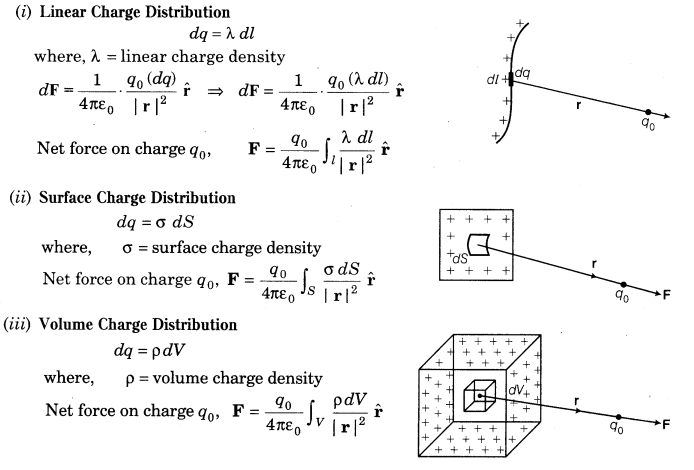
11. Electrostatic Force due to Continuous Charge Distribution
The region in which charges are closely spaced is said to have continuous distribution of charge. It is of three types given as below:
12. Electric Field Intensity The electric field intensity at any point due to source charge is defined as the force experienced per unit positive test charge placed at that point without disturbing the source charge. It is expressed as
13. Electric Field Intensity (EFI) due to a Point Charge
14. Electric Field due to a System of Charges
Same as the case of electrostatic force, here we will apply principle of superposition, i.e.
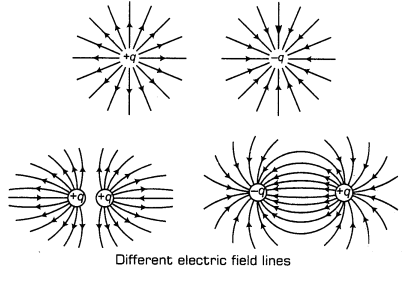
15. Electric Field Lines Electric field lines are a way of pictorially mapping the electric field around a configuration of charge(s). These lines start on positive charge and end on negative charge. The tangent on these lines at any point gives the direction of field at that point.
16. Electric field lines due to positive and negative charge and their combinations are shown as below:
17. Electric Dipole Two point charges of same magnitude and opposite nature separated by a small distance altogether form an electric dipole.
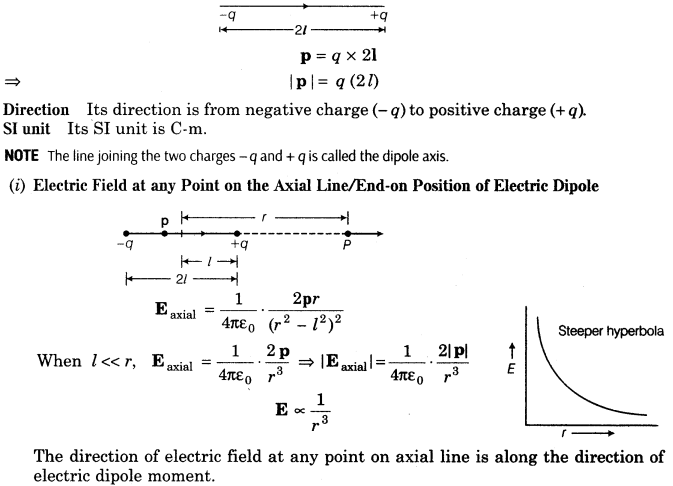
18. Electric Dipole Moment The strength of an electric dipole is measured by a vector quantity known as electric dipole moment (p) which is the product of the charge (q) and separation between the charges (2l).
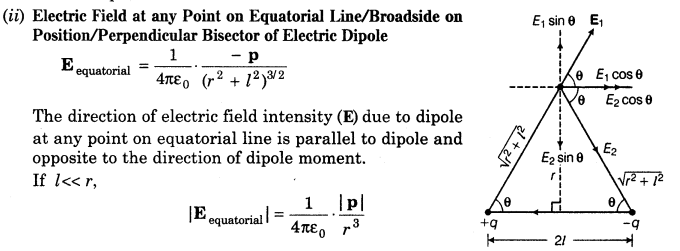
19. Electric Field due to a Dipole Electric field of an electric dipole is the space around the dipole in which the electric effect of the dipole can be experienced.
21. Torque on an electric dipole placed in a uniform electric field (E) is given by
24. Dipole is in stable equilibrium in uniform electric field when angle between p and E is 0° and in unstable equilibrium when angle θ= 180°.
25. Net force on electric dipole placed in a uniform electric field is zero.
26. There exists a net force and torque on electric dipole when placed in non-uniform electric field.
27. Work done in rotating the electric dipole from θ1 to θ2 is W = pE (cos θ1 – cos θ2)
28. Potential energy of electric dipole when it rotates from θ1 = 90° to θ2 =0
U = pE (cos 90° – cosθ) = -pE cos θ = – p .E
29. Work done in rotating the dipole from the position of stable equilibrium to unstable equilibrium, i.e. when θ1 = 0° and θ2 = π.
W = 2 pE
30. Work done in rotating the dipole from the position of stable equilibrium to the position in which dipole experiences maximum torque, i.e. when θ1 = 0° and θ2 = 90°.
W = pE
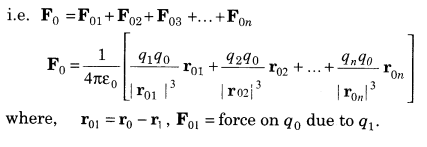
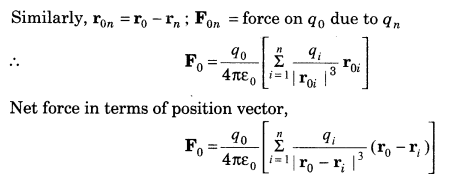

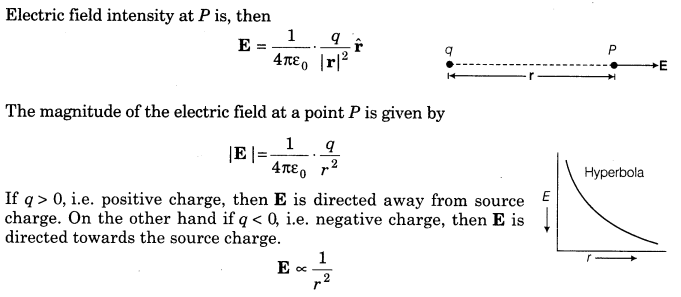
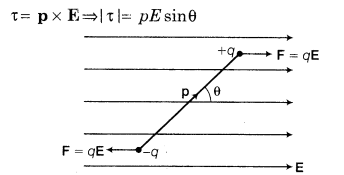

Leave a Reply