Notes For All Chapters Physics Class 12 CBSE
1. Electrostatic Potential The electrostatic potential at any point in an electric field is equal to the amount of work done per unit positive test charge or in bringing the unit positive test charge from infinite to that point, against the electrostatic force without acceleration.
NOTE: Electrostatic potential is a state dependent function as electrostatic forces are conservative forces.
2. Electrostatic Potential Difference The electrostatic potential difference between two points in an electric field is defined as the amount of work done in moving a unit positive test charge from one point to the other point against of electrostatic force without any acceleration (i.e. the difference of electrostatic potentials of the two points in the electric field).
where, is work done in taking charge q0 from A to B against of electrostatic force.
Also, the line integral of electric field from initial position A to final position B along any path is termed as potential difference between two points in an electric field, i.e.
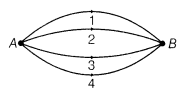
NOTE: As, work done on a test charge by the electrostatic field due to any given charge configuration is independent of the path, hence potential difference is also same for any path.
For the diagram given as below, potential difference between points A and B will be same for any path.
3. Electrostatic potential due to a point charge q at any point P lying at a distance r from it is given by
4. The potential at a point due to a positive charge is positive while due to negative charge, it is negative.
5. When a positive charge is placed in an electric field, it experiences a force which drives it from points of higher potential to the points of lower potential. On the other hand, a negative charge experiences a force driving it from lower potential to higher.
6. Electrostatic potential due to an electric dipole at any point P whose position vector is r w.r.t. mid-point of dipole is given by
7. The electrostatic potential on the perpendicular bisector due to an electric dipole is zero.
8. Electrostatic potential at any point P due to a system of n point charges q1, q2, ……………, qn whose position vectors are r1,r2,…,rn respectively, is given by
where, r is the position vector of point P w.r.t. the origin.
9. Electrostatic potential due to a thin charged spherical shell carrying charge q and radius R respectively, at any point P lying
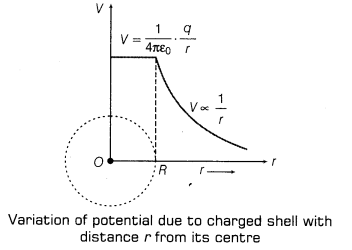
10. Graphical representation of variation of electric potential due to a charged shell at a distance r from centre of shell is given as below:
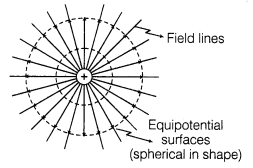
11 Equipotential Surface A surface which have same electrostatic potential at every point on it, is known as equipotential surface.
The shape of equipotential surface due to
(i) line charge is cylindrical.
(ii) point charge is spherical as shown along side:
(a) Equipotential surfaces do not intersect each other as it gives two directions of electric field E at intersecting point which is not possible.
(b) Equipotential surfaces are closely spaced in the region of strong electric field and vice-versa.
(c) Electric field is always normal to equipotential surface at every point of it and directed from one equipotential surface at higher potential to the equipotential surface at lower potential.
(d) Work done in moving a test charge from one point of equipotential surface to other is zero.
12. Relationship between electric field and potential gradient
where, negative sign indicates that the direction of electric field is from higher potential to lower potential, i.e. in the direction of decreasing potential.
NOTE: (i) Electric field is in the direction of which the potential decreases steepest.
(ii) Its magnitude is given by the change in the magnitude of potential per unit displacement normal to the equipotential surface at the point.
13. Electrostatic Potential Energy The work done against electrostatic force gets stored as potential energy. This is called electrostatic potential energy.
∆U = UB-UA =WAB
14. The work done in moving a unit positive test charge over a closed path in an electric field is zero. Thus, electrostatic forces are conservative in nature.
15. Electrostatic potential energy of a system of two point charges is given by
16. Electrostatic potential of a system of n point charges is given by
17. Potential Energy in an External Field
(i) Potential Energy of a single charge in external field Potential energy of a single charge q at a point with position vector r, in an external field is qV(r),
where V(r) is the potential at the point due to external electric field E.
(ii) Potential Energy of a system of two charges in an external field
18. Potential energy of a dipole in a uniform electric field E is given by
Potential energy = -p .E
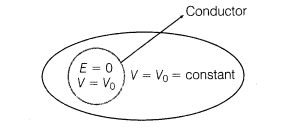
19. Electrostatic Shielding The process which involves the making of a region free from any electric field is known as electrostatic shielding.
It happens due to the fact that no electric field exist inside a charged hollow conductor. Potential inside a shell is constant. In this way we can also conclude that the field inside the shell (hollow conductor) will be zero.
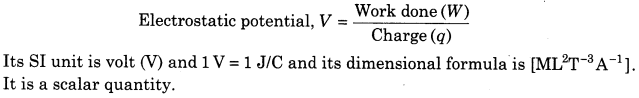
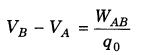
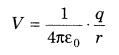
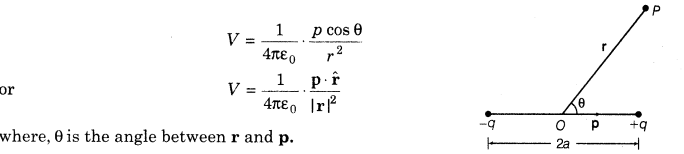
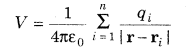
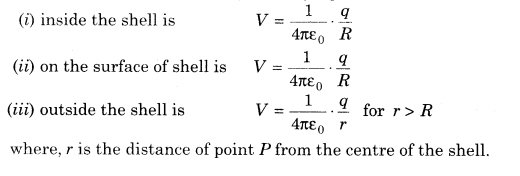
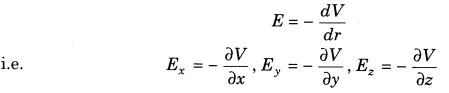
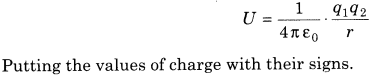
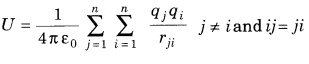
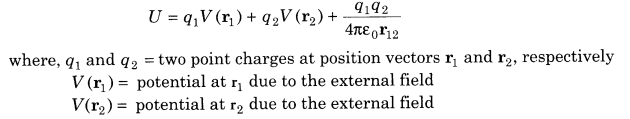

Leave a Reply