Notes For All Chapters Physics Class 12 CBSE
1. The space in the surroundings of a magnet or a current-carrying conductor in which its magnetic influence can be experienced is called magnetic field. Its SI unit is Tesla (T).
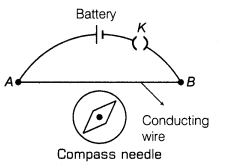
2. Oersted experimentally demonstrated that the current-carrying conductor produces magnetic field around it.
When key K is closed, then deflection occurs in the compass needle and vice-versa,
3. Biot-Savart’s Law According to this law, the magnetic field due to small; current-carrying element dl at any nearby point P is given by
4. The relationship between μ0, ε0 and c is
where, c is velocity of light, ε0 is permittivity of free space and μ0 is magnetic permeability.
5. Magnetic field at the centre of a circular current-carrying conductor/coil.
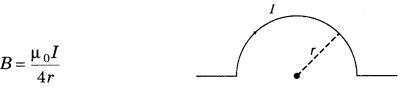
6. Magnetic field at the centre of semi-circular current-carrying conductor.
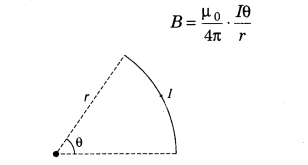
7. Magnetic field at the centre of an arc of circular current-carrying conductor which subtends an angle 0 at the centre.
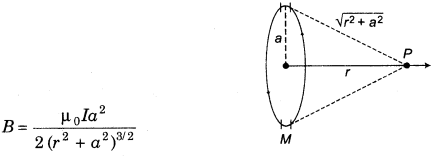
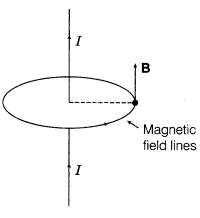
8. Magnetic field at any point lies on the axis of circular current-carrying conductor
9. Magnetic field due to straight current-carrying conductor at any point P at a distance r from the wire is given by
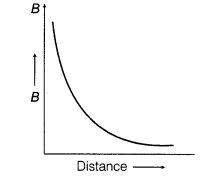
10. The following figure shows the graphical representation of variation of B with distance from straight conductor.
11. Ampere’s Circuital Law The line integral of the magnetic field B around any closed loop is equal to μ0 times the total current I threading through the loop, i.e.
Magnitude of magnetic field of a straight wire using Ampere’s law
12. Maxwell introduced the concept of displacement current.
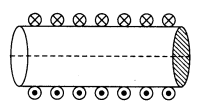
13. Magnetic Field due to a Straight Solenoid
(i) At any point inside the solenoid,
B = μ0nI
where, n = number of turns per unit length.
(ii) At the ends of the solenoid,
B = 1/2 μ0nI
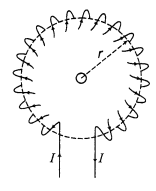
14. Magnetic Field due to Toroidal Solenoid
(i) Inside the toroidal solenoid,
B =μ0nI, here, n =N/2πr ,N= total number of turns
(ii) In the open space, interior or exterior of toroidal solenoid,
B= 0
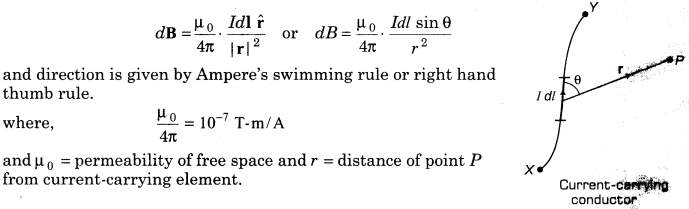
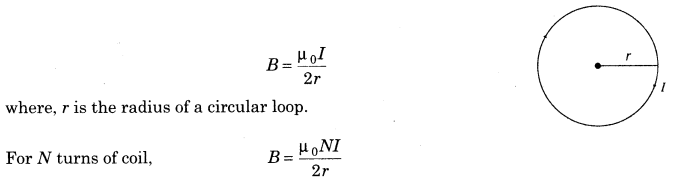
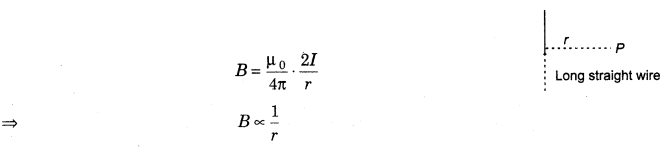
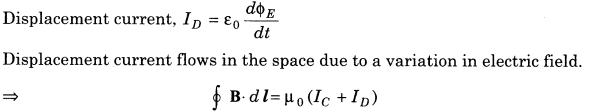

Leave a Reply