Notes For All Chapters Physics Class 12 CBSE
1. In every atom, the positive charge and mass are densely concentrated at the centre of the atom forming its nucleus. More than 99.9% mass of the atom is concentrated in the nucleus.
2. Atomic Mass Unit (amu) The unit to express atomic masses is called atomic mass
unit. Atomic mass unit is defined as 1/12 th of the mass of carbon atom (C12).
3. Composition of Nucleus The composition of a nucleus can be described by using the following terms and symbols.
(i) Atomic Number Z Atomic number of an element is the number of protons present inside the nucleus of an atom of the element.
Atomic number = Number of protons = Number of electrons
(ii) Mass Number A Mass number of an element is the total number of protons and neutrons inside the atomic nucleus of the element.
Mass number = Number of protons + Number of neutrons = Number of electrons + Number of neutrons i.e. A=Z.+ N
4. Size of Nucleus If R is the radius of the nucleus having mass number A, then
5. Nuclear Density Density of nuclear matter is the ratio of mass of nucleus and its volume.
6. Radioactivity It is the phenomenon of spontaneous disintegration of the nucleus of an atom with emission of one or more radiations like α-particle, β-particle or γ-rays.
7. Radioactive Decay It is a nuclear transformation process in which the radioactive rays are emitted from the nucleus of the atom. This process cannot be accelerated and slow down by any physical or chemical process.
8. Radioactivity Decay Law According to this law, the rate of decay of radioactive atoms at any instant is proportional to the number of atoms present at that instant.
9. Half-life Half-life of a radioactive element is defined as the time during which half the number of atoms present initially in the sample of the element decay.
10. Mean Life/Average Life Average life of a radioactive element can be obtained by calculating the total life time of all the atoms of the radioactive element and dividing it by the total number of atoms present initially in the sample of the element.
11. Time required to decay from N0 to N
12. Decay Constant The radioactive decay constant may be defined as the reciprocal of the time during which the number of atoms in a radioactive substance reduces to 36.8% of their initial number.
13. Radioactive Displacement Law The law of radioactive displacement is also known as Fajan’s and Soddy law. This law describes which chemical element and isotope is created during the particular type of radioactive decay.
(i) α- Decay In α-decay, the mass number of the product nucleus is four less than that of decaying nucleus while the atomic number decreases by two.
(ii) β-Decay In β-decay, the mass number of product nucleus remains same but atomic number increases or decreases by one.
In beta-minus decay (β– ),an electron and an antineutrino are created and emitted from the nucleus via the reaction given below:
In beta-plus decay (β+), a positron and a neutrino are created and emitted from the nucleus via the reaction given below:
(iii) γ-Decay A γ- ray is emitted when a or β-decay results in a daughter nucleus in an excited state. Atom then returns to ground state by a single photon transition or successive transitions involving more than one photon.
14. The SI unit of radioactivity is Becquerel (Bq).
1 Becquerel(Bq) = 1 disintegration/second Other units
(i) Curie The activity of a radioactive sample is said to be one curie.
1 curie (Ci) = 3.7 x 1010 decays/second
(ii) Rutherford The activity of a radioactive sample is said to be one rutherford.
1 rutherford (Rd) = 106 decays/second

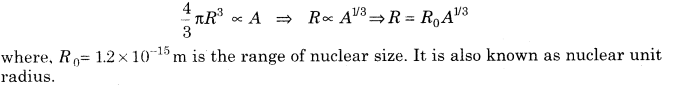
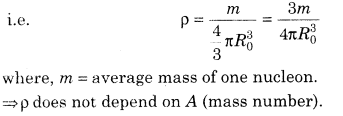
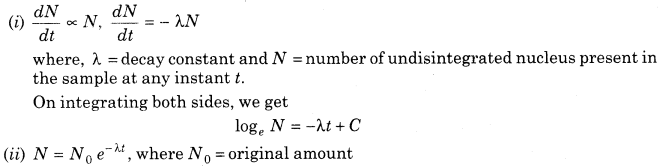
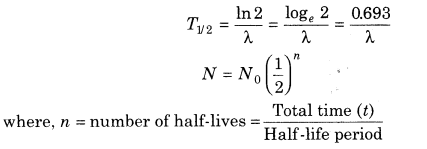
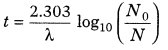
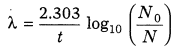
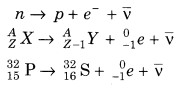
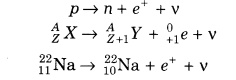

Leave a Reply