Notes For All Chapters Physics Class 12 CBSE
1. Ray Optics or Geometrical Optics In this optics, the light is considered as a ray which travels in a straight line. It states that for each and every object, there is an image.
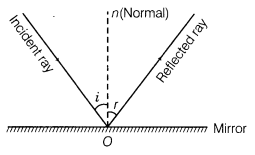
2. Reflection Reflection is the phenomenon of changing the path of light without any change in the medium.
3. Reflection of Light The returning back of light in the same medium from which it has come after striking a surface is called reflection of light.
4. Laws of Reflection
Two laws of reflection are given as below:
(i) The angle of incidence i is equal to the angle of reflection r.
i.e. ∠i = ∠r.
(ii) The incident ray, reflected ray and normal to the reflecting surface at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
5. Total number of images formed by two plane mirrors inclined at an angle θ with each other is given by
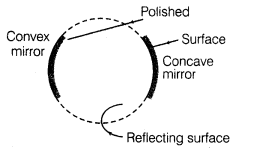
6. Reflecting surface of a spherical mirror is a part of a hollow sphere. Spherical mirrors are of two types, (i) Concave spherical mirror (ii) Convex spherical mirror.
7. Sign Convention All measurements should be taken from pole of mirror. All measurements along the direction of incident ray will be positive and opposite to incident ray are negative. All the measurements for the distances above the principal axis are taken as positive and below the principal axis are taken as negative.
8. For a real object, u is negative whereas v is negative for real image and positive for virtual image.
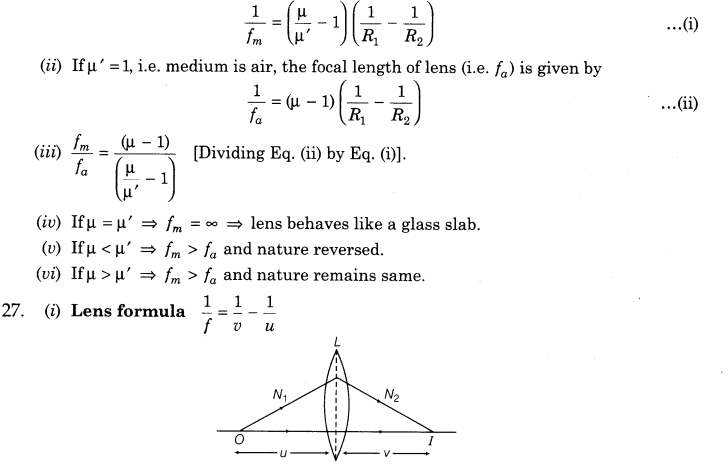
9. Mirror Formula Mirror formula is a relation between focal length of the mirror and distances of objects and image from the mirror.
11. Linear Magnification The ratio of the size of the image formed by a spherical mirror I to the size of the object O is called the linear magnification produced by the spherical mirror.
12. Magnification (m) It is negative corresponding to real image and positive for virtual image.
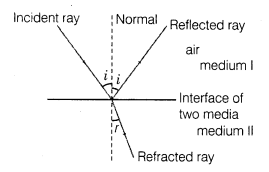
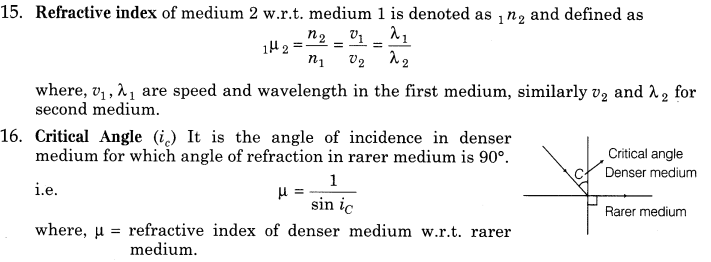
13. Refraction The phenomenon of changing in the path of light as it goes from one medium to another is called refraction.
14. Laws of Refraction
Two laws of refraction are given as below:
(i) The incident ray, refracted ray and the normal to the refracting surface at the point of incidence lie in the same plane.
(ii) The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction is constant for the two given media. This constant is denoted by n and is called the relative refractive index.
n = sin i/sin r (Snell’s law)
where, n is refractive index of the second medium when first medium is air.
17. Total Internal Reflection (TIR) When a ray of light travelling from denser medium to rarer medium is incident at the interface of two medium at an angle greater than the critical angle for the two media, the ray is totally reflected back to denser medium. This phenomenon is called Total Internal Reflection. It occurs only when angle of incidence in denser medium is greater (not equal) than critical angle, i.e. i> ic.
18. Principle of reversibility of light states that when final path of a ray of light after any number of reflections and refractions is reversed, the ray retraces its entire path.
22. Optical fibre, mirage, sparkling of diamond, totally reflecting prism, etc. work on the principle of total internal reflection.
24. Lens is a transparent medium bounded by two surfaces of which one or both surfaces are spherical.
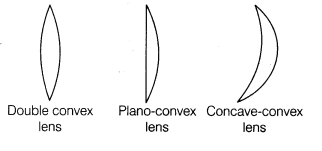
(i) Convex or Converging Lens A lens which is thicker at the centre and thinner at its end is called convex lens.
Convex lenses are of three types which are given as below:
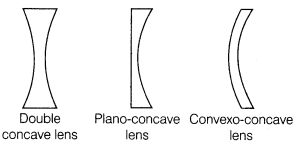
(ii) Concave or Diverging Lens A lens which is thinner at the centre and thicker at its ends is called a concave lens.
Concave lenses are of three types which are given as below:
25. Lens maker’s formula
26. When lens of refractive index μ is immersed in a medium of refractive index μ, then
(i) When lens is taken in another medium, then focal length changes to fm which is given by
28. Power of Lens The ability of a lens to converge or diverge the rays of light incident on it is called the power of the lens.
29. Power of combination lenses in contact is given by
30. Magnification by combination of lenses
m = m1 × m2 × m3 ………..
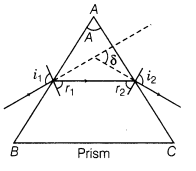
31. (i) Prism have got the property of bending the incident light towards its base.
A prism is a portion of a transparent medium bounded by two plane faces inclined to each other at a suitable angle.
(ii) When the prism is adjusted at angle of minimum deviation, then
(a) angle of incidence is equal to the angle of emergence
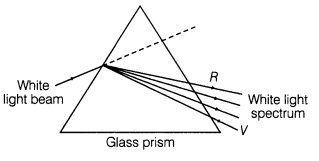
31. Dispersion by a Prism The phenomenon of splitting of light into its component colours is known as dispersion.
Angular Dispersion Angular dispersion produced by a prism for white light is the difference in the angles of deviation for two extreme colours i.e. violet and red.
Dispersive Power Dispersive power of a prism is defined as the ratio of angular dispersion to the mean deviation produced by the prism.
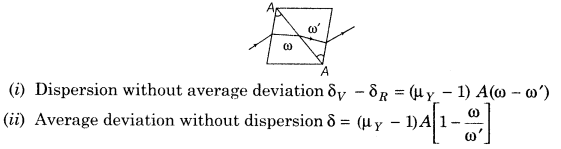
33. Combining two thin prisms we can study two conditions


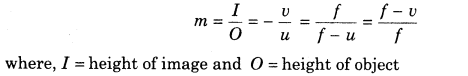
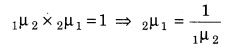


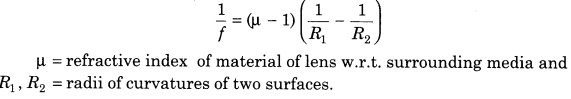
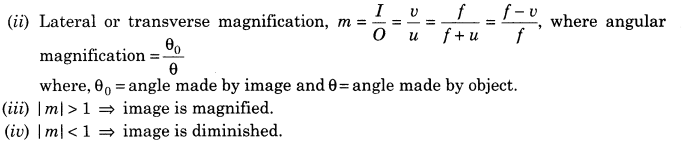
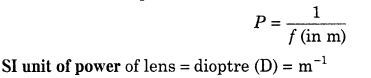
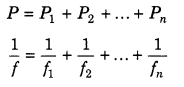
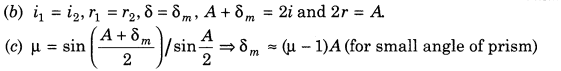
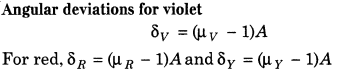
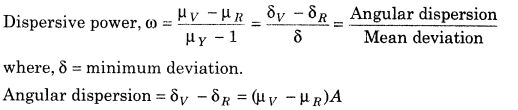


Leave a Reply