Notes For All Chapters Physics Class 12 CBSE
1. Wave Optics Describes the connection between waves and rays of light. According to wave theory of light, light is a form of energy which travels through a medium in the form of transverse wave.
2. Wave front The locus of all those particles which are vibrating in the same phase at any instant is called wave front. Thus, wave front is a surface having same phase of vibrating particles at any instant at every point on it.
3. Phase Speed Phase speed is the speed with which wave front moves and it is equal to wave speed.
4. The shape of wavefront due to a
(i) point source is spherical
(ii) line source is cylindrical
(iii) source at infinity is a plane.
5. A line perpendicular to a wave front is called a ray. The direction of rays are always perpendicular to the wave front along the direction of propagation of wave.
6. Huygens’ Principle Huygens’ principle is essentially a geometrical construction, which gives the shape of the wave front at any time, allows us to determine the shape of the wave front at a later time. According to Huygens’ principle,
(i) Every point on a wave front behaves like a light source and emits secondary wavelets.
(ii) The secondary wavelets spread in all directions in space (vacuum) with the velocity of light.
(iii) The envelope of wave front of secondary wavelets, after a given time, along forward direction gives the new position of wave front.
7. The laws of reflection and refraction can be verified using Huygens’ wave theory.
8. Huygens’ wave theory successfully explains the phenomenon of interference, diffraction and polarisation.
9. As, frequency v is characteristic of the source, therefore v = 1/T remains the same as light travels from one medium to another.
10. Wavelength is inversely proportional to refractive index (μ) of the medium
i.e. λ’ = λ/μ
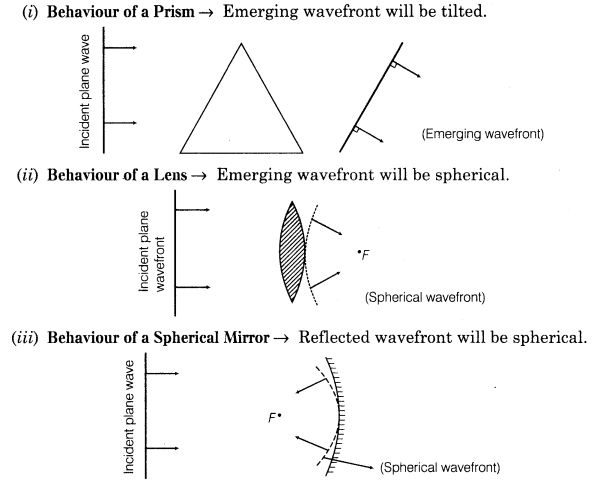
11. Behaviour of a Prism, Lens and Spherical Mirror towards Plane Wave front
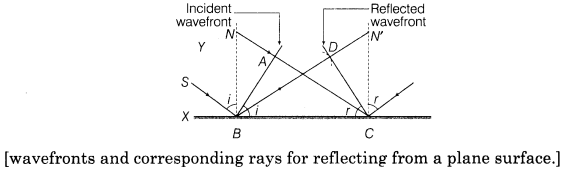
12. Laws of reflection on the basis of Huygens’ wave theory As shown in figure, consider a plane wave front AB incident on the reflecting surface XY, both the wave front and the reflecting surface being perpendicular to the plane of paper.
First the wave front touches the reflecting surface at B and then at the successive points towards C. In accordance with Huygens’ principle, from each point on BC, secondary wavelets start growing with the speed c. During the time the disturbance from A reaches the point C the secondary wavelets from B must have spread over a hemisphere of radius BD = AC = ct, where t is the time taken by the disturbance to travel from A to C. The tangent plane CD drawn from the point C over this hemisphere of radius ct will be the new reflected wave front.
Let angles of incidence and reflection be i and r, respectively . In AABC and ADCB, we have
i.e. the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. The proves the first law of reflection.
Further, since the incident ray SB, the normal BN and the reflected ray BD are respectively perpendicular to the incident wave front AB, the reflecting surface XY and the reflected wave front CD (all of which are perpendicular to the plane of the paper) therefore, they all lie in the plane of the paper i.e. in the same plane. This proves the second law of reflection.
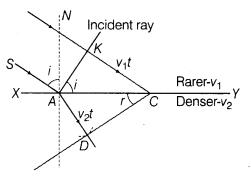
13. Law of refraction on this basis of Huygens’ wave theory Consider a plane wavefront AB incident on a plane surface XY, separating two media 1 and 2, as shown in Figure.
Let v1 and v2 be the velocities of light in two media, with v1 <v2.
The wave front first strikes at point A and then at the successive points towards C. According to Huygens’ principle, from each point on AC, the secondary wavelets starts growing in the second medium with speed v2. Let the disturbance take time t to travel from B to C, then BC = v1t. During the time the disturbance from B reaches the point C, the secondary wavelets from point A must have spread over a hemisphere of radius AD = v2t in the second medium. The tangent plane CD drawn from point C over this hemisphere of radius v2t will be the new refracted wave front.
Let the angles of incidence and refraction be i and r, respectively.
From right AABC, we have
This proves Snell’s law of refraction. The constant 1μ2 is called the refractive index of the socond medium with respect to first medium.
Further, since the incident ray SA, the normal AN and the refracted ray AD are respectively perpendicular to the indicent wave front AB, the dividing surface XY and the refracted wave front CD (all perpendicular to the plane of the paper), therefore, they all lie in the plane of the paper, i.e. in the same plane. This proves another law of refraction.

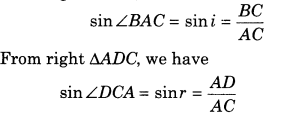
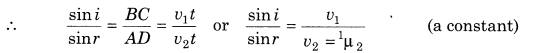

Leave a Reply