Solutions For All Chapters – English Poorvi Class 7
Let us discuss
Page No. 61
I. Work in pairs. Identify the true statements. Check your answers with the teacher.
1. The poet says that she had never heard such an amusing song.
2. The funny man was quite ill-mannered.
3. The funny man wore two hats on his feet.
4. The funny man hopped on his head to reach home.
5. The funny man gave a rose to the poet.
6. The funny man smiled at the poet.
Answer:
- True – The poet mentions, “You never heard in all your life / Such a funny feeling sound,” indicating the song was amusing.
- False – The poem states, “His manners were polite,” so the funny man was not ill-mannered.
- True – The poem says, “My friend, why do you wear two hats / Upon your feet?”
- True – The poem describes, “And hopped home on his head.”
- False – The funny man offered a currant bun, saying it was a rose, but did not give an actual rose.
- True – The poem notes, “He raised the shoe and smiled at me.”
II. Identify the words from the poem based on the meanings given. Share your answers with your classmates and the teacher.
1. a small seedless raisin – C __ R __ __ __ T
2. moved unsteadily – S __ __ G G __ __ __ D
Answer:
1. currant
2. staggered
III. Complete the following sentences with a reason.
1. The tone of the poem is ___________ because ___________.
2. The rhyme scheme of the poem is ___________; and it gives a ___________ quality to the poem.
3. The poet has frequently repeated the word ‘funny’ in order to ___________.
Answer:
1. light-hearted/ humorous, the man’s absurd actions create comedy.
2. AABB, musical /playful
3. to emphasise the man’s ridiculous, silly behaviour.
IV Choose the correct answer from the options given in the brackets.
1. The poem uses vivid imagery to create a _______________________ (humorous and nonsensical/ confusing but thought-provoking) scene.
2. The structure of the poem is in ___________ (monologue/ dialogue) form.
3. The phrases ‘sounding sight’ and ‘hopped home’ are examples of ___________. (alliteration/simile)
Answer:
- humorous and nonsensical
- dialogue
- alliteration
V. Rewrite the following line from the poem in the correct order.
1. But never had I seen before
Such a funny sounding sight
Answer: But never before had I seen such a funny sounding sight.
2. Why has the poet used phrases like ‘funny sounding sight’ and ‘funny feeling sound’ with reference to the funny man?
Answer: The poet uses these phrases to highlight the man’s absurdity. “Funny sounding sight” suggests his appearance is so strange it seems to produce sound, while “funny feeling sound” implies his song evokes physical amusement, blending senses for comic effect.
VI. Can you think of any real-world situations where people do similar things for fun, entertainment, or performance? Share with your classmates and the teacher.
- Street Performers or Clowns: Like the funny man in the poem, street performers or clowns often dress in unusual ways (e.g., colorful costumes or mismatched clothing) and perform unexpected acts, such as juggling or mime, to entertain passersby and evoke laughter.
- Performance Art or Abstract Theatre: The funny man’s actions, such as singing a song and hopping on his head, resemble performance art or abstract theatre, where artists use unconventional behavior or props to break norms and create humorous or thought-provoking experiences.
- Children’s Entertainment and Comedy Shows: The funny man’s playful and nonsensical behavior is similar to characters in children’s shows or comedy programs, where exaggerated actions and silly antics are used to engage and amuse young audiences.
Let us think and reflect
Page No. 62
I. Read the extracts given below and answer the questions that follow.
1. He said, “Allow me to present
Your Highness with a rose.”
And taking out a currant bun
He held it to my nose
I staggered back against the wall
And then I answered, “Well!”
(i) Why does the funny man address the poet as ‘Your Highness’?
Answer: He addresses her as “Your Highness’ to mock formal politeness in a humorous way.
(ii) Choose a phrase from the extract which indicates a polite request.
Answer: “Allow me to present” indicates a polite request.
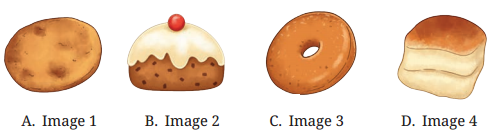
(iii) Choose the option which shows a ‘currant bun’
Answer: Image 2 is of Currant Bun, (image 1 is of Bread, image 3 is of Donut and image 4 is of Loaf.)
(iv) Complete the sentence with an appropriate reason.
When the poet says, ‘Well!’, it expresses surprise. This was so because ___________.
Answer: the man offered a Currant Bun instead of a rose, which was unexpected.
2. You never heard in all your life
Such a funny feeling sound.
“My friend, why do you wear two hats
Upon your feet?” I said.
He turned the other way about,
And hopped home on his head.
(i) Choose the line from the extract which tells us that the sound was unique.
Answer: “You never heard in all your life such a funny feeling sound.”
(ii) Complete the sentence with an appropriate reason. The poet calls the funny man ‘my friend’ because ___________.
Answer: The poet calls him ‘my friend’ because she finds him amusing and non-threatening.
(iii) What does the reaction of the funny man to the poet’s question tell us about him?
Answer: His reaction shows he enjoys being absurd and doesn’t take things seriously.
(iv) Choose the correct option to complete the sentence.
The last line of the extract makes the readers feel ____________.
A. dreamy B. impatient C. worried D. cheerful
Answer: D. cheerful
II. Answer the following questions.
1. Which character trait of the funny man was most appealing to you? Why?
Answer: The most appealing trait of the funny man is his playful and whimsical nature. This is appealing because his absurd actions, like wearing a shoe on his head and hopping home, create a sense of joy and light-heartedness, making the poem entertaining and memorable.
2. The funny man does unusual things in the poem. How does it affect the overall mood of the poem?
Answer: The funny man’s unusual actions, such as wearing hats on his feet and offering a currant bun as a rose, create a humorous and whimsical mood. These actions evoke laughter and surprise, making the poem feel light-hearted and playful, encouraging readers to embrace the absurdity.
3. What alternative title would you suggest for the poem? Give reason(s) for your choice.
Answer: An alternative title could be “The Whimsical Wanderer”. This title reflects the funny man’s quirky and unpredictable behavior as he wanders down the street, performing nonsensical acts that captivate the poet and readers, capturing the poem’s essence of humor and imagination.
4. Why do you think the poet has included dialogues in the poem?
Answer: The poet includes dialogues to enhance the interactive and lively nature of the poem. The exchanges between the poet and the funny man, such as the poet’s questions and the man’s playful responses, add a conversational tone, making the poem more engaging and emphasizing the humor in their interaction.
5. What does the poet wish to convey by highlighting the unusual behaviour of the funny man?
Answer: By highlighting the funny man’s unusual behavior, the poet wishes to celebrate creativity, imagination, and the joy of def flavorfulying conventions. The man’s actions encourage readers to appreciate the humor in absurdity and embrace a playful perspective on life, free from rigid expectations.
Let us learn
Page No. 63
Read the following phrases from the poem.
• walking down • taking out • sat down
These are phrasal verbs
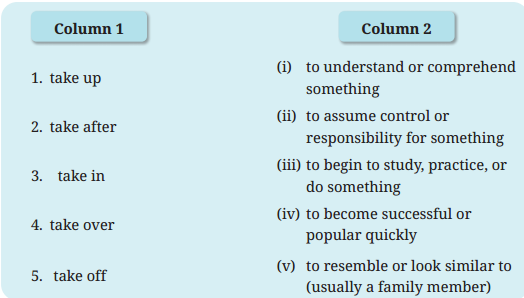
I Match the phrasal verbs in Column 1 with their correct meaning in Column 2.
Answer:
1. take up – (iii),
2. take after – (ii),
3. take in – (i),
4. take over – (ii),
5. take off – (iv)
Now, fill in the blanks with suitable phrasal verbs from the table given in I. You may change the tense of the verb, if required.
1. The new technology is set to _________________ traditional methods of communication.
2. I tried hard to _________________ what the writer wanted to say but was unsuccessful.
3. Arjun decided to _________________ painting as a hobby.
4. The smartphone quickly _________________ the sales in the market.
5. Sheela _________________ her father; they have the same smile.
Answer:
- take over
- take in
- take up
- take off
- take after
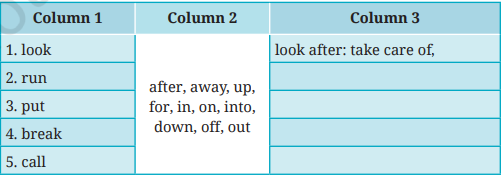
II. Match the verbs in Column 1 with any suitable adverbs or prepositions in Column 2. Write their meanings in Column 3. An example has been done for you.
Now, frame sentences of your own using any five phrasal verbs.
Answer:
1. look + for = to Search
I need to look for my lost keys before I leave.
2. run + away = to escape
The puppy tried to run away when it heard loud fireworks.
3. put + off = to postpone
They put off the meeting until Tuesday.
4, break + down = to stop working
The car broke down on the highway.
5. call + off = to cancel
We called off the picnic due to rain.
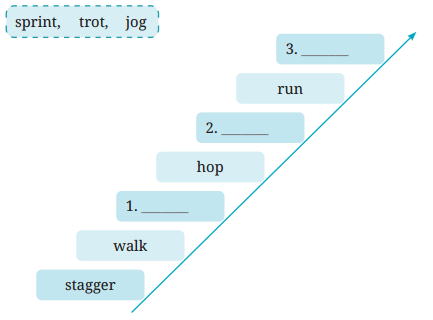
III. Read the following words from the poem.
walking, staggered, hopped
The given words denote the different ways of walking. Arrange the words given in the box in increasing order of pace.
Answer:
1. jog-walk
2. trot-hop
3. sprint-run
Let us listen
Page No. 35
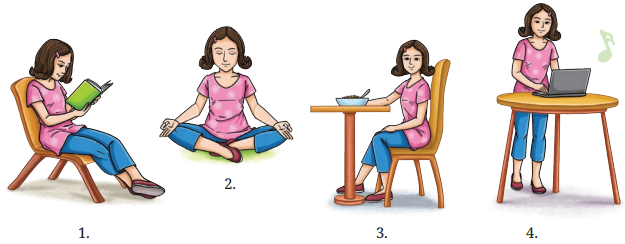
I. You will listen to a girl narrate a personal incident. As you listen, select the picture related to the narration. (Transcript for the teacher on pg. 88)
Answer: Picture 3
II. You will once again listen to the girl narrate a personal incident. As you listen, arrange the events in order of occurrence.
1. Ate lunch
2. Took off shoes
3. Put shoes in the room
4. Laughed at the mistake
5. Placed the plate in the room
6. Prepared for the presentation
7. Put the plate in the kitchen
Answer: Events in order of occurrence are as follows.
6. Prepared for the presentation
2. Took off shoes
1. Ate lunch
5. Placed the plate in the room
4. Laughed at tile mistake
3. Put shoes in the room
7. Put the plate in the kitchen
Let us speak
Page No. 66
Read the joke given below.
A man is talking to God.
The man says, “God, how long is a million years?”
God replies, “For me, it’s about a minute.”
The man asks, “How much is a million rupees?”
God smiles and replies, “It’s less than a rupee for me.”
The man quickly requests, “God, may I have a rupee?”
God promptly says, “Wait a minute.”
Work in pairs and take turns to tell the joke.
Remembr:
• Narrator’s voice – your own voice (speak in a matter-of-fact manner)
• Man’s voice – change to louder voice (speak with respect)
• God’s voice – deep voice (speak in a pleasant tone)
Now, work in pairs to create a joke and tell it in front of the class.
Answer:
1. For the given joke, students should practice:
- Narration in a neutral tone
- Man’s lines in a louder, respectful voice
- God’s lines in a deep, calm voice
Let us write
page No. 66
I. A limerick is a nonsensical and funny verse consisting of five lines. Study the limerick given below and identify the rhyme scheme.
1. There was an Old Man with a beard,
Who said, “It is just as I feared!
Two Owls and a Hen,
Four Larks and a Wren,
Have all built their nests in my beard!”
Edward Lear
Now, read another limerick
2. There were two friends in Bengaluru’s lanes,
One loved books, the other flew planes.
They’d laugh and they’d play,
In their own unique way,
Creating stories and flying in dreams’ trains.
Remember all limericks have the same rhyme scheme AABBA.
Answer:
1. Rhyme scheme: AABBA (hand/ feared, Hen/Wren, beard)
2. Rhyme scheme: AABBA (lands/ planes, play/way, trains)
II. Follow the structure given below and write a limerick on your own.
Answer:
There was a child from Pune,
Who ate soup with a spoon,
Then danced in the rain,
And forgot all her pain,
Now she howls at the full moon!
Let us explore
Page No. 67
I. In ancient Indian literature and mythology, there are several humorous or funny characters who play important roles in the stories. These characters often represent wit, humour and mischief while conveying deeper moral lessons. Here are a few well-known funny characters:
Take any story to read and share it with your classmates and the teacher.
Answer: (Summary of a Tenali Rama story)
Once, Tenali Rama tricked a greedy merchant by. pretending that an ordinary rock was magical. The merchant fell into the trap and, bought it. Later he found it was worthless. This taught him the lesson that greed leads to loss.
II. We can identify the acts of the funny man with certain modernday activities that have playfulness, or unconventional behaviour.
For example:
Street Performers or Clowns: Like the funny man in the poem, modernday street performers or clowns often dress in unusual ways and do
unexpected acts to entertain people.
Performance Art or Abstract Theatre: The funny man’s actions, such as singing a song and hopping on his head, resemble performance art or abstract theatre, where artists break conventional rules to create thought-provoking, often humorous experiences.
Children’s Entertainment and Comedy Shows: The funny man’s behaviour is reflected in children’s shows to evoke laughter.
In these examples, the common theme is humour, imagination, and defying logic or expectation, which is exactly what the funny man in the poem represents.
Answer:
1. Street performers: Like wearing shoes on head for laughs.
2. Clown acts: Similar to offering fake “roses” (like the bun).
3. Comedy shows: Use absurd dialogue like the poem.
4. Children’s entertainers: Do head- stands/hops like the funny man.
III. Sukumar Ray, an Indian poet and illustrator, wrote poems in a similar style in his book Abol Tabol.
You may also share a similar poem from your native language with your classmates and the teacher.
Answer:
(Example Hindi poem):
“Bandar mama pahan pajama,
Neeli dhoti lal rumal,
Jab bhi aate ghar hamare,
Karte hain bahut tamasha!”







Leave a Reply