Notes For All Chapters Geography Class 7
Our atmosphere is surrounded by a huge blanket of air called atmosphere.
Composition of the Atmosphere
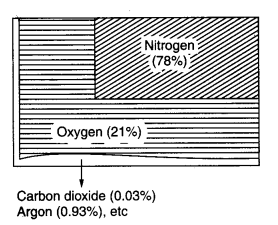
(i) Nitrogen and oxygen are the two gases which make up the bulk of the atmosphere.
(ii) Carbon dioxide, helium, ozone, argon and hydrogen are found in lesser quantities.
(iii) Apart from these gases, tiny dust particles are also present in the air.
Structure of the Atmosphere
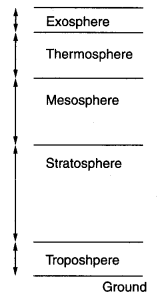
(i) Our atmosphere is divided into five layers starting from the earth’s surface.
(ii) The first layer is the Troposphere whose average height is 13 km. The troposphere is the layer in which the air we breathe exist. Almost all weather phenomena occur here.
(iii) The second layer is the Stratosphere which extends up to 50 km.
(iv) The third layer is the Mesosphere which extends up to the height of 80 km.
(v) The fourth layer is the Thermosphere which extends from 80 km to 400 km.
(vi) The uppermost layer of the atmosphere is Exosphere which has very thin air.
Weather and Climate
(i) Weather is the Hour-to-hour, day-to-day condition of the atmosphere.
(ii) Climate is the weather conditions for a large period and of a large area.
Temperature
(i) The degree of hotness and coldness of the air is called temperature.
(ii)The temperature of the atmosphere changes not only between day and night but also from season to season, an important factor that influences the distribution of temperature is insolation.
(iii) Insolation is the incoming solar energy intercepted by the earth.
(iv) The amount of insolation decreases from the equator towards the poles.
(v) Temperature is measured in Celsius and Fahrenheit.
Air Pressure
(i) Air pressure is defined as the pressure exerted by the weight of air on the earth’s surface.
(ii) Horizontally the distribution of air pressure is influenced by the temperature of the air at a given place.
(iii) In areas having a lower temperature, the air is cold.
(iv) The air always moves from high-pressure areas to low-pressure areas.
Wind
(i) The movement of air from high-pressure areas to the low-pressure area is called Wind.
(ii) Winds can be broadly divided into three types: permanent winds, seasonal winds and local winds.
(iii) On 25 October 1999, cyclonic winds originated as depression and affected Odisha killing thousands of people.
Moisture
(i) When water evaporates from land and other water bodies, it becomes water vapour.
(ii) Moisture in the air at any time is known as humidity.
(iii) When the water vapour rises, it starts cooling. The water vapour condenses causing the formation of droplets of water.
(iv) When these droplets of water become too heavy to float in the air, they come down as precipitation.
(v) Precipitation is the falling of moisture in the form of rainfall, snow, fog, sleet and hailstones.
(vi) On the basis of mechanism, there are three types of rainfall: the convectional rainfall, the orographic rainfall and the cyclonic rainfall.
(vii) Rainfall is very important for the survival of plants and animals.
The atmosphere is a thin blanket of air that surrounds the earth. It protects us from the harmful rays of the sun. It consists of the main nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%). Carbon dioxide, helium, ozone, argon and hydrogen are found in lesser quantities.
Nitrogen is very important for plants. Their survival depends on this gas.
Oxygen is essential for humans and animals. They breathe in oxygen, produced by green plants during photosynthesis.
Green plants take in carbon dioxide which is released by humans and animals. Thus, there is a mutual relation between the plants and the humans or animals. Hence, we should protect plants and trees for our own benefit.
The atmosphere is divided into five layers starting from the earth’s surface. These layers are—Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere, Thermosphere and Exosphere.
The troposphere is the layer in which the air we breathe exists. Almost all weather phenomena occur here.
The stratosphere contains a layer of ozone gas.
The mesosphere extends up to the height of 80 km. Meteorites burn up in this layer on entering from the space.
Thermosphere helps in radio transmission.
Exosphere is the uppermost layer, where the air is very thin.
Weather is hour-to-hour, day-to-day condition of the atmosphere.
Climate is the average weather condition of a place for a longer period of time.
The temperature of the atmosphere remains changing. The degree of hotness and coldness of the air is known as temperature.
Insolation is an important factor that influences the distribution of temperature. The amount of insolation decreases from the equator towards the poles. Therefore, the temperature decreases in the same way.
Air above us presses us from all directions with a great force on our body and our body exerts a counter pressure.
Air pressure is the pressure exerted by the weight of air on the earth’s surface. As we go up the layers of the atmosphere, the pressure falls rapidly.
Low pressure is associated with cloudy skies and wet weather. High pressure is associated with clear and sunny skies. The air always moves from high-pressure areas to a low-pressure area.
Wind is the movement of air from the high-pressure area to low pressure areas. Wind may be gentle. At times it may be strong and devastating.
Winds are of three types—Permanent winds, Seasonal winds and Local winds.
Moisture means humidity. A humid day is one when the air is the fall of water vapour. On a humid day, clothes take longer to dry and sweat from our body does not evaporate easily.
Clouds are masses of water droplets. When these droplets of water become very heavy they come down as precipitation. Precipitation that comes down to the earth in liquid form is called rain.
There are three types of rain on the basis of mechanism—the conventional rainfall, the orographic rainfall and the cyclonic rainfall.
Constituents of air
Atmosphere: Atmosphere is a thin blanket of air that surrounds the earth.
Global warming: When the temperature of the earth’s atmosphere increases due to the increases in carbon dioxide, it is known as global warming.
Weather: The hour-to-hour, day-to-day condition of the atmosphere is known as weather.
Climate: The average weather condition of a place for a longer period of time is known as the climate of a place.
Temperature: The degree of hotness and coldness of the air is known as temperature.
Isolation: Isolation is the incoming solar energy intercepted by the earth.
Air pressure: The pressure exerted by the weight of air on the earth’s surface is known as air pressure.
Wind: Wind is the movement of air from the high-pressure area to low pressure areas.
Moisture: Water vapour present in the atmosphere is known as moisture.
Humidity: Moisture in the air is known as humidity.
Cloud: It is a mass of water droplets.
Precipitation: Falling of water on the earth in the form of rainfall is known as precipitation.
Thermometer: It is an instrument that measures temperature.
Barometer: It measures atmospheric pressure.
Rain gauge: It measures the amount of rainfall.
Wind vane: It shows the direction of the wind.

Evidyarthi is best