Notes For All Chapters Geography Class 7
Human beings are dependent on the environment.
To grow food, build homes and develop better means of transport and communication, human beings have modified the environment.
Settlements
(i) Settlements are places where people build their homes.
(ii) The settlements earlier grew near the river valleys as the water was easily available and the land was fertile.
(iii) Settlements can be permanent or temporary.
(iv) Settlements which are occupied for a short time are called temporary settlements.
(v) In permanent settlements, people build homes to live in.
(vi) Settlements can be rural or urban. Rural settlements can be compact or scattered.
(vii) People in rural areas practice agriculture. In the urban area, people are mostly engaged in services.
Transport
(i) Transport is the means by which people and goods move.
(ii) With the invention of the wheel, transport became easier.
(iii) Earlier donkeys, mules, bullocks and camels were used for transportation.
(iv) Earlier traders took the land route or sea route for transportation. Now it takes only 6-8 hours to travel from India to Europe.
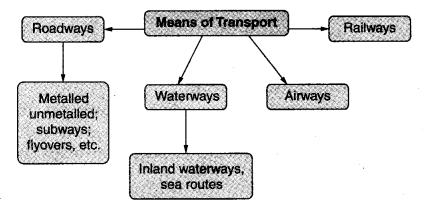
(v) The four major means of transport are roadways, railways, waterways and airways.
Roadways
(i) The most commonly used means of transport, especially for short distances, are roads. They can be metalled or unmetalled.
Railways
(i) Railways are the fastest means of land transport and can carry bulky materials over a long distance.
(ii) The railways carry people over long distances quickly and economically.
(iii) The invention of the steam engine and the industrial revolution helped in the speedy development of rail transport.
(iv) Diesel and electric engine have largely replaced the steam engines.
(v) Now superfast trains have been introduced to make travelling faster.
(vi) Indian Railways network is the largest in Asia.
Waterways
(i) Waterways are the cheapest means of transportation for carrying heavy and bulky goods over long distances.
(ii) There are mainly two types of routes, inland waterways and sea routes.
(iii) Navigable rivers and lakes are used as inland waterways.
(iv) Sea routes are connected through ports.
Airways
(i) Airways are the fastest and most expensive mode of transport.
(ii) It is the only mode of transport to reach the most remote and distant areas especially where there are no roads and railways.
(iii) Some major airports in the world are Delhi, Mumbai, New York, London, Paris, Frankfurt and Cairo etc.
Communication
(i) Process of conveying the message to others is known as communication.
(ii) Different modes of communication are used to provide information, to educate as well as to entertain.
(iii) Communication is of two types namely, personal and mass communication.
(iv) Through newspaper, radio and television, we can communicate with a large number of people. They are, therefore, called mass media.
(v) Satellites, Internet, Wireless telephone are the main modes of communication.
Places, where people build their homes, are called settlements. Early settlements grew near the river valleys because of the easy availability of water and fertile land there.
By and by human settlements became larger with the development of trade, commerce and manufacturing.
Settlements are of two types—permanent and temporary.
People make their temporary settlements in deep forests, hot and cold deserts and mountains and practise hunting, gathering, shifting cultivation, etc. Under permanent settlements, people build homes to live in.
Human settlements may be rural and urban. The villages are rural settlement where people do farming, fishing, forestry, etc.
Rural settlements can be compact or scattered. In a compact settlement, houses are built closely to each other. In a scattered settlement house are spaced over an extensive area.
Houses under rural settlements are built of mud, clay, stones, straw, etc.
Urban settlements are found in towns and cities. People here are engaged in manufacturing, trading and services.
Transport is essential to go from one place to another. In the early days, people travelled long distances on foot. They used animals to carry their goods. Gradually, several means of transport developed, although animals like donkeys, mules, bullocks and camels continued to be used even today.
An aeroplane is the fastest mode of transport. It saves our precious time and energy.
The four means of transport are—roadways, railways, waterways and airways.
Roads can be metalled and unmetalled.
Manali-Leh highway in the Himalayan Mountain is one of the highest roadways in the world.
Roads built underground are called subways/under paths. Flyovers are built over raised structures.
The railways carry people and heavy goods over long distances. The railway network is well developed over the plain areas.
The Indian railway network is well developed and is the largest in Asia.
Waterways are the cheapest means of transport. They are used for carrying heavy and bulky goods over long distances. There are two types of waterways inland waterways and sea routes.
Navigable rivers and lakes are used as inland waterways.
Sea routes and oceanic routes are mostly used for transporting merchandise and goods from one country to another. These routes are connected with the ports.
Some important ports of the world are—Singapore and Mumbai in Asia, New York, Los Angeles in North America, Rio de Janeiro in South America, Durban and Cape Town in Africa, Sydney in Australia, London and Rotterdam in Europe.
Airways are the fastest means of transport. It is the only mode of transport to reach the most remote and distant areas especially where there are no roads and railways.
Helicopters are useful in most inaccessible areas and in the time of calamities for rescuing people and other associated works.
Some important airports are Delhi, Mumbai, New York, London, Paris, Frankfurt and Cairo.
The process by which we convey messages to others is known as communication.
Newspapers, radio and television are important means of communication. They are called mass media because we can communicate with a large number of people at the same time.
The satellites have made communication even faster.
Wireless telephonic communications through cellular phones have become very popular today.
The Internet provides us with worldwide information and interaction.
Settlement: It refers to a place where people build their homes. ,
Site: It refers to a place where a building or a settlement develops.
Transhumance: It is a seasonal movement of people.
Compact settlement: It is a closely built area of dwellings.
Scattered settlement: When dwellings are spaced over an extensive area.
Transport: It is the means by which people and goods move from one place to another.
Metalled roads: These are pucca roads and are used in all the weather.
Unmetalled roads: These are Kutcha roads. They are out of work during the rainy season.
Subways: Underground roads are called subways.
Flyovers: These are built over raised structures.
Communication: The process through which we convey messages to others.
Mass Media: Newspapers, radio and television are called mass media because they communicate with a large number of people at the same time.

Leave a Reply