Solutions For All Chapters Maths Class 7
Ex 4.1 Class 7 Maths Question 1.
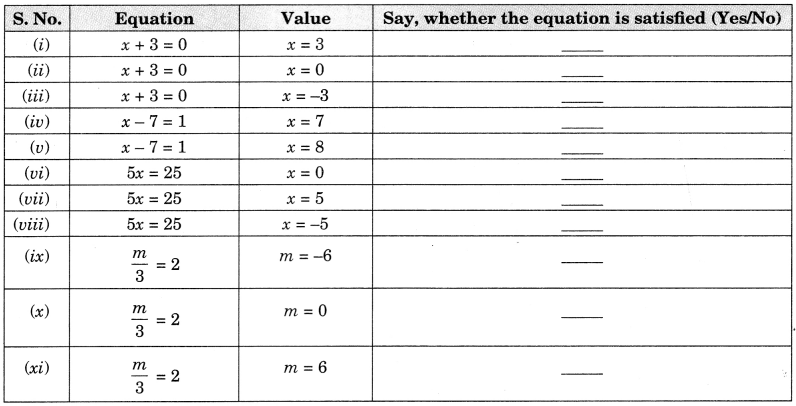
Complete the given column of the table:
Solution:
Ex 4.1 Class 7 Maths Question 2.
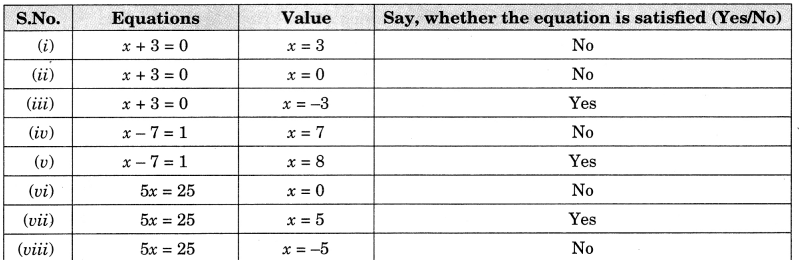
Check whether the value given in the brackets is a solution to the given equation or not:
(a) n + 5 = 19; (n = 1)
(b) 7n + 5 = 19; in – -2)
(c) 7n + 5 = 19; (n = 2)
(d) 4p – 3 = 13; (p = 1)
(e) 4p – 3 = 13; (p = -4)
(f) 4p-3 = 13; (p = 0)
Solution:
(a) n + 5 = 19 (n = 1)
Put n = 1 in LHS
1 + 5 = 6 ≠ 19 (RHS)
Since LHS ≠ RHS
Thus n = 1 is not the solution of the given equation.
(b) 7n + 5 = 19; (n = -2)
Put n = – 2 in LHS
7 × (-2) + 5 = -14 + 5 = -9 ≠ 19 (RHS)
Since LHS ≠ RHS
Thus, n = -2 is not the solution of the given equation.
(c) 7n+ 5 = 19; (n = 2)
Put n = 2 in LHS
7 × 2 + 5 = 14 + 5 = 19 = 19 (RHS)
Since LHS = RHS
Thus, n – 2 is the solution of the given equation.
(d) 4p – 3 = 13; (p = 1)
Put p = 1 in LHS
4 × 1 – 3 = 4 – 3 = 1 ≠ 13 (RHS)
Since LHS ≠ RHS
Thus, p = 1 is not the solution of the given equation.
(e) 4p – 3 = 13; (p = -A)
Put p = -4 in LHS
4 × (-4) – 3 = -16 – 3 = -19 ≠ 13 (RHS)
Since LHS ≠ RHS
Thus p = -4 is not the solution of the given equation.
(f) 4p – 3 = 13; (p = 0)
Put p = 0 in LHS
4 × (0) – 3 = 0 – 3 = -3 ≠ 13 (RHS)
Since LHS ≠ RHS
Thus p – 0 is not the solution of the given equation.
Ex 4.1 Class 7 Maths Question 3.
Solve the following equations by trial and error method:
(i) 5p + 2 = 17
(ii) 3m – 14 = 4
Solution:
(i) 5p + 2 = 17
For p = 1, LHS
= 5 × 1 + 2 = 5 + 2 = 7 ≠ 17 (RHS)
For p = 2, LHS = 5 × 2 + 2
= 10 + 2 = 12 ≠ 17 (RHS)
For p = 3, LHS = 5 × 3 + 2
= 15 + 2 = 17 = 17 (RHS)
Since the given equation is satisfied for p = 3 Thus, p = 3 is the required solution.
(ii) 3m – 14 = 4
For m = 1, LHS = 3 × 1 – 14
= 3 – 14 = -11 ≠ 4 (RHS)
For m = 2, LHS = 3 × 2 – 14 = 6 – 14
= -8 ≠ 4 (RHS)
For m = 3, LHS = 3 × 3 – 14 = 9 – 14
= -5 ≠ 4 (RHS)
Form m = 4, LHS = 3 × 4 – 14
= 12 – 14 = -2 ≠ 4 (RHS)
For m = 5, LHS = 3 × 5 – 14
= 15 – 14 = -1 ≠ 4 (RHS)
For m = 6, LHS = 3 × 6 – 14
= 18 – 14 = 4 (=) 4 (RHS) .
Since, the given equation is satisfied for m = 6.
Thus, m = 6 is the required solution.
Ex 4.1 Class 7 Maths Question 4.
Write equations for the following statements:
(i) The sum of numbers x and 4 is 9.
(ii) 2 subtracted from y is 8.
(iii) Ten times a is 70.
(iv) The number b divided by 5 gives 6.
(v) Three-fourth of t is 15.
(vi) Seven times m plus 7 gets you 77.
(vii) One-fourth of a number x minus 4 gives 4.
(viii) If you take away 6 from 6 times y, you get 60.
(ix) If you add 3 to one-third of z, you get 30.
Solution:
Ex 4.1 Class 7 Maths Question 5.
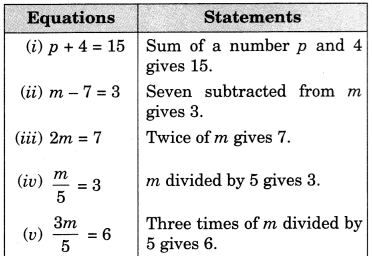
Write the following equations in statement forms.
Solution:
Ex 4.1 Class 7 Maths Question 6.
Set up an equation in the following cases:
(i) Irfan says that he has 7 marbles more than five times the marbles Parmit has. Irfan has 37 marbles. (Take m to be the number of Parmit’s marbles)
(ii) Laxmi’s father is 49 years old. He is 4 years older than three times Laxmi’s age. (Take Laxmi’s age to be y years)
(iii) The teacher tells the class that the highest marks obtained by a student in her class is twice the lowest marks plus 7. The highest score is 87. (Take the lowest score to be 1)
(iv) In an isosceles triangle, the vertex angle is twice either base angle. (Let the base angle be b in degrees. Remember that the sum of angles of a triangle is 180 degrees).
Solution:
(i) Let m be the Parmit’s marbles.
∴ Irfan’s marble = 5m + 7
Total number of Irfan’s marble is given by 37.
Thus, the required equation is 5m + 7 = 37
(ii) Let Laxmi’s age bey years.
∴ Laxmi’s father’s age = 3y + 4
But the Laxmi’s father age is given by 49
Thus the required equation is 3y + 4 = 49
(iii) Let the lowest score be l.
∴ The highest score = 2l + 1
But the highest score is given by 87.
Thus, the required equation is 2l + 1 = 87
(iv) Let each base angle be ‘b’ degrees.
∴ Vertex angle of the triangle = 2b
Sum of the angles of a triangle = 180°
∴ Required equation is b + b + 2b = 180° or 4b = 180°


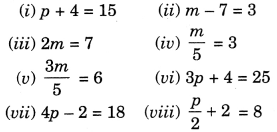


Leave a Reply