Solutions Chapter 3 How the State Government Works
1. Use the terms ‘constituency’ and ‘represent’ to explain who an MLA is and how is the person elected?
Answer: A state is divided into several constituencies on the basis of population. Every constituency elects one representative for the Legislative Assembly. The person elected as representative represents that particular constituency. He/She is called as a Member of Legislative Assembly Le. MLA. An MLA is elected through a general election. He/She may be a member of a recognised political party or independent. One who gets the maximum votes becomes the MLA of that constituency.
2. How did some MLAs become Ministers? Explain.
Answer: The party which is elected in majority for the Legislative Assembly forms the government. As per constitutional provisions the ruling party elects its leader who is called the Chief Minister as the head of the government. The Chief Minister, in consultation with the Governor, constitutes a cabinet which includes members of his/her party as ministers. The MLAs who become ministers are allotted with a portfolio. Here the MLAs turned ministers become accountable for the entire state for that particular portfolio.
3. Why should decisions taken by the Chief Minister and other ministers be debated in the Legislative Assembly?
Answer: The decisions taken by the Chief Minister and other ministers must be debated in the Legislative Assembly. It is because during debate it is discussed whether a particular decision is in interest of the people at large or net. It is also discussed whether it is urgent or not, how much would it cost the government, is there anything objectionable for any particular community, etc.
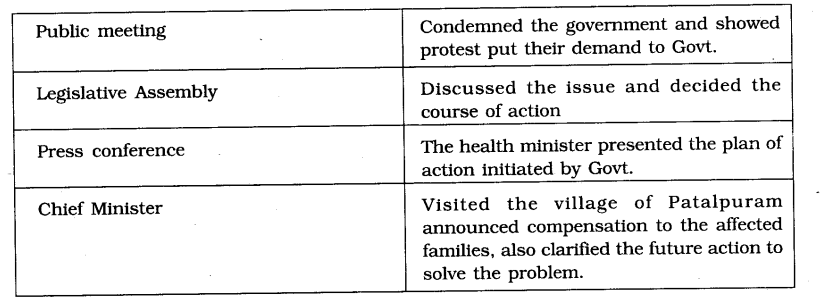
4. What was the problem in Patalpuram? What discussion/actions was taken by the following? Fill in the table.
Answer: Patalpuram was facing acute crisis of water
5. What is the difference between the work that MLAs do in the Assembly and the work done by government departments?
Answer: The difference between the work that MLAs do in the Assembly and the work done by government departments is that every department is headed by a minister who is also an MIA. The minister approves any work done or proposed by the department. The department is responsible for the projections and complition of the work where as MLAs or ministers coordinate between the Assembly and the departments.
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. How is the Governor of a state appointed? [V. Imp.]
Answer: The Governor of a state is appointed by the Central Government.
2. Whose responsibility is it to nm various government departments or ministers?
Answer: It is the responsibility of the Chief Minister and other ministers to run various government departments or ministers.
3. How will you define a Legislative Assembly?
Answer: A Legislative Assembly is a place where all the MLAs, from the ruling party as well as the opposition, meet to discuss various things.
4. Define the term ‘government’. [Imp.]
Answer: The term ‘government’ refers to the government departments and various ministers who head them.
5. Who is the head of the executive?
Answer: The Chief Minister is the head of the executive.
6. Why did the Chief Minister and the minister for health visit Patalpwam district?
Answer: They went to visit the families who had lost their relatives due to the spread of diarrhea. They also visited people in the hospitals.
7. Why are press conferences organised?
Answer: Press conferences are oragnised to discuss various current issues.
8. What do you know about a wallpaper?
Answer: A wallpaper is an interesting activity through which research can be done on particular topics of interest.
9. Why do people in a democratic set up organise meetings? [V. Imp.]
Answer: They do so to voice their opinions and protest against the government if any of its actions is not in their favour.
10. The government works at three levels. Name them.
Answer: The government works at three levels namely
1. Local
2. State
3. Natural
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. What do you mean by an MLA? Is it necessary to become a member of any political party to become a MLA? [V. Imp.]
Answer: The term MLA stands for a Member of Legislative Assembly. He/She is elected through a general election and represents a particular constituency. It is not necessary for one to be a member of a political party to become a MLA. He/she can contest the election as an independent candidate also. In some cases, he/ she is sponsored by a political party. But one thing is necessary that he/she must be a citizen of India and fulfil the requisite qualifications for the post.
2. What is the process of formation of government in a state? [Imp.]
Answer: A general election is conducted to elect representatives from various constituencies. The party which earns more than half of the total seats is said to be in a majority. That party is usually called for forming the government.
Sometimes, no party gains clear majority. In that case the party with maximum elected members tries to get support from the like-minded parties or independent candidates. The party that proves to have maximum supporters in that way is allowed to form government. Otherwise there would be re-election,
3. What is role of the party that does not form government? [V. Imp.]
Answer: As per the Constitution all the parties which do not take part in the formation of government are called opposition parties. In our democratic set up the role of the opposition parties is in no way less important than the ruling party. The opposition parties keep a watch over the functioning of the ruling party. They take part in every discussion and debate held in the Assembly. They can check and protest any wrong action of the government.
4. Who becomes a Chief Minister? What is his/her role in a state? [Imp.]
Answer: Chief Minister is the leader of the ruling party. He/She is elected out of the total members of the party gaining majority in the general election. He/she is the executive head of the government. He/She is responsible for every action of the government. He/she also coordinates between the government at the centre and the state.
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. How does a government function in a state? [V. Imp.]
Answer: A government is headed by the Chief Minister. The Chief Minister, in order to manage the functioning of the government, appoints ministers at various levels like cabinet ministers, state ministers and deputy ministers. Every government departments is headed by a cabinet minister who is directly accountable for the functioning of the particular department. The heads of the government departments who are bureaurates, are responsible for the handling of the government decisions. The bureaurates project and get the works completed. The ministers give approval to the works.

Leave a Reply