Page 16.5 Ex. 16.1
Q1.
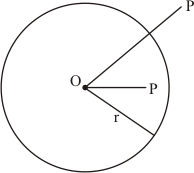
(i) All points lying inside or outside a circle are called interior points or exterior points.
Let the point P, Q and R are lie inside, outside or on the circle C(O, r) in such a way as given in the figure
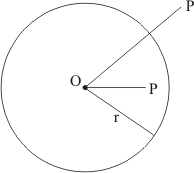
Thus the answer is
(ii) Given that the circles having the same centre and different radii are called
As we know that the circles having the same centre and different radii are called concentric circle.
Thus the answer is
(iii) As we know that appoint whose distance from the centre of a circle is greater than its radius lies in the exterior of the circle as shown in the figure
Thus the answer is
(iv) As we know that a continuous piece of a circle is an arc of the circle.
Let P and Q be points on the circle C (O, r) then the piece are arcs of the circle C (O, r)
Thus the answer is arc.
(v) Given that the largest chord of the circle is a diameter of the circle.
As we know that a circle having so many diameters and a diameter of a given circle is one of the largest chords of the circle.
Thus the answer is diameter.
(vi) Given that an arc a semicircle when its ends are the ends of the diameter.
As we know that a diameter of a circle divides it into two equal parts which are arcs and each of two arcs is called a semicircle.
Thus the answer is semicircle.
(vii) As we know that segment of a circle is the region between arc and chord of the circle.
Let PQ be a chord of the circle C (O, r), then PQ divides the region enclosed by the circle into two parts. Each of the part is called segment of the circle.
Thus the answer is chord.
(viii) As we know that a circle divides the plane on which it lies in three parts as shown in the figure.
Thus the answer is three.
Q2.
(i) Given that a circle is a plane figure.
As we know that a circle is a collection of those points in a plane that are at a given constant distance from affixed point in the plane.
Thus the given statement is
(ii) Given that line segment joining the centre to any point on the circle is a radius of the circle.
As we know that line segment joining the centre to any point on the circle is a radius of the circle.
Thus the given statement is
(iii) Given that if a circle is divided into three equal arcs each is a major arc.
As we know that if points P, Q and R lies on the given circle C(O, r)in such a way that
Then each arc is called major arc.
Thus the given statement is
(iv) It is given that a circle has only finite number of equal chords.
As we know that a circle having infinite number of unequal chords.
Thus the given statement is.
(v) Given that a chord of the circle, which is twice as long as its radius is diameter of the circle.
As we know that a chord of a circle which is largest to others and passing through the centre of the circle and twice as long as its radius is called diameter of the circle.
Thus the given statement is .
(vi) It is given that sector is the region between the chord and its corresponding arc.
As we know that the region between the chord and its corresponding arc is called sector.
Thus the given statement is.
(vii) Given that the degree measure of an arc is the complement of the central angle containing the arc.
As we know that the degree measure of a minor arc is the measure of the central angle containing the arc and that of a major arc is 360° minus the degree measure of the corresponding minor arc.
Let degree measure of an arc is ? of a given circle
is denoted by
Thus the given statement is.
(viii) Given that the degree measure of a semi-circle is 180°.
As we know that the diameter of a circle divides into two equal parts and each of these two arcs are known as semi-circle.
and
are semi circle
Hence,
Thus the given statement is.
Page 16.24 Ex. 16.2
Q1.
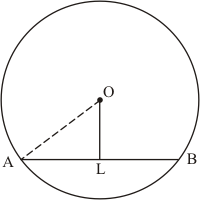
Let AB be a chord of a circle with centre O and radius 8 cm such that
AB = 12 cm
We draw and join OA.
Since, the perpendicular from the centre of a circle to a chord bisects the chord.
Now in we have
Hence the distance of chord from the centre
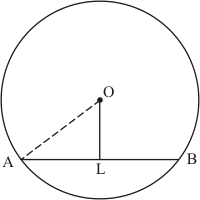
Q2.
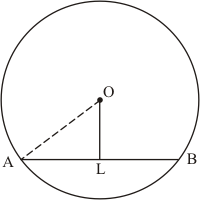
Given that OA = 10 cm and OL = 5 cm, find the length of chord AB.
Let AB be a chord of a circle with centre O and radius 10 cm such that AO = 10 cm
We draw and join OA.
Since, the perpendiculars from the centre of a circle to a chord bisect the chord.
Now in we have
Hence the length of chord
Q3.
Given that and
, find the length of chord AB.
Let AB be a chord of a circle with centre O and radius 6 cm such that
We draw and join OA.
Since, the perpendicular from the centre of a circle to a chord bisects the chord.
Now in we have
Hence the length of chord
Q4.
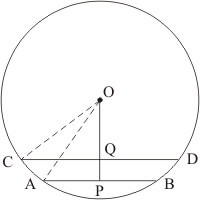
Let AB and CD be two parallel chord of the circle with centre O such that AB = 5cm and CD = 11cm. let the radius of the circle be cm.
Draw and
as well as point O, Q, and P are collinear.
Clearly,
Let then
In we have
…… (1)
And
…… (2)
From equation (1) and (2) we get
Putting the value of x in equation (2) we get,
Q5.
Let A, B and C are three distinct points on a circle whose radius is
Now join AB and BC and draw their perpendicular bisectors.
The point of intersection of the perpendicular bisectors is the centre of given circle.
Hence O is the centre of circle.
Q6.
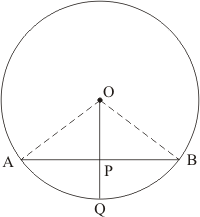
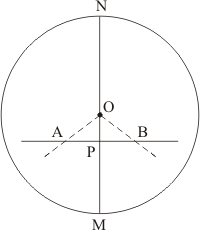
Let P is the mint of chord AB of circle C(O, r) then according to question, line OQ passes through the point P.
Then prove that OQ bisect the arc AB.
Join OA and OB.
In
(Both are equal to radius).
(Mid point of chord AB)
(Common side)
Therefore,
Thus
Arc AQ = arc BQ
Hence Proved.
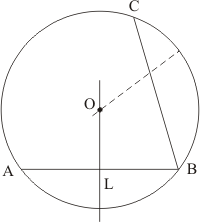
Q7.
Let MN is the diameter and chord AB of circle C(O, r) then according to question
AP = BP.
Then prove that .
Join OA and OB.
In ?AOP and ?BOP
(Each equal to radius).
AP = BP
(Mid point of chord AB)
OP = OP
(Common side)
Therefore,
Hence, proved.
Page 16.25 Ex. 16.2
Q8.
Prove that two different circles cannot intersect each other at more than two points.
Let the two circles intersect in three points A, B and C.
Then as we know that these three points A, B and C are non-collinear. So, a unique circle passes through these three points.
This is a contradiction to the fact that two given circles are passing through A, B, C.
Hence, two circles cannot intersect each other at more than two points.
Hence, proved.
Q9.
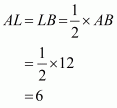
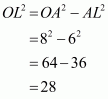
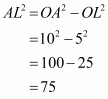
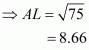
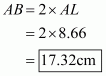
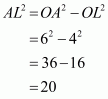
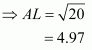
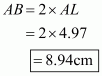
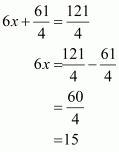
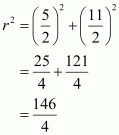
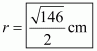

Leave a Reply