Page 11.6 Ex. 11.1
Q1.
Answer :
The following points are given below.
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
(v)
(vi)
(vii)
(viii)
(ix)
(x)
Letand
be the coordinate axes.
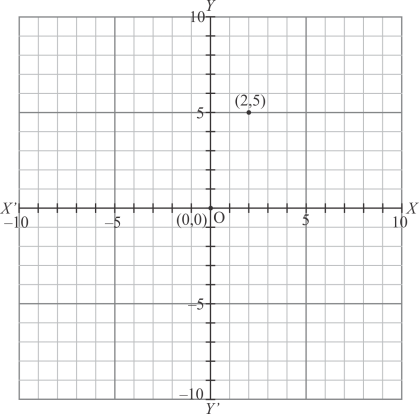
(i) Here for the given point the abscissa is 2 units and ordinate is 5 units.
The point is in the first quadrant. So it will look like as shown in the following figure.
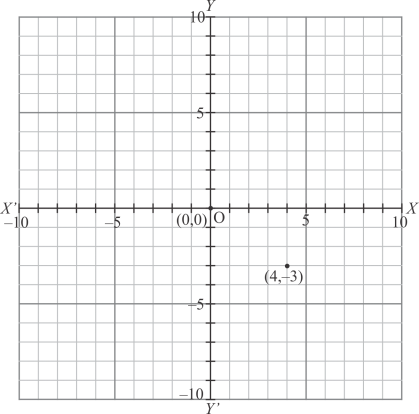
(ii) Here for the given point the abscissa is 4 units and ordinate is -3 units.
The point is in the fourth quadrant. So it will look like as shown in the following figure.
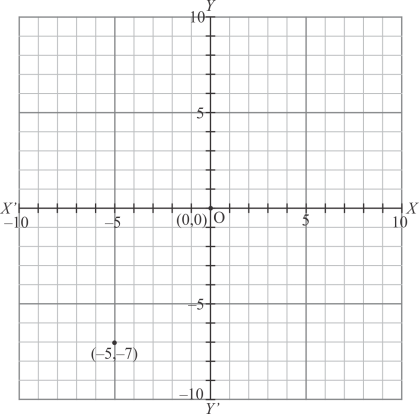
(iii) Here for the given point the abscissa is -5 units and ordinate is -7 units.
The point is in the third quadrant. So it will look like as shown in the following figure.
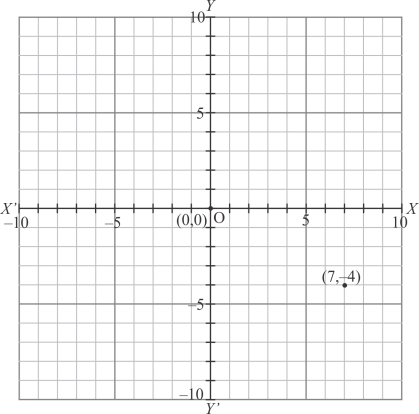
(iv) Here for the given point the abscissa is 7 units and ordinate is -4 units.
The point is in the fourth quadrant. So it will look like as shown in the following figure.
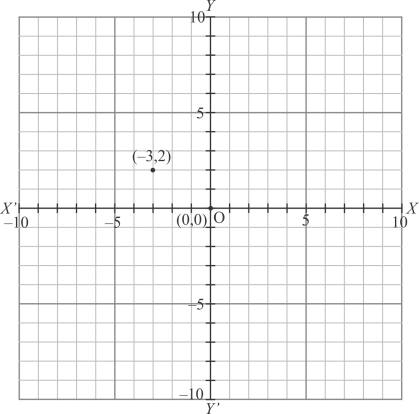
(v) Here for the given point the abscissa is -3 units and ordinate is 2 units.
The point is in the second quadrant. So it will look like as shown in the following figure.
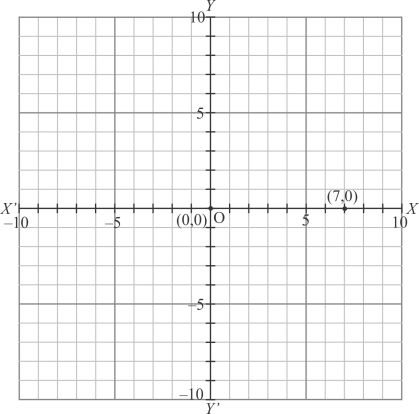
(vi) Here for the given point the abscissa is 7 units and ordinate is 0 units.
The point is on the x-axis. So it will look like as shown in the following figure.
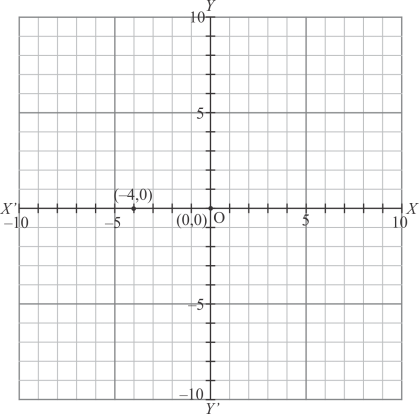
(vii) Here for the given point the abscissa is -4 units and ordinate is 0 units.
The point is on the x-axis. So it will look like as shown in the following figure.
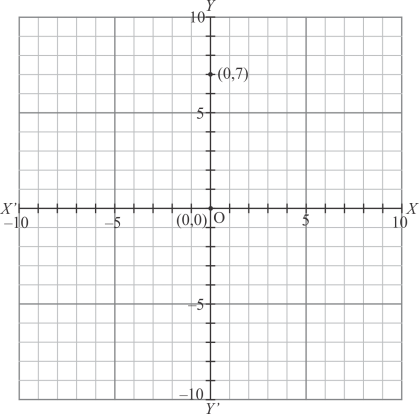
(viii) Here for the given point the abscissa is 0 units and ordinate is 7 units.
The point is on the y-axis. So it will look like as shown in the following figure.
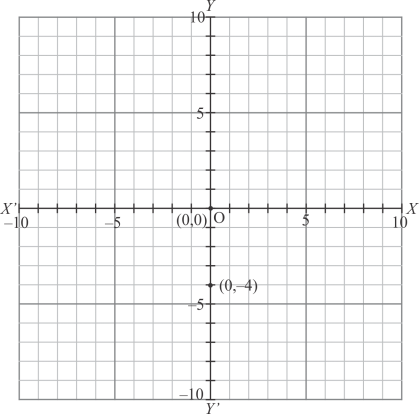
(ix) Here for the given point the abscissa is 0 units and ordinate is -4 units.
The point is on the y-axis. So it will look like as shown in the following figure.
(x) Here for the given point the abscissa is 0 units and ordinate is 0 units.
The point is basically intersection of the coordinate axes. So it will look like as shown in the following figure.
Q2.
Answer :
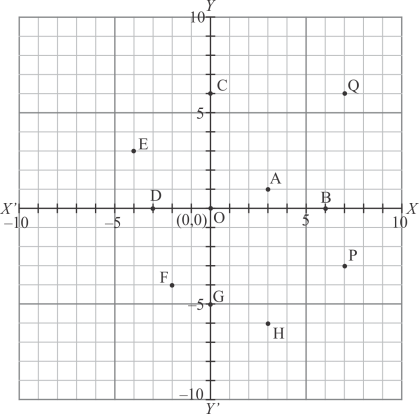
The following graph is given in the question with the marked points and we are asked to write down their coordinates.
The distance of point A from y-axis is 3 units and that of from x-axis is 1 units. Since A lies in the first quadrant, so its coordinates are.
The distance of point B from y-axis is 6 units and that of from x-axis is 0 units. Since B lies on x-axis, so its coordinates are.
The distance of point C from y-axis is 0 units and that of from x-axis is 6 units. Since C lies on y-axis, so its coordinates are.
The distance of point D from y-axis is -3 units and that of from x-axis is 0 units. Since D lies on x-axis, so its coordinates are.
The distance of point E from y-axis is -4 units and that of from x-axis is 3 units. Since E lies in the second quadrant, so its coordinates are.
The distance of point F from y-axis is -2 units and that of from x-axis is -4 units. Since F lies in the third quadrant, so its coordinates are.
The distance of point G from y-axis is 0 units and that of from x-axis is -5 units. Since G lies on y-axis, so its coordinates are.
The distance of point H from y-axis is 3 units and that of from x-axis is -6 units. Since H lies in the fourth quadrant, so its coordinates are.
The distance of point P from y-axis is 7 units and that of from x-axis is -3 units. Since P lies in the fourth quadrant, so its coordinates are.
The distance of point Q from y-axis is 7 units and that of from x-axis is 6 units. Since Q lies in the first quadrant, so its coordinates are.
Page 11.7 Formative Assessment_MCQ
Q1.
Answer :
As we know that:
The distance of a point from y−axis is called its x−coordinate or abscissa.
The distance of a point from x−axis is called its y−coordinate or ordinate.
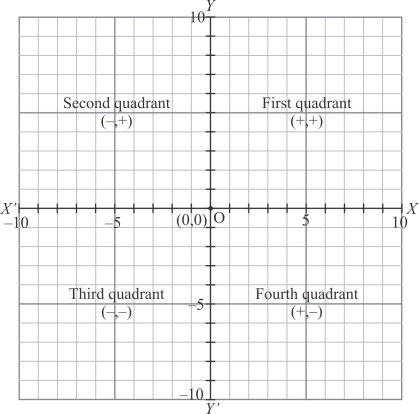
The coordinate axes divide the plane into four equal parts which are known as quadrants.
The point of intersection of the coordinate axes is called the origin and the coordinates of origin are.
Example is shown in the graph
Thus the correct answer is (d).
Q2.
Answer :
As we know that:
The distance of a point from y−axis is called its x−coordinate or abscissa.
The distance of a point from x−axis is called its y−coordinate or ordinate.
The coordinate axes divide the plane into four equal parts which are known as quadrants.
The point of intersection of the coordinate axes is called the origin and the coordinates of origin are.
The origin is shown in the graph
Thus the correct answer is (a).
Q3.
Answer :
As we know that x−axis and y−axis intersect to each other at point O and perpendicular to each other. So, the angle between the coordinate axes is.
Thus the correct answer is (b).
Q4.
Answer :
As shown in graph that a point whose abscissa and ordinate areand
respectively lies in the fourth quadrant.
Thus the correct answer is (d).
Q5.
Answer :
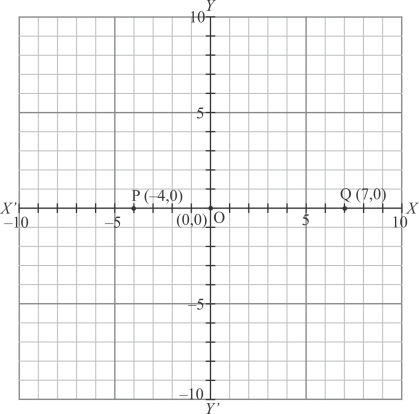
Let the points P and Q whose coordinates are and
respectively. Locate the points and you will see that they lie on x-axis.
Thus the correct answer is (a).
Q6.
Answer :
We know that the y−coordinates of every point on x−axis are zero. So, the coordinates of any point on the x−axis are of the form.
Thus the correct answer is (a).
Q7.
Answer :
We know that the x−coordinate of every point on y-axis is zero. So, the coordinates of any point on the x−axis are of the form.
Thus the correct answer is (a).
Q8.
Answer :
The signs of coordinates of a point in various quadrants are shown in the following graph:
Thus the correct answer is (d).
Q9.
Answer :
As we know that
In the first quadrant
In the second quadrant
In the third quadrant
In the fourth quadrant
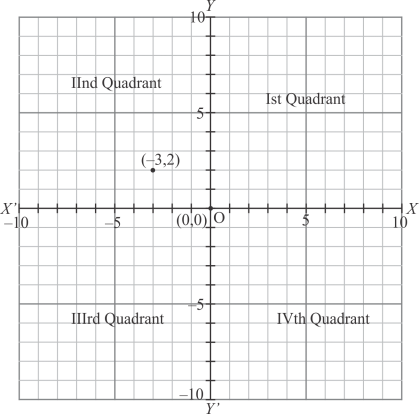
The point whose abscissa is −3 which is negative and ordinate 2 is positive, so this point lies in the second quadrant.
Thus the correct answer is (b).
Q10.
Answer :
Let the points and
having the same abscissa but different ordinates be shown in the graph given below:
Fig: (location of two considered points)
And these points lie on a line parallel to y−axis
Thus the correct answer is (c).
Q11.
Answer :
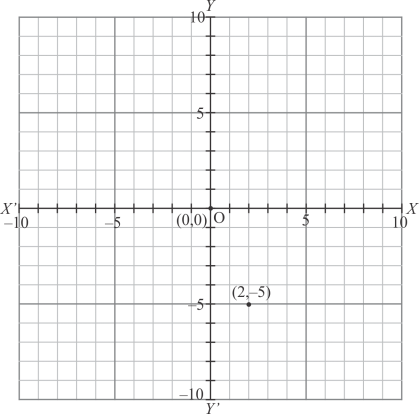
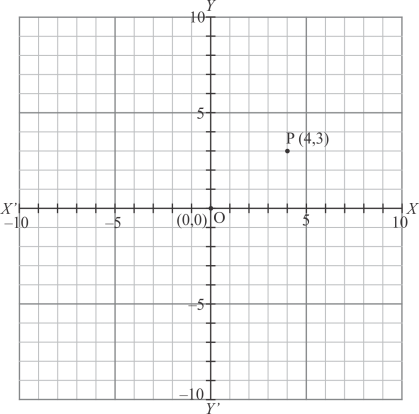
The point is shown in the graph given below:
Fig: Location of given point
Thus the perpendicular distance of the point from x−axis is 3 units.
Thus the correct answer is (b).
Q12.
Answer :
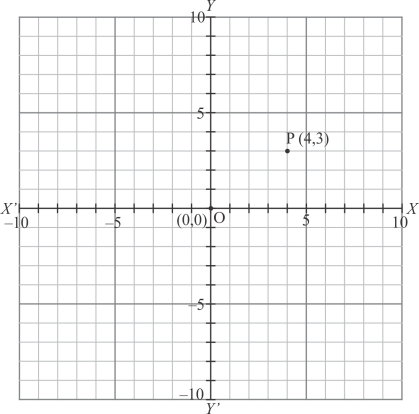
The point is shown in the graph given below:
Fig: Location of the given point
Thus the perpendicular distance of the point from y−axis is 4.
Thus the correct answer is (a).
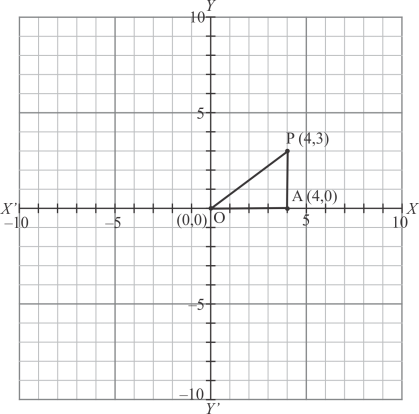
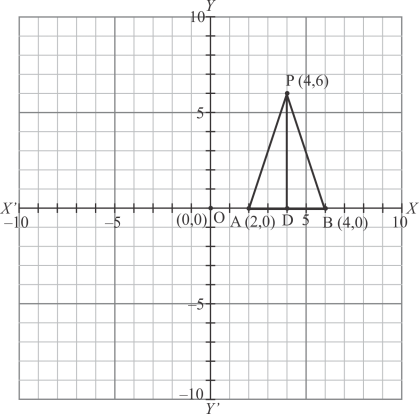
Q13.
Answer :
The point is shown in the graph given below:
Fig: Location of the given point
In is right angled triangle where
By using Pythagoras theorem:
Thus the distance of the pointfrom the origin is 5.
Thus the correct answer is (c)
Q14.
Answer :
Given that points A, B
and C
form a triangle which is shown in the figure. We are asked to find the area of the triangle ΔABC.
Given that
Hence:
By using formula,
Thus the correct answer is (b).
Q15.
Answer :
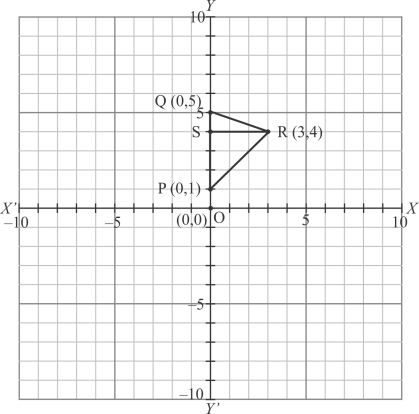
Given that the points,
and
form a triangle.
We are asked to find the area of the triangle ΔPQR which is shown in the figure.
Given that
Hence
By using formula,
Thus the correct answer is (d).
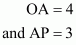
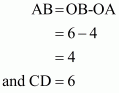
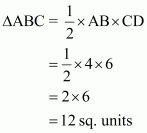
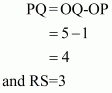
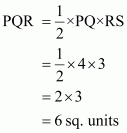

Leave a Reply