Solutions For All Chapters Science Class 9
Questions from NCERT Text Book
Question 1. Compare the properties of electrons, protons and neutrons.
Answer:
| Electrons | Protons | Neutrons |
|---|---|---|
| Negatively charged. | Positively charged | No charge |
| Mass is negligible (1/1800 times of protons). | Mass is 1 a.m.u. | Mass is 1 a.m.u. |
| Get attracted towards +ve charge. | Get attracted towards -ve charge. | Do not get attracted, as they are neutral. |
| Present outside the nucleus. | Present in the nucleus. | Present in the nucleus of an atom. |
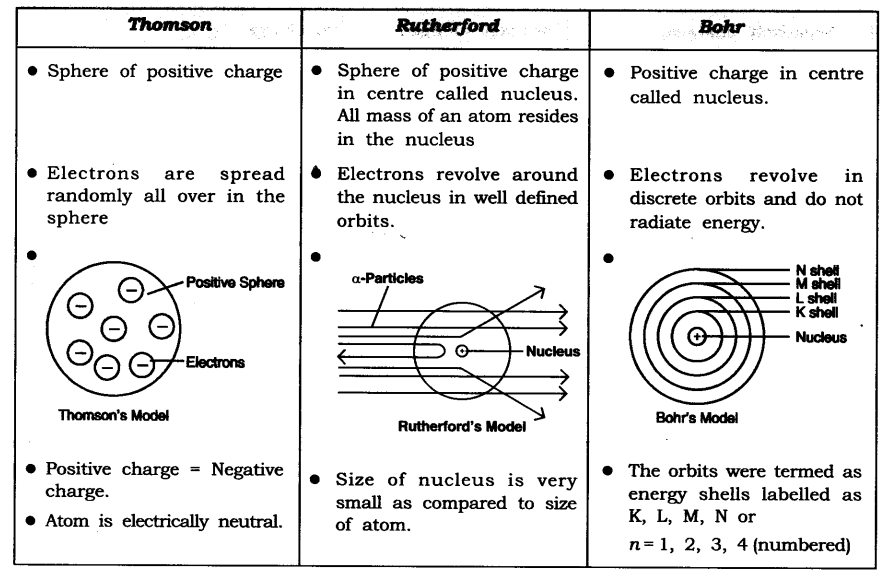
Question 2. What are the limitations of J.J. Thomson’s model of the atom?
Answer: According to J.J. Thomson’s model of an atom, the electrons are embedded all over in the positively charged spheres. But experiments done by other scientists showed that protons are present only in the centre of the atom and electrons are distributed around it.
Question 3. What are the limitations of Rutherford’s model of the atom?
Answer: According to Rutherford’s model of an atom the electrons are revolving in a circular orbit around the nucleus. Any such particle that revolves would undergo acceleration and radiate energy. The revolving electron would lose its energy and finally fall into the nucleus, the atom would be highly unstable. But we know that atoms are quite stable.
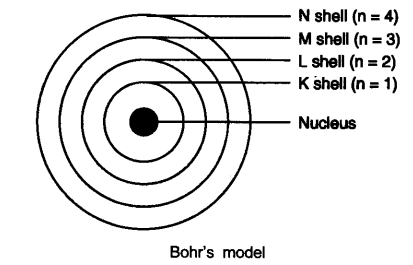
Question 4. Describe Bohr’s model of the atom.
Answer: Bohr’s model of the atom
(1) Atom has nucleus in the centre.
(2) Electrons revolve around the nucleus.
(3) Certain special orbits known as discrete orbits of electrons are allowed inside the atom.
(4) While revolving in discrete orbits the electrons do not radiate energy.
(5) These orbits or shells are called energy levels.
(6) These orbits or shells are represented by the letters K, L, M, N or the numbers n = 1, 2, 3, 4
Question 5. Compare all the proposed Bohr’s models of an atom given in this chapter.
Answer:
Question 6. Summarise the rules for writing of distribution of electrons in various shells for the first eighteen elements.
Answer: The rules for writing of distribution of electrons in various shells for the first eighteen elements are:
(i) The maximum number of electrons present in a shell is given by the formula-2 n2
∵ n = orbit number i.e., 1, 2, 3
∵ Maximum number of electrons in different shells are:
(ii) The maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated in the outermost orbit is 8.
(iii) Electrons are not accommodated in a given shell unless the inner shells are filled. (Shells are filled step-wise).
Question 7. Define valency by taking examples of silicon and oxygen.
Answer: Valency is the combining capacity of an atom.
Atomic number of oxygen = 8 Atomic number of silicon = 14 K L M
Electronic configuration of oxygen = 2 6 –
Electronic configuration of silicon =2 8 4
In the atoms of oxygen the valence electrons are 6 (i.e., electrons in the outermost shell). To fill the orbit, 2 electrons are required. In the atom of silicon, the valence electrons are 4. To fill this orbit 4 electrons are required.
Hence, the combining capacity of oxygen is 2 and of silicon is 4.
i.e., Valency of oxygen = 2
Valency of silicon = 4
Question 8. Explain with examples:
(i) Atomic number
(ii) Mass number,
(iii) Isotopes and
(iv) Isobars.
Give any two uses of isotopes.
Answer: (i) Atomic number: The atomic number of an element is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus of its atom. e.g., Oxygen has 6 protons hence atomic no. = 6.
(ii) Mass number: The mass number of an atom is equal to the number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus.
Nucleons = number of protons + number of neutrons Example: Protons + Neutrons = Nucleus = Mass number 6 + 6 = 12
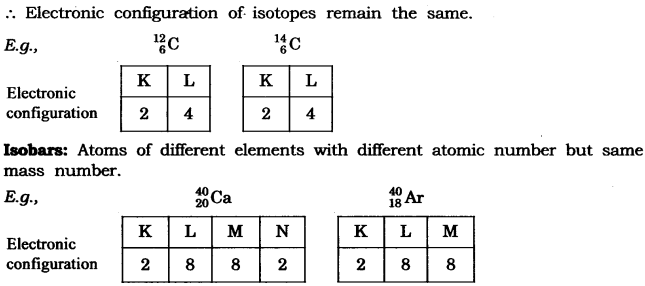
(iii) Isotopes: Isotopes are atoms of the same element which have different mass number but same atomic number.
(iv) Isobars: Isobars are atoms having the same mass number but different atomic numbers.
Both calcium and argon have same mass number but different atomic number.
Two uses of isotopes are:
(i) An isotope of iodine is used in the treatment of goitre.
(ii) An isotope of uranium is used as a fuel in nuclear reactors.
Question 9. Na+ has completely filled K and L shells. Explain.
Answer: Sodium atom (Na), has atomic number =11
Number of protons =11
Number of electrons = 11
Electronic configuration of Na = K L M – 2 8 1
Sodium atom (Na) looses 1 electron to become stable and form Na+ ion. Hence it has completely filled K and L shells.
Question 10. If bromine atom is available in the form of say, two isotopes and
, calculate the average atomic mass of bromine atom.
Answer:
Question 11. The average atomic mass of a sample of an element X is 16.2 u. What are the percentages of isotopes in the sample?
Answer: Let the percentage of 168X be x and the percentage of 168X be 100 – x.
Question 12. If Z = 3, what would be the valency of the element? Also, name the element.
Answer: Z = 3, (i.e, atomic number —> z)
∴ Electronic configuration = 2, 1
Valency = 1
Name of the element is lithium.
Question 13. Composition of the nuclei of two atomic species X and Y are given as under
X – Y
Protons =6 6
Neutrons = 6 8
Give the mass number of X and Y. What is the relation between the two species?
Answer: Mass number of X = Protons + Neutrons
= 6 + 6 = 12
Mass number of Y = Protons + Neutrons = 6 + 8 = 14
As the atomic number is same i.e., = 6.
[atomic number = number of protons].
Both X and Y are isotopes of same element.
Question 14. For the following statements, write T for True and F for False.
(a) J.J. Thomson proposed that the nucleus of an atom contains only nucleons.
(b) A neutron is formed by an electron and a proton combining together. Therefore,it is neutral.
(c) The mass of an electron is about 1/2000 times that of proton.
(d) An isotope of iodine is used for making tincture iodine, which is used as a medicine.
Answer: (a) False (b) False
(c) True (d) False
Put tick against correct choice and cross (x) against wrong choice in questions 15, 16 and 17.
Question 15. Rutherford’s alpha-particle scattering experiment was responsible for the discovery of
(a) Atomic nucleus (c) Proton
(b)Electron (d)neutron
Answer: (a) Atomic nucleus
Question 16.Isotopes of an element have
(a) the same physical properties (c) different number of neutrons
(b)different number of neutrons (d) different atomic numbers.
Answer: (c) different number of neutrons
Question 17. Number of valence electrons in Ct ion are :
(a) 16 (b) 8
(c) 17 (d) 18
Answer: (b) 8
Question 18. Which one of the following is a correct electronic configuration of sodium?
(a) 2, 8
(b) 8, 2, 1
(c) 2, 1, 8
(d) 2, 8, 1
Answer: (d) 2, 8, 1
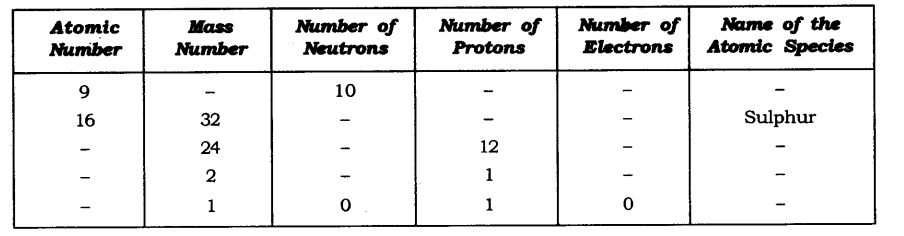
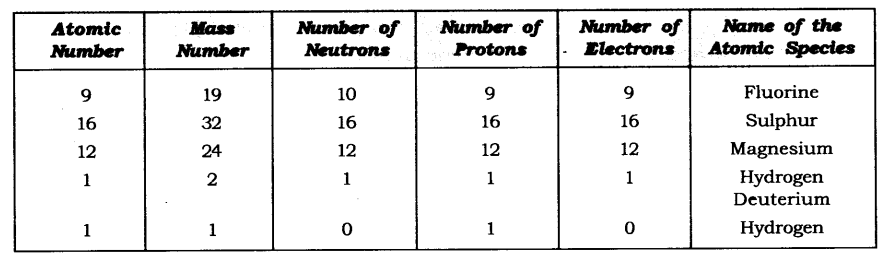
Question 19. Complete the following table.
Answer:
NCERT Textbook for Class 9 Science – Page 39
Question 1. What are canal rays?
Answer: Canal rays are positively charged radiations which led to the discovery of positively charged sub-atomic particle called proton.
Question 2. If an atom contains one electron and one proton, will it carry any charge or not?
Answer: The atom will be electrically neutral as one – ve charge balances one + ve charge.
Class 9 Science NCERT Textbook – Page 41
Question 1. On the basis of Thomson’s model of an atom, explain how the atom is neutral as a whole.
Answer: According to Thomson’s model of an atom
(i) An atom consists of a positively charged sphere and the electrons are embedded in it,
(ii) The negative and positive charges are equal in magnitude. So the atom is electrically neutral.
Question 2. On the basis of Rutherford’s model of an atom, which sub-atomic particle is present in the nucleus of an atom?
Answer: As per Rutherford’s model of an atom, the protons which are positively charged are present in the nucleus of an atom.
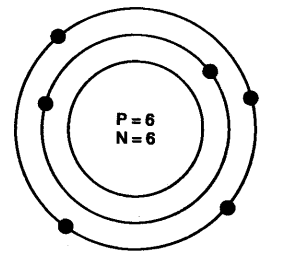
Question 3. Draw a sketch of Bohr’s model of an atom with three shells.
Answer:
Question 4. What do you think would be the observation if the a-particle scattering experiment is carried out using a foil of a metal other than gold?
Answer: On using any metal foil, the observations of the a-particle scattering experiment would remain the same as all atoms would have same structure.
Class 9 Science NCERT Textbook – Page 41
Question 1. Name the three sub-atomic particles of an atom.
Answer: The sub-atomic particles of an atom are
Question 2. Helium atom has an atomic mass of 4 u and two protons in its nucleus. How many neutrons does it have?
Answer:
NCERT Textbook for Class 9 Science – Page 42
Question 1. Write the distribution of electrons in carbon and sodium atoms.
Answer:
Question 2. If K and L shells of an atom are full, then what would be the total number of electrons in the atom?
Answer: K shell can hold 2 electrons and L shell can hold 8 electrons.When both the shells are full, there will be (8 + 2) 10 electrons in the atom.
Class 9 Science NCERT Textbook – Page 44
Question 1. How will you find the valency of chlorine, sulphur and magnesium?
Answer:
NCERT Textbook for Class 9 Science – Page 44
Question 1. If number of electrons in an atom is 8 and number of protons is also 8, then
(i) What is the atomic number of the atom? and
(ii) What is the charge on the atom?
Answer:
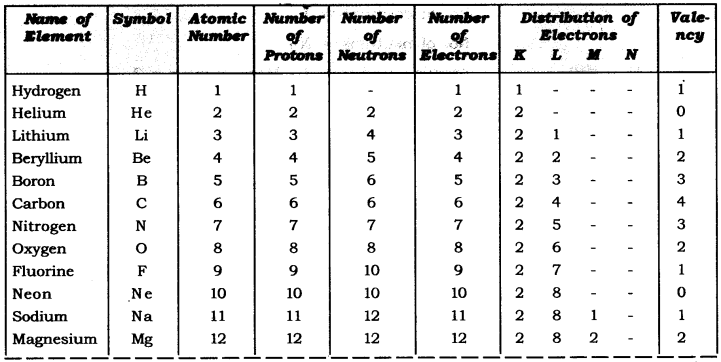
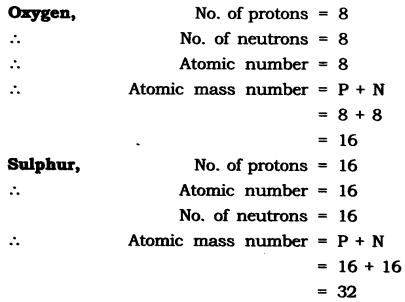
Question 2. With the help of given Table 4.1, find out the mass number of oxygen and sulphur atom.
Table: Composition of Atoms of the First Eighteen Elements with Electron Distribution in Various Shells
Answer:
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 4 Textbook – Page 45
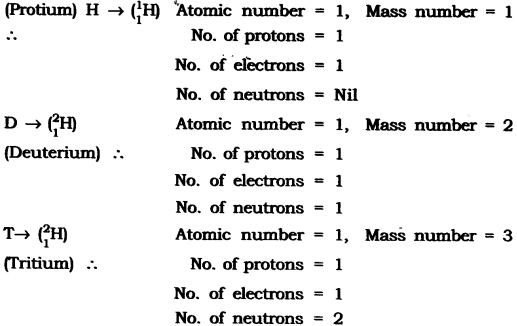
Question 1. For the symbol H, D and T tabulate three sub-atomic particles found in each of them
Answer:
Question 2. Write the electronic configuration of any one pair of isotopes and isobar.
Answer. Isotopes: Atoms of same element having same atomic number but different mass number.
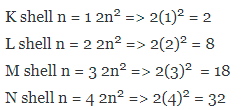


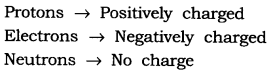
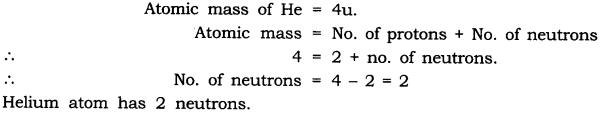





Leave a Reply