Notes For All Chapters Science Class 9 CBSE
1. Introduction
Ancient Indian philosopher Maharishi Kanad (around 500 BC) proposed that matter can be divided into smaller and smaller particles until we reach indivisible particles called Parmanu.
Pakudha Katyayama further said these particles exist in combined forms to form different substances.
Around the same time, Greek philosophers like Democritus and Leucippus called these indivisible particles atoms (meaning “indivisible”).
These ideas were philosophical; experimental proof came much later.
2. Laws of Chemical Combination
By the late 18th century, scientists distinguished between elements and compounds and began studying how elements combine.
Antoine Lavoisier established two important laws:
2.1 Law of Conservation of Mass
- Statement: Mass can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
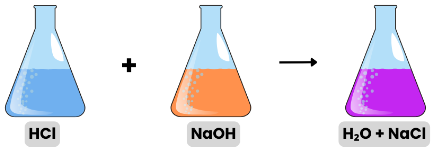
- Example Activity: When two solutions react in a closed flask, the total mass before and after reaction remains the same.
- For example, ( Reactant ) A + B → AB ( Product )
2.2 Law of Constant Proportions (Law of Definite Proportions)
- Statement: In a chemical substance, elements are always present in a definite proportion by mass.
- Example:
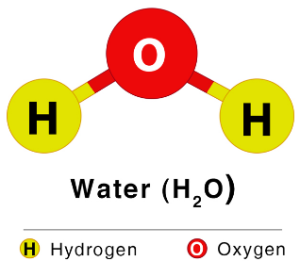
- In water (H₂O) → hydrogen and oxygen are always in the ratio 1:8 by mass.
- In ammonia (NH₃) → nitrogen and hydrogen are in the ratio 14:3 by mass.
- This law was given by Joseph Proust.
3. Dalton’s Atomic Theory (1808)
John Dalton explained these laws by proposing the Atomic Theory.
Postulates:
- All matter is made of very tiny particles called atoms.
- Atoms are indivisible and indestructible in chemical reactions.
- All atoms of a given element are identical in mass and chemical properties.
- Atoms of different elements have different masses and properties.
- Atoms combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds.
- In a given compound, the relative number and kinds of atoms are constant.
Dalton’s theory explained:
- Law of conservation of mass.
- Law of definite proportions.
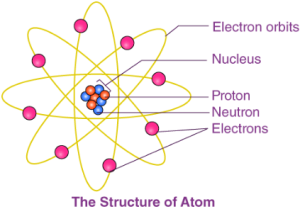
4. What is an Atom?
- Definition: The smallest particle of matter that cannot usually exist independently and retains all its chemical properties.
- Size: Extremely small; millions of atoms stacked together make a layer as thin as paper.
- Measurement: Atomic radius measured in nanometres (1 nm = 10⁻⁹ m).
| Example | Approx. Size (m) |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen atom | 10⁻¹⁰ |
| Water molecule | 10⁻⁹ |
| Grain of sand | 10⁻⁴ |
| Apple | 10⁻¹ |
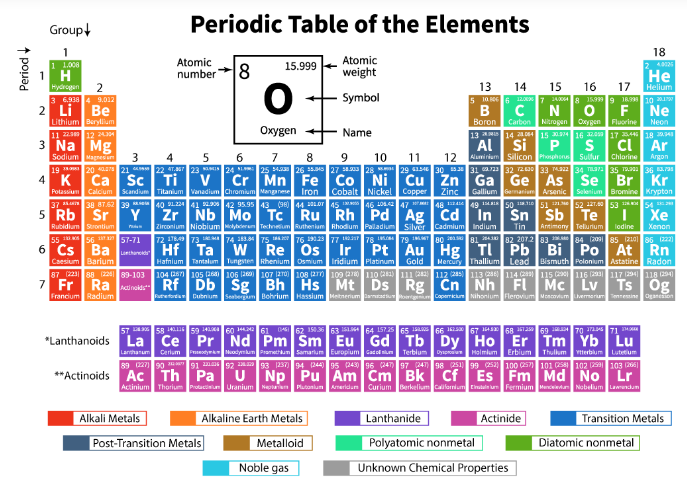
5. Modern Symbols of Elements
Dalton used pictorial symbols, but later Berzelius suggested using letters.
Rules for Symbols:
- One or two letters from the element’s English name.
- First letter – capital, second letter – small.
- Example: H (Hydrogen), Al (Aluminium), Co (Cobalt)
- Some are derived from Latin names:
- Fe (Ferrum) for Iron, Na (Natrium) for Sodium, K (Kalium) for Potassium.
IUPAC approves all element names and symbols.
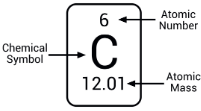
6. Atomic Mass
Dalton proposed that every element has a characteristic atomic mass.
Since measuring the mass of a single atom is difficult, scientists use relative atomic mass.
1 atomic mass unit (1 u) = 1/12 the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
Table: Some Atomic Masses
| Element | Atomic Mass (u) | Element | Atomic Mass (u) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 1 | Nitrogen | 14 |
| Carbon | 12 | Oxygen | 16 |
| Sodium | 23 | Sulphur | 32 |
| Magnesium | 24 | Chlorine | 35.5 |
| Calcium | 40 |
7. Molecules
7.1 Molecule Definition
- Smallest particle of an element or compound capable of independent existence and showing all properties of that substance.
7.2 Molecules of Elements
- Formed by atoms of the same element.
- Monoatomic: Ar, He
- Diatomic: O₂, H₂, N₂, Cl₂
- Triatomic: O₃
- Polyatomic: P₄, S₈
| Element | Type | Atomicity |
|---|---|---|
| Helium | Monoatomic | 1 |
| Oxygen | Diatomic | 2 |
| Phosphorus | Tetra-atomic | 4 |
| Sulphur | Polyatomic | 8 |
7.3 Molecules of Compounds
- Atoms of different elements combine in fixed ratios.
- Water (H₂O): H:O = 2:1 by number of atoms.
- Carbon dioxide (CO₂): C:O = 1:2
- Ammonia (NH₃): N:H = 1:3
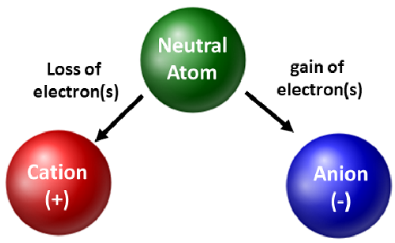
8. Ions
Definition: Charged species formed when atoms lose or gain electrons.
- Cation: Positively charged ion (e.g., Na⁺, Ca²⁺).
- Anion: Negatively charged ion (e.g., Cl⁻, O²⁻).
Polyatomic ions: Groups of atoms with a charge (e.g., NH₄⁺, SO₄²⁻, OH⁻, CO₃²⁻).
9. Chemical Formulae
Rules:
- The valencies of ions must balance.
- Write metal first, then non-metal.
- Use brackets for polyatomic ions if more than one group is present.
Examples:
| Compound | Formula |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen chloride | HCl |
| Magnesium chloride | MgCl₂ |
| Aluminium oxide | Al₂O₃ |
| Sodium carbonate | Na₂CO₃ |
| Calcium hydroxide | Ca(OH)₂ |
| Ammonium sulphate | (NH₄)₂SO₄ |
10. Molecular Mass and Formula Unit Mass
10.1 Molecular Mass
- Definition: Sum of atomic masses of all atoms in a molecule.
- Example: H₂O = (2 × 1) + 16 = 18 u
- HNO₃ = 1 + 14 + (3 × 16) = 63 u
10.2 Formula Unit Mass
Used for ionic compounds (not molecules).
Example:
- NaCl = 23 + 35.5 = 58.5 u
- CaCl₂ = 40 + (2 × 35.5) = 111 u

Very nice and it verymuch helped in annual exam for me
MAKE IT EASY
Thoda easy samjhaya kro