Important Questions For All Chapters – Science Class 9
Short Questions
1. Who discovered the cell?
Answer: Robert Hooke discovered the cell in 1665 while examining a thin slice of cork through a self-designed microscope.
2. What is the basic structural and functional unit of life?
Answer: The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life.
3. What is diffusion?
Answer: The movement of substances from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration is called diffusion.
4. What is osmosis?
Answer: The movement of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane from a region of higher water concentration to lower water concentration is called osmosis.
5. What is plasmolysis?
Answer: The shrinkage of the cell’s contents away from the cell wall due to loss of water by osmosis is called plasmolysis.
6. Why is the plasma membrane called selectively permeable?
Answer: Because it allows only certain substances to pass in and out of the cell.
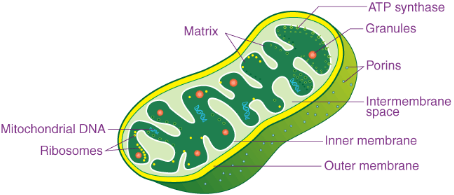
7. Which cell organelle is known as the powerhouse of the cell?
Answer: Mitochondria are known as the powerhouse of the cell because they produce energy in the form of ATP.
8. Name two organelles that contain their own DNA.
Answer: Mitochondria and plastids contain their own DNA.
9. What are chromoplasts that contain chlorophyll called?
Answer: Chromoplasts containing chlorophyll are called chloroplasts.
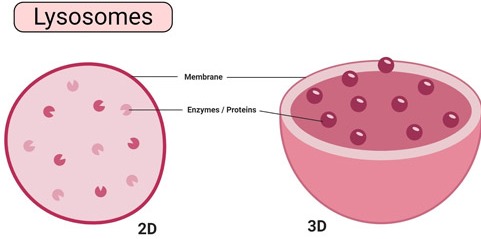
10. What is the function of lysosomes?
Answer: Lysosomes digest worn-out cell organelles and foreign materials; hence, they are called the “suicide bags” of the cell.
Long Questions
1. Explain the discovery of the cell and the development of cell theory.
Answer: Robert Hooke discovered cells in 1665. Leeuwenhoek observed living cells in 1674. Robert Brown discovered the nucleus in 1831, and Purkinje coined the term “protoplasm” in 1839. Schleiden and Schwann proposed the cell theory that all plants and animals are made up of cells and cells are the basic unit of life. Later, Virchow added that all cells arise from pre-existing cells.
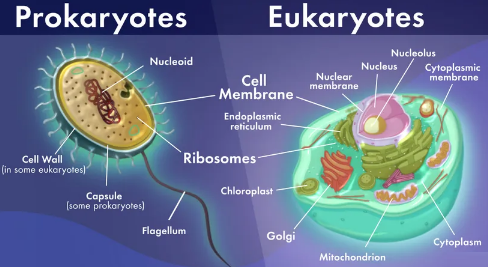
2. Differentiate between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Answer:
| No. | Prokaryotic Cell | Eukaryotic Cell |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Size is generally small (1-10 µm). | Size is generally large (5-100 µm). |
| 2. | Nuclear region is not well-defined and is called nucleoid. | Nuclear region is well-defined and surrounded by a nuclear membrane. |
| 3. | Contains a single chromosome. | Contains more than one chromosome. |
| 4. | Membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, etc., are absent. | Membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria, plastids, and Golgi apparatus are present. |
| 5. | Cell division is simple and occurs by binary fission. | Cell division occurs by mitosis or meiosis. |
| 6. | Examples: Bacteria, Blue-green algae (Cyanobacteria). | Examples: Plants, Animals, Fungi, Protists. |
3. Describe the structure and function of the plasma membrane.
Answer: The plasma membrane is the outermost covering of the cell made up of lipids and proteins. It separates the cell contents from the external environment. It controls the movement of substances into and out of the cell through diffusion and osmosis, hence it is called a selectively permeable membrane.
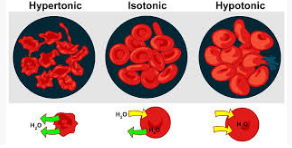
4. What happens to a cell in hypotonic, isotonic, and hypertonic solutions?
Answer:
- In a hypotonic solution, the cell gains water and swells.
- In an isotonic solution, there is no net movement of water, and the cell remains the same size.
- In a hypertonic solution, the cell loses water and shrinks.
5. Explain the structure and function of the cell wall.
Answer: The cell wall is a rigid outer covering present in plant cells made mainly of cellulose. It provides structural strength to the cell. It helps plant cells withstand hypotonic conditions without bursting.
6. Describe the structure and function of the nucleus.
Answer: The nucleus has a double-layered nuclear membrane with pores. It contains chromosomes made of DNA and proteins. DNA carries hereditary information and directs all cellular activities. The nucleus controls cell growth and reproduction.
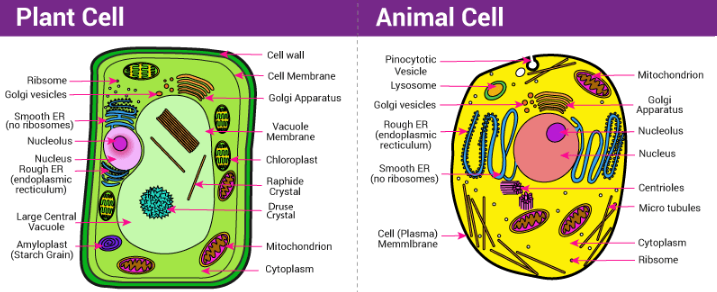
7. Explain the differences between plant and animal cells.
Answer:
| No. | Plant Cell | Animal Cell |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Has a cell wall made up of cellulose outside the plasma membrane. | Cell wall is absent; only plasma membrane is present. |
| 2. | Contains plastids (such as chloroplasts) which help in photosynthesis. | Plastids are absent. |
| 3. | Has a large central vacuole that maintains turgidity and stores cell sap. | Vacuoles are small and temporary. |
| 4. | Generally has a fixed, rectangular shape. | Usually has a round or irregular shape. |
| 5. | Stores energy mainly in the form of starch. | Stores energy mainly in the form of glycogen. |
| 6. | Centrioles are absent (except in lower plant forms). | Centrioles are present and help in cell division. |
8. Describe the structure and functions of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
Answer: The ER is a network of membrane-bound tubes. RER (with ribosomes) synthesises proteins, and SER synthesises lipids. ER helps in transport of materials and formation of the cell membrane.
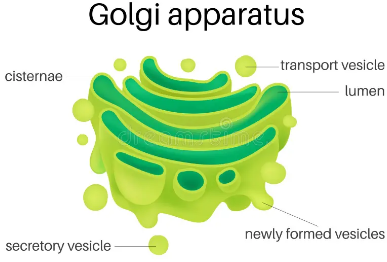
9. What are the functions of the Golgi apparatus?
Answer: The Golgi apparatus stores, modifies, and packages materials in vesicles. It helps in the formation of lysosomes and in making complex sugars from simple sugars.
10. What are lysosomes? Why are they called ‘suicide bags’?
Answer: Lysosomes are membrane-bound sacs containing digestive enzymes. They digest worn-out organelles and foreign materials. When a cell is damaged, lysosomes burst and digest their own cell, hence called suicide bags.
11. Explain the structure and functions of mitochondria.
Answer: Mitochondria have two membranes – an outer porous membrane and a folded inner membrane forming cristae. They release energy in the form of ATP during respiration. They have their own DNA and ribosomes, enabling them to make proteins.
12. Describe plastids and their types.
Answer:
Plastids are present only in plant cells and are of two main types:
- Chromoplasts (coloured plastids) – include chloroplasts that contain chlorophyll for photosynthesis.
- Leucoplasts – colourless plastids that store starch, proteins, and oils.
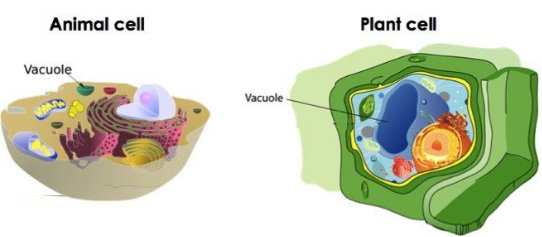
13. What is the role of vacuoles in plant and animal cells?
Answer: Vacuoles store substances like sugars, amino acids, and waste. Plant cells have large central vacuoles that maintain turgidity and rigidity, while animal cells have small vacuoles.
14. What is cell division? Describe its two types.
Answer: Cell division is the process by which new cells are formed.
- Mitosis produces two identical daughter cells and helps in growth and repair.
- Meiosis produces four cells with half the number of chromosomes, responsible for gamete formation.
15. Why is the cell called the fundamental unit of life?
Answer: All living organisms are made up of cells. Each cell performs vital functions such as respiration, excretion, and reproduction. Hence, it is the structural and functional unit of life.

Leave a Reply