Important Questions For All Chapters – Science Class 9
Short Questions
1. What is motion?
Answer: Motion is a change in the position of an object with time.
2. What is the SI unit of speed?
Answer: The SI unit of speed is metre per second (m/s).
3. Define displacement.
Answer: The shortest distance measured from the initial to the final position of an object is called displacement.
4. What is uniform motion?
Answer: When an object covers equal distances in equal intervals of time, it is said to be in uniform motion.
5. What is non-uniform motion?
Answer: When an object covers unequal distances in equal intervals of time, it is said to be in non-uniform motion.
6. Define acceleration.
Answer: Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity of an object per unit time.
7. Write the three equations of motion.
Answer:
8. What does the odometer of a car measure?
Answer: The odometer measures the distance travelled by a vehicle.
9. What is uniform circular motion?
Answer: When an object moves in a circular path with uniform speed, it is called uniform circular motion.
10. What quantity is represented by the area under a velocity-time graph?
Answer: The area under a velocity-time graph represents the distance travelled by the object.
Long Questions
1. Differentiate between distance and displacement.
Answer:
- Distance: It is the total path length covered by an object.
- Displacement: It is the shortest distance between initial and final positions of an object.
Distance is a scalar quantity whereas displacement is a vector quantity.
2. Explain the difference between uniform motion and non-uniform motion with examples.
Answer:
- Uniform Motion: Equal distances in equal intervals of time, e.g., car moving at constant speed.
- Non-uniform Motion: Unequal distances in equal intervals of time, e.g., a car moving in traffic.
3. Define speed and velocity and state their differences.
Answer:
- Speed: The rate of change of distance per unit time.
- Velocity: The rate of change of displacement per unit time.
Speed has only magnitude (scalar) while velocity has both magnitude and direction (vector).
4. What is meant by acceleration? Derive the formula for acceleration.
Answer:
Acceleration = Change in velocity / Time taken
If initial velocity = u, final velocity = t, then
a = \(\frac{v-u}{t}\)
5. Explain how distance-time graphs are used to study motion.
Answer: In a distance-time graph, time is taken on the X-axis and distance on the Y-axis.
- A straight line indicates uniform motion.
- A curved line indicates non-uniform motion.
- A horizontal line indicates the object is at rest.
6. Derive the equation v = u+at using a velocity-time graph.
Answer: In a velocity-time graph for uniform acceleration,
Initial velocity = u, final velocity = v, time = t, acceleration = a.
From graph, \(\frac{v-u}{t}\)
So, v = u + at
7. Derive the second equation of motion s = ut + \(\frac{1}{2}\)at2
Answer: From the velocity-time graph, distance = area under the graph
= area of rectangle + area of triangle
ut + \(\frac{1}{2}\)at2
8. Derive the third equation of motion v2 − u2 = 2as.
Answer: From v = u + at → t = \(\frac{v-u}{a}\)
Substitute in s = ut + \(\frac{1}{2}\)at2
v2 − u2 = 2as
9. Explain the concept of uniform circular motion with an example.
Answer: When an object moves in a circular path with constant speed, its direction changes continuously, so it is in accelerated motion.
Example: Motion of the moon around the Earth.
10. What is average speed and average velocity?
Answer:
- Average Speed = Total distance travelled / Total time taken
- Average Velocity = Total displacement / Total time taken
They are equal only when the motion is in a straight line without change in direction.
11. Explain with an example when displacement is zero but distance is not zero.
Answer: If an object moves in a circular path and returns to its starting point, displacement = 0 but distance = circumference of the circle.
12. What are the uses of velocity-time graphs?
Answer: Velocity-time graphs help to determine:
- Acceleration of an object (from slope).
- Distance travelled (from area under graph).
- Nature of motion — uniform or non-uniform.
13. A car accelerates uniformly from rest to 20 m/s in 10 s. Find the acceleration and distance travelled.
Answer:
14. What is the significance of area under a velocity-time graph? Explain with an example.
Answer: The area under a velocity-time graph gives the displacement or distance travelled.
Example: For uniform velocity, distance = area of rectangle under the line.
15. Describe the motion of a freely falling body.
Answer: A freely falling body moves with uniform acceleration due to gravity. Its velocity increases equally in equal intervals of time, making it an example of uniformly accelerated motion.
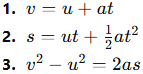
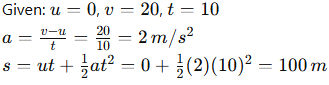

Leave a Reply