Important Questions For All Chapters – Science Class 9
Short Questions
1. What is gravitation?
Answer: Gravitation is the force of attraction between any two objects in the universe.
2. Who discovered the universal law of gravitation?
Answer: Sir Isaac Newton discovered the universal law of gravitation.
3. Write the formula for the universal law of gravitation.
Answer:
4. What is the value of the universal gravitational constant (G)?
Answer: G = 6.673×10−11Nm2kg−2
5. What is free fall?
Answer: When an object falls towards the earth under the influence of gravitational force alone, it is said to be in free fall.
6. Define acceleration due to gravity.
Answer: The acceleration produced in a body due to the gravitational pull of the earth is called acceleration due to gravity, denoted by g.
7. State the relation between weight and mass.
Answer: W = m×g
8. What is the average value of g on the surface of the earth?
Answer: The value of g on the surface of the earth is 9.8 m/s2.
9. What is buoyant force?
Answer: The upward force exerted by a fluid on a body immersed in it is called buoyant force.
10. State Archimedes’ principle.
Answer: When a body is immersed fully or partially in a fluid, it experiences an upward force equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by it.
Long Questions
1. State and explain the universal law of gravitation.
Answer: The universal law of gravitation states that every object in the universe attracts every other object with a force which is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Mathematically,
where
G is the universal gravitational constant.
2. Mention four importance points of the universal law of gravitation.
Answer:
(i) It binds us to the Earth.
(ii) It explains the motion of the Moon around the Earth.
(iii) It explains the motion of planets around the Sun.
(iv) It explains tides due to the Moon and the Sun.
3. Derive the formula for acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the Earth.
Answer:
4. Why does the value of g vary from place to place on Earth?
Answer: The Earth is not a perfect sphere; its radius increases from the poles to the equator. Therefore, g is greater at the poles and smaller at the equator.
5. Explain the difference between mass and weight.
Answer:
- Mass: The quantity of matter in a body. It is constant everywhere.
- Weight: The force with which the Earth attracts a body; varies from place to place.
Relation: W = m×g.
6. Why is the weight of an object on the Moon one-sixth of its weight on Earth?
Answer: The Moon’s mass is smaller than the Earth’s mass, and its radius is also smaller.
Hence, gm = \(\frac{1}{6}\)ge, so weight on the Moon = \(\frac{1}{6}\) of the weight on Earth.
7. Define thrust and pressure. Derive their relationship.
Answer:
- Thrust: Force acting perpendicular to a surface.
- Pressure: Force per unit area.
P = \(\frac{F}{A}\)
Thus, pressure depends inversely on the area on which a force acts.
8. Explain with an example why cutting tools have sharp edges.
Answer: Sharp edges reduce the area of contact, thus increasing pressure for the same force, making cutting easier.
9. What is buoyancy? Explain with an activity.
Answer: Buoyancy is the upward force exerted by a fluid on a body immersed in it.
For example, when a bottle is pushed into water, it experiences an upward push that increases with depth—this shows buoyant force.
10. State the conditions under which an object will float or sink in water.
Answer:
- If the density of the object < density of water → it floats.
- If the density of the object > density of water → it sinks.
11. What is Archimedes’ principle? Mention its applications.
Answer: Archimedes’ principle: When a body is immersed fully or partially in a fluid, it experiences an upward force equal to the weight of the displaced fluid.
Applications:
(i) Designing ships and submarines.
(ii) Lactometer to test milk purity.
(iii) Hydrometer to measure liquid density.
12. Explain the term “free fall” and derive the equations of motion for freely falling bodies.
Answer: In free fall, objects fall under gravity alone.
Equations of motion become:
13. Why do paper and stone not fall at the same rate in air?
Answer: Due to air resistance. The paper experiences more air friction than the stone. In a vacuum, both would fall at the same rate.
14. What happens to the gravitational force between two objects when:
(i) the distance between them is halved,
(ii) the mass of one object is doubled?
Answer:
- (i) Force becomes four times greater when distance is halved.
- (ii) Force becomes twice when the mass of one object is doubled.
15. Describe an activity to show the existence of buoyant force.
Answer:
Take a stone tied to a spring balance and note its reading in air. Now immerse it in water — the reading decreases. The decrease shows an upward force called buoyant force acting on the stone.
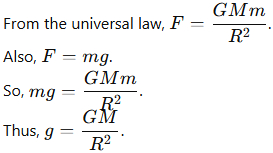
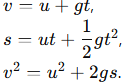

Leave a Reply