Important Questions For All Chapters – Science Class 9
Short Questions
1. What causes the production of sound?
Answer: Sound is produced due to the vibrations of an object.
2. What type of wave is a sound wave?
Answer: Sound waves are longitudinal waves.
3. Through which medium does sound travel fastest?
Answer: Sound travels fastest in solids.
4. What is the unit of frequency?
Answer: The SI unit of frequency is hertz (Hz).
5. What is the audible range of the human ear?
Answer: The audible range of the human ear is from 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz.
6. What is an echo?
Answer: Echo is the reflection of sound that is heard after a time gap from the original sound.
7. Name one use of ultrasound in medicine.
Answer: Ultrasound is used in ultrasonography to obtain images of internal organs of the human body.
8. What is reverberation?
Answer: The persistence of sound due to repeated reflection is called reverberation.
9. What is the relationship between speed, frequency, and wavelength of sound?
Answer: The relationship is given by:
v = λν
where v = speed, λ = wavelength, ν = frequency.
10. Which property of sound determines its loudness?
Answer: Loudness depends on the amplitude of the sound wave.
Long Questions
1. What is sound and how is it produced?
Answer: Sound is a form of energy that produces a sensation of hearing in our ears. It is produced when an object vibrates. These vibrations disturb the particles of the surrounding medium, transferring energy from one particle to another until the sound reaches our ear. For example, when we pluck a stretched rubber band, it vibrates and produces sound.
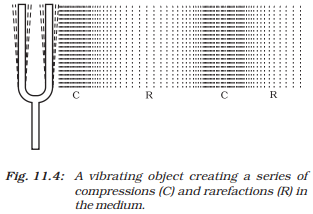
2. Describe with a diagram how compressions and rarefactions are produced in air near a source of sound.
Answer: When a vibrating object moves forward, it pushes the air particles creating a region of high pressure called compression. When it moves backward, a region of low pressure called rarefaction is formed. These alternate compressions and rarefactions travel through the medium as sound waves.
3. Explain the difference between longitudinal and transverse waves.
Answer: In longitudinal waves, particles of the medium vibrate parallel to the direction of propagation, e.g., sound waves.
In transverse waves, particles vibrate perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation, e.g., light waves or waves on a string.
4. Explain the characteristics of a sound wave.
Answer: The main characteristics of a sound wave are:
- Amplitude (A): It determines the loudness of sound.
- Frequency (ν): It determines the pitch of sound.
- Wavelength (λ): Distance between two compressions or rarefactions.
- Time Period (T): Time taken for one oscillation.
- Speed (v): Distance travelled by the wave per second.
They are related by the formula u = λν.
5. What is the difference between loudness and intensity of sound?
Answer: Loudness is a physiological response of the ear to sound intensity, while intensity is the amount of sound energy passing through a unit area per second. Loudness depends on amplitude, whereas intensity depends on power and area.
6. State and explain the laws of reflection of sound.
Answer: Sound follows the same laws of reflection as light:
- The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection.
- The incident ray, reflected ray, and the normal all lie in the same plane.
These laws are demonstrated using materials like walls or metal sheets which act as reflecting surfaces.
7. What is an echo? Explain the condition necessary for hearing an echo.
Answer: Echo is the repetition of sound caused by its reflection from a surface.
For a distinct echo, the minimum distance between the source and the reflector should be 17.2 meters (since the time gap should be at least 0.1 s).
8. What is reverberation and how can it be reduced?
Answer: Reverberation is the persistence of sound due to repeated reflections in a hall.
It can be reduced by:
- Using sound-absorbing materials like curtains, carpets, or fibreboards.
- Designing halls with curved ceilings and non-reflective materials.
9. What is the range of hearing in humans and other animals?
Answer: Humans can hear sounds between 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz.
Sounds below 20 Hz are called infrasound (used by whales, elephants), while sounds above 20,000 Hz are called ultrasound (used by bats, dolphins, and dogs).
10. What are ultrasonic waves? Mention two of their applications.
Answer: Ultrasonic waves have frequencies above 20,000 Hz.
Applications:
- Used in medical imaging like ultrasonography.
- Used to detect flaws and cracks in metal blocks.
11. How is ultrasound used in medical diagnosis?
Answer: Ultrasound is used in ultrasonography to capture images of internal organs like the liver, kidney, or uterus. The reflected waves from tissue boundaries create images that help doctors detect abnormalities like stones or tumours.
12. How is ultrasound used to detect defects in metal blocks?
Answer: Ultrasonic waves are passed through metal blocks. If there is a flaw or crack, the waves are reflected back and detected. This method helps find internal defects invisible to the eye.
13. Why is sound heard after lightning seen during a thunderstorm?
Answer: Light travels much faster (3×10⁸ m/s) than sound (≈344 m/s). Hence, we see lightning almost instantly but hear thunder after some time due to the slower speed of sound.
14. What is the relationship between frequency, wavelength, and speed of sound? Explain with an example.
Answer: The relationship is v = λν.
For example, if a sound has a frequency of 2000 Hz and wavelength 0.35 m,
v = 0.35×2000 = 700m/s.
Thus, the speed of the sound wave is 700 m/s.
15. Explain how multiple reflection of sound is used in instruments like megaphones and stethoscopes.
Answer:
- Megaphones use multiple reflections inside their conical shape to direct sound waves in one direction.
- Stethoscopes use multiple reflections of sound through rubber tubes to carry the heartbeat sound clearly to the doctor’s ears.

Leave a Reply