Notes For All Chapters Science Class 9
1. Introduction
- Every living being needs energy for daily activities like playing, reading, running, etc.
- Energy for life processes comes from food.
- Machines and living beings both need energy to perform work.
- In this chapter, we study Work, Energy, and Power — three closely related concepts.
2. WORK
Daily-Life Meaning vs Scientific Meaning
- In everyday life, any physical or mental effort is called “work”.
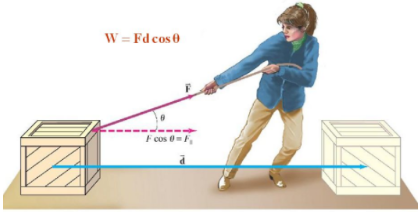
- In science, work is done only when a force applied on an object causes displacement in the direction of that force.
Why sometimes not much work is done inspite of working hard?
→ Reading, writing, drawing, thinking, analysing are all energy consuming. But in scientific manner, no work is done in above cases.
→ Example: A man is completely exhausted in trying to push a rock (wall), but work done is zero as wall is stationary.
→ A man standing still with heavy suitcase may be tired soon but he does no work in this situation as he is stationary.
When force is applied on the wall, the wall doesn’t move. Therefor, no work is done here.
Conditions for Work to be Done
Work is said to be done only if:
- A force acts on an object, and
- The object gets displaced.
If either of these conditions is not satisfied, no work is done.
Work is said to be done when:
(i) a moving object comes to rest.
(ii) an object at rest starts moving.
(iii) velocity of an object changes.
(iv) shape of an object changes.
Scientific Conception of Work
→ Work is done when a force produces motion in a body.
→ Work is said to be done when a force is applied on a body and the body moves under the influence of force.
Condition of Work
(i) Force should be applied on the body.
(ii) Body should be displaced.
• Work is done when:
(i) A cyclist is pedaling the cycle.
(ii) A man is lifting load in upward or downward direction.
• Work is not done when:
(i) A coolie carrying some load on his head stands stationary.
(ii) A man is applying force on a big rock.
Work Done by a Fixed Force
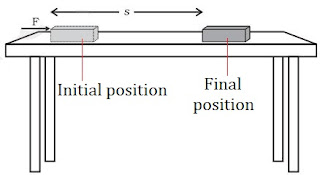
→ Work done in moving a body is equal to the product of force and displacement of body in the direction of force.
Work = Force × Displacement
W = F × S
→ Work is a scalar quantity.
Unit of Work
→ Unit of work is Newton metre or Joule.
→ When a force of 1 Newton moves a body through a distance of 1 metre in its own direction, then the work done is 1 Joule.
1 Joule = 1 Newton × 1 metre
1 J = 1 Nm
Types of Work
1. Positive Work:
- When the force and displacement are in the same direction.
- Example: Lifting an object upwards.
2. Negative Work:
- When the force acts opposite to the direction of displacement.
- Example: Friction, or gravity acting on a falling object.
3. ENERGY
Definition
Energy is the capacity to do work.
When an object does work, it loses energy; the object on which work is done gains energy.
- Unit of Energy: Joule (J)
- 1 kJ = 1000 J
3.1 Forms of Energy
- Mechanical Energy (Potential + Kinetic)
- Heat Energy
- Chemical Energy
- Electrical Energy
- Light Energy
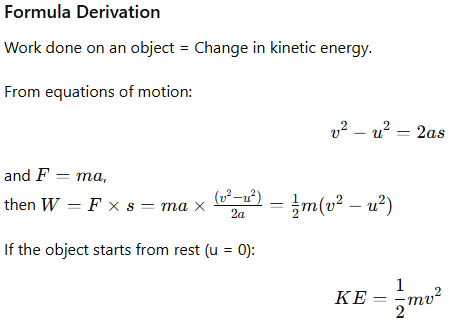
3.2 KINETIC ENERGY (KE)
Definition
The energy possessed by an object due to its motion is called kinetic energy.
Examples:
- A moving car, flowing river, flying aircraft, moving bullet.
3.3 POTENTIAL ENERGY (PE)
Definition
Energy possessed by an object due to its position or configuration is called Potential Energy.
Examples:
- A stretched rubber band.
- A compressed spring.
- Water stored in a dam.
3.4 Gravitational Potential Energy
When an object is raised to a height h, work is done against gravity and stored as gravitational potential energy.
PE = mgh
- m: mass (kg)
- g: acceleration due to gravity (9.8 m/s²)
- h: height (m)
3.5 Interconversion of Energy
Energy can be converted from one form to another but cannot be created or destroyed.
Examples
- Electric energy → Light energy (Bulb)
- Solar energy → Chemical energy (Photosynthesis)
- Potential energy → Kinetic energy (Falling stone)
- Chemical energy → Heat energy (Burning fuel)
3.6 Law of Conservation of Energy
Statement:
Energy can neither be created nor destroyed; it can only be transformed from one form to another. The total energy remains constant.
Example: Free Fall
- Object of mass m falls from height h:
- At top: Only potential energy (mgh)
- During fall: PE decreases, KE increases
- Just before hitting ground: PE = 0, KE = mgh
Total energy always remains constant.
4. RATE OF DOING WORK (POWER)
Definition
Power is the rate of doing work or rate of energy transfer.
Unit
SI Unit: Watt (W)
1 W = 1 J/s
Larger unit: 1 kW = 1000 W = 1000 J/s
Average Power
If power varies with time, average power is the total energy consumed divided by total time taken.


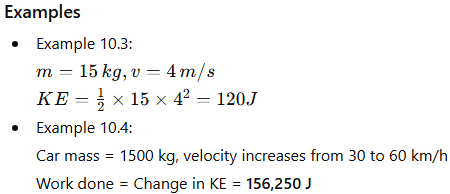

VERY GOOD