Q1. Define the following:
(a) Exocrine gland
Exocrine glands are glands that have ducts and secrete their products onto an epithelial surface or into body cavities. Examples include salivary glands, sweat glands, and sebaceous glands.
(b) Endocrine gland
Endocrine glands are ductless glands that release hormones directly into the bloodstream, which then travel to target organs to regulate physiological functions. Examples include the thyroid gland, adrenal gland, and pancreas (endocrine part).
(c) Hormone
A hormone is a chemical messenger produced by endocrine glands, released into the blood in trace amounts, and acts on specific target organs to regulate various bodily functions such as metabolism, growth, and reproduction.
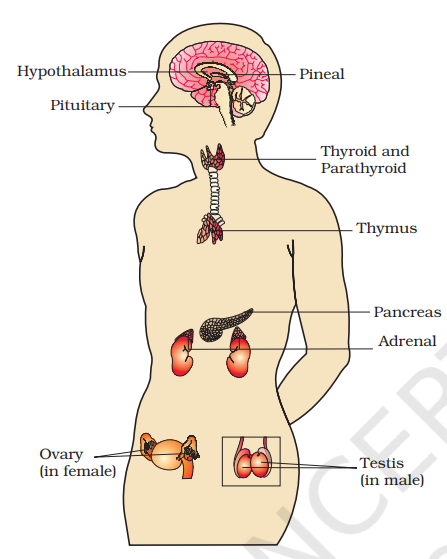
Q2. Diagrammatically indicate the location of the various endocrine glands in our body.
Diagram:
- Hypothalamus and pituitary gland (in the brain)
- Pineal gland (dorsal side of the forebrain)
- Thyroid and parathyroid glands (near the trachea)
- Thymus (between lungs)
- Adrenal glands (above kidneys)
- Pancreas (near the stomach)
- Gonads (testes in males and ovaries in females)
Q3. List the hormones secreted by the following:
(a) Hypothalamus
Releasing hormones (e.g., GnRH, TRH, CRH) and inhibiting hormones (e.g., somatostatin).
(b) Pituitary
- Anterior pituitary: GH, PRL, TSH, ACTH, LH, FSH, MSH
- Posterior pituitary: Oxytocin, vasopressin (ADH)
(c) Thyroid
Thyroxine (T₄), Triiodothyronine (T₃), and Thyrocalcitonin (TCT).
(d) Parathyroid
Parathyroid hormone (PTH).
(e) Adrenal
- Medulla: Adrenaline, noradrenaline
- Cortex: Glucocorticoids (e.g., cortisol), mineralocorticoids (e.g., aldosterone), and androgens.
(f) Pancreas
Insulin, glucagon.
(g) Testis
Androgens (e.g., testosterone).
(h) Ovary
Estrogens, progesterone.
(i) Thymus
Thymosins.
(j) Atrium
Atrial natriuretic factor (ANF).
(k) Kidney
Erythropoietin.
(l) G-I Tract
Gastrin, secretin, cholecystokinin (CCK), gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP).
Q4. Fill in the blanks:
(a) Hypothalamic hormones → Pituitary gland
(b) Thyrotrophin (TSH) → Thyroid gland
(c) Corticotrophin (ACTH) → Adrenal cortex
(d) Gonadotrophins (LH, FSH) → Gonads
(e) Melanotrophin (MSH) → Melanocytes
Q5. Write short notes on the functions of the following hormones:
(a) Parathyroid Hormone (PTH):
Source: Secreted by the parathyroid glands.
Function:
- Regulation of Blood Calcium Levels: PTH increases calcium levels in the blood by:
- Stimulating bone resorption (breaking down of bone matrix to release calcium and phosphate into the blood).
- Enhancing calcium reabsorption in the renal tubules, reducing calcium loss through urine.
- Promoting calcium absorption from the intestine through activation of vitamin D.
- Role in Phosphate Regulation: It reduces phosphate reabsorption in the kidneys, which helps in maintaining the calcium-phosphate balance in the blood.
(b) Thyroid Hormones (T₃ and T₄):
Source: Secreted by the thyroid gland.
Function:
- Regulation of Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR): Thyroid hormones increase oxygen consumption and heat production in cells, raising the body’s overall metabolism.
- Metabolism: They regulate the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats by stimulating glycogenolysis, lipolysis, and protein synthesis.
- Growth and Development: Essential for normal growth, especially of the nervous and skeletal systems.
- Erythropoiesis: Stimulates red blood cell production.
- Water and Electrolyte Balance: Maintains balance by influencing renal functions.
(c) Thymosins:
Source: Secreted by the thymus gland.
Function:
- T-Cell Maturation: Thymosins play a key role in the differentiation and maturation of T-lymphocytes, which are critical for cell-mediated immunity.
- Humoral Immunity: They stimulate the production of antibodies by promoting the activity of B-lymphocytes.
- Immune System Maintenance: Thymosins ensure proper immune responses, which tend to decline with age as the thymus degenerates.
(d) Androgens:
Source: Produced by the Leydig cells of the testis and adrenal cortex.
Function:
- Development of Secondary Sexual Characteristics: Promotes growth of facial, pubic, and axillary hair, deepening of the voice, and increased muscle mass.
- Spermatogenesis: Stimulates the production and maturation of sperm cells in the seminiferous tubules.
- Anabolic Effects: Increases protein synthesis, leading to muscle growth and maintenance.
- Behavioral Influence: Influences aggression and libido (sexual behavior).
(e) Estrogens:
Source: Produced by ovarian follicles and corpus luteum in females.
Function:
- Development of Secondary Sexual Characteristics: Influences high-pitched voice, breast development, and distribution of fat in the hips and thighs.
- Regulation of Menstrual Cycle: Stimulates endometrial growth during the proliferative phase.
- Support for Pregnancy: Prepares the uterus for implantation of the fertilized egg.
(f) Insulin and Glucagon:
Source: Secreted by the pancreas (Islets of Langerhans).
Insulin Function:
- Decreases Blood Glucose Levels: Enhances glucose uptake by cells, promoting glycogenesis (conversion of glucose into glycogen).
- Fat and Protein Metabolism: Stimulates fat synthesis and inhibits protein breakdown.
Glucagon Function:
- Increases Blood Glucose Levels: Stimulates glycogenolysis (breakdown of glycogen into glucose) and gluconeogenesis (formation of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources).
- Prevents Hypoglycemia: Ensures steady glucose supply during fasting.
Q6. Give example(s) of:
(a) Hyperglycemic hormone: Glucagon, Hypoglycemic hormone: Insulin
(b) Hypercalcemic hormone: Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
(c) Gonadotrophic hormones: LH, FSH
(d) Progestational hormone: Progesterone
(e) Blood pressure lowering hormone: Atrial natriuretic factor (ANF)
(f) Androgens and estrogens: Testosterone, Estrogen
Q7. Which hormonal deficiency is responsible for the following?
(a) Diabetes Mellitus:
- Cause: Deficiency of insulin or resistance to insulin.
- Mechanism: Insulin regulates blood glucose levels. Its deficiency leads to hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), glucose loss in urine, and production of ketone bodies, causing complications like neuropathy, nephropathy, and retinopathy.
(b) Goitre:
- Cause: Iodine deficiency or thyroid hormone deficiency (hypothyroidism).
- Mechanism: Inadequate iodine intake reduces thyroxine (T₄) synthesis, leading to thyroid gland enlargement (goitre) to compensate for reduced hormone levels.
(c) Cretinism:
- Cause: Deficiency of thyroid hormones during fetal or early childhood development.
- Mechanism: Thyroid hormones are essential for brain development and physical growth. Deficiency results in stunted growth, mental retardation, low intelligence quotient, abnormal skin, and deaf-mutism.
Q8. Briefly mention the mechanism of action of FSH.
Answer :
Source: Secreted by the anterior pituitary (pars distalis).
Mechanism:
- Target Organs:
- In females: Acts on ovarian follicles.
- In males: Acts on Sertoli cells in seminiferous tubules.
- Receptor Binding:
- FSH binds to specific membrane-bound receptors on the target cells.
- This binding activates intracellular signaling pathways involving secondary messengers like cyclic AMP (cAMP).
- Effects:
- In Females: Stimulates growth and maturation of ovarian follicles and promotes estrogen secretion by the granulosa cells.
- In Males: Supports spermatogenesis by enhancing Sertoli cell activity, which provides nourishment and structural support for developing sperm.
Q9. Match the following:
Answer :
| Column I | Column II |
|---|---|
| (a) T₄ | (ii) Thyroid |
| (b) PTH | (iv) Parathyroid |
| (c) GnRH | (i) Hypothalamus |
| (d) LH | (iii) Pituitary |

Leave a Reply