Notes For All Chapters Physics Class 11 CBSE
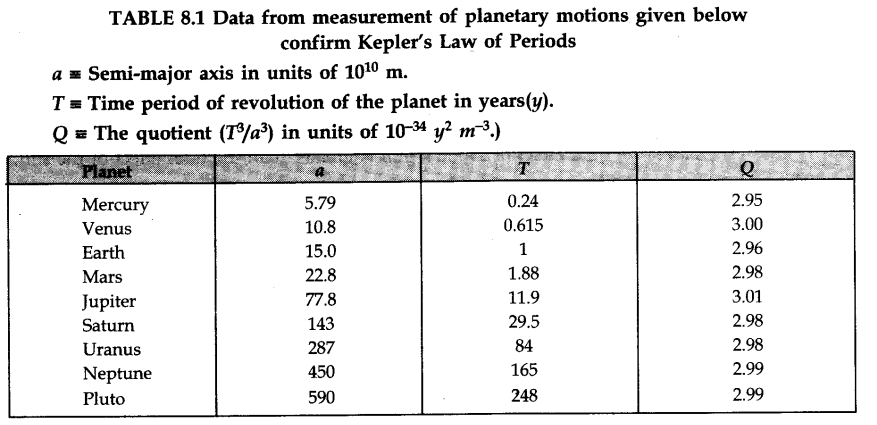
• Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion
Johannes Kepler formulated three laws which describe planetary motion. They are as follows:
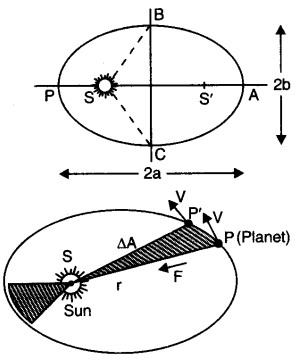
(i) Law of orbits. Each planet revolves around the sun in an elliptical orbit with the sun at one of the foci of the ellipse.
(ii) Law of areas. The speed of planet varies in such a way that the radius, vector drawn from the sun to planet sweeps out equal areas in equal times.
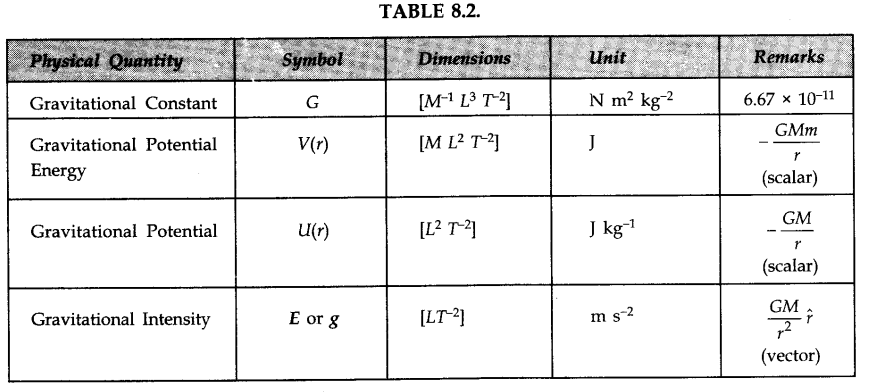
• Newton’s Law of Gravitation
Newton’s law of gravitation states that every particle in the universe attracts every other particle with a force directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. The direction of the force is along the line joining the particles.
• Universal constant of gravitation G is numerically equal to the force of attraction between two particles of unit mass each separated by unit distance.
• Important Characteristics of Gravitational Force
(i) Gravitational force between two bodies is a central force i.e., it acts along the line joining the centres of the two interacting bodies.
(ii) Gravitational force between two bodies is independent of the nature of the intervening medium.
(iii) Gravitational force between two bodies does not depend upon the presence of other bodies.
(iv) It is valid for point objects and spherically symmetrical objects.
(v) Magnitude of force is extremely small.
• Principle of Superposition of Gravitation
• Acceleration Due to Gravity
The acceleration produced in a body on account of the force of gravity is known as acceleration due to gravity. It is usually denoted by ‘g’. It is always towards the centre of Earth.
If a body of mass ‘m’ lying on the surface of the earth, the gravitational force acting on the body is given by
• Mass and Mean Density of Earth
Mass and Mean density of Earth is given in the following manner.
• Variation of Acceleration Due to Gravity
The value of acceleration due to gravity changes with height (i.e., altitude), depth, shape of the earth and rotation of earth about its own axis.
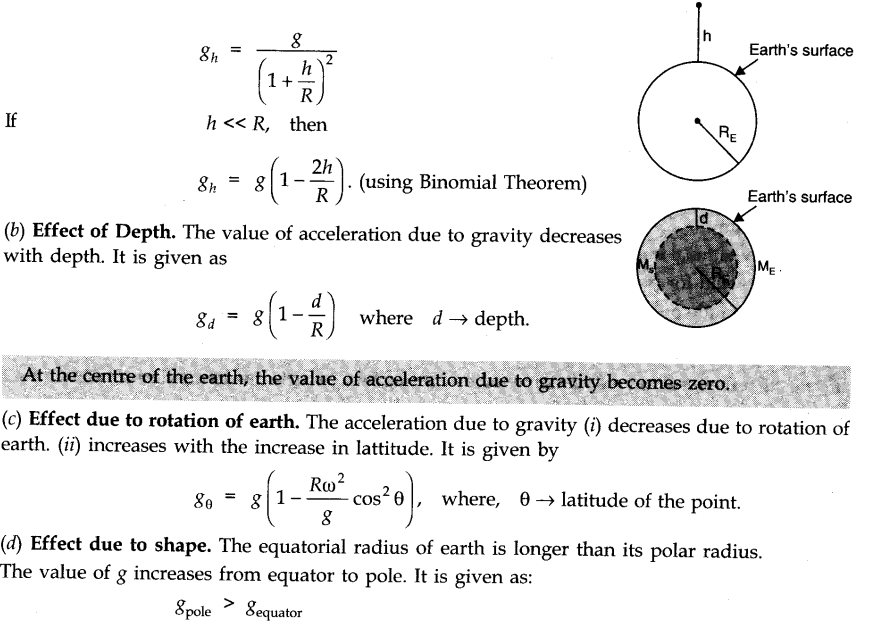
(a) Effect of Altitude. As one goes above the surface of Earth, value of acceleration due to gravity gradually goes on decreasing. If gh be the value of acceleration due to gravity at a height h from the surface of Earth, then
• Gravitational Field
The space around a body within which its gravitational force of attraction is experienced by other bodies is called gravitational field.
• Intensity of Gravitational Field
The intensity of the gravitational field of a body at a point in the field is defined as the force experienced by a body of unit mass placed at that point provided the presence of unit mass does not disturb the original gravitational field.
• Gravitational Potential
The gravitational potential at a point in the gravitational field of a body is defined as the amount of work done in bringing a body of unit mass from infinity to that point.
Gravitational potential at a point situated at a distance r from a body or particle of mass M is given by
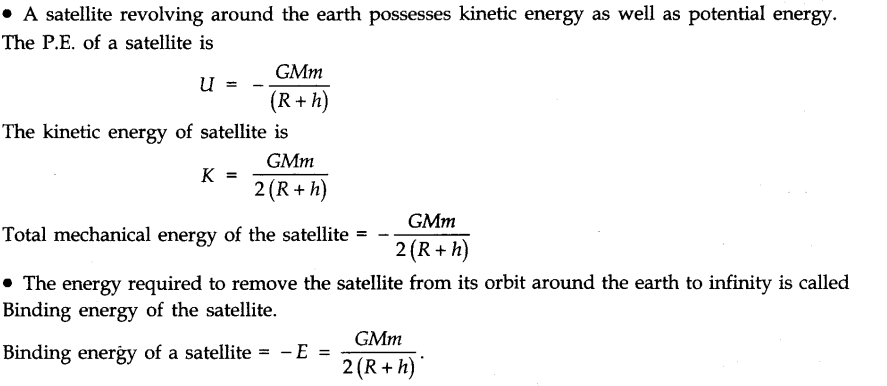
• Gravitational Potential Energy
The work done in carrying a mass ‘m’ from infinity to a point at distance r is called gravitational potential energy.
The gravitational potential energy of the system is given by
i.e., Gravitational potential energy = gravitational potential x mass of the body.
It is a scalar quantity and measured in joule.
• Escape Velocity
The minimum velocity required to project a body vertically upward from the surface of earth so that it comes out of the gravitational field of earth is called escape velocity.
• Satellite
A satellite is a body which is revolving continuously in an orbit around a comparatively much larger body.
The orbit may be either circular or elliptical. A man-made object revolving in an orbit around a planet is called an artificial satellite.
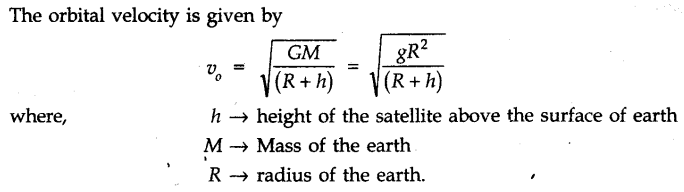
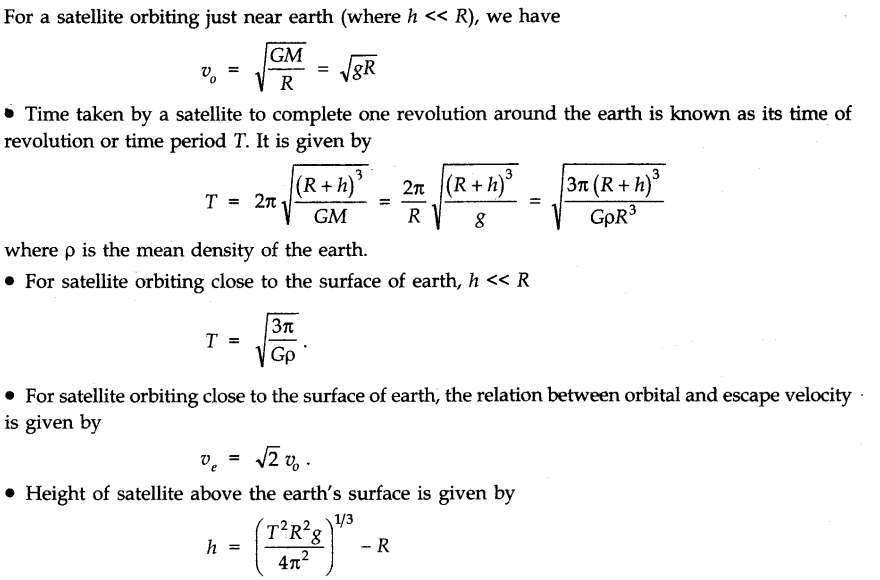
• Orbital Velocity
Orbital velocity of a satellite is the minimum velocity required to put the satellite into a given orbit around earth.
• Geostationary Satellite
The satellite having the same time period of revolution as that of the earth is called geostationary satellite. Such satellites should rotate in the equatorial plane from west to east.
The orbit of a geostationary satellite is called ‘parking orbit’. These satellites are used for communication purposes.
A geostationary satellite revolves around the earth in a circular orbit at a height of about 36,000 km from the surface of earth.
• IMPORTANT TABLES

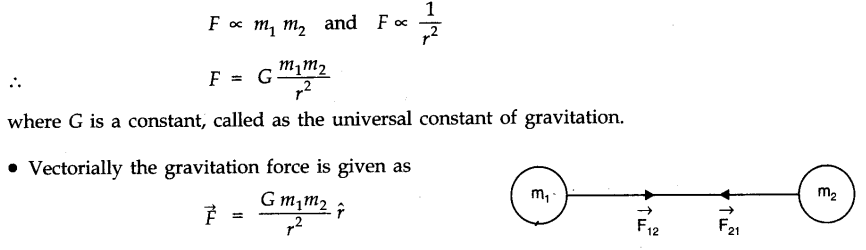

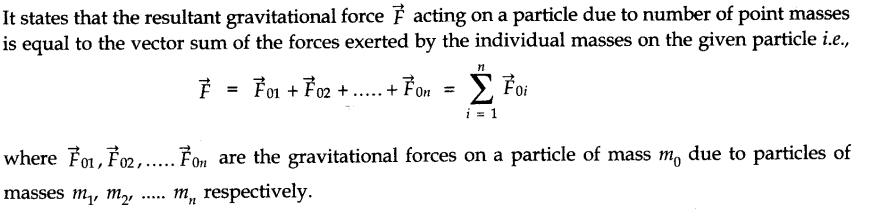
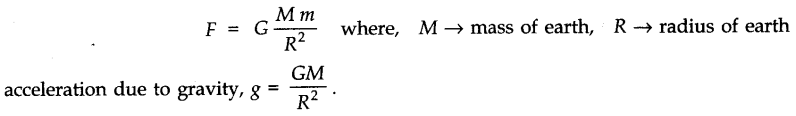


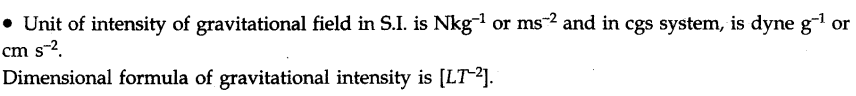
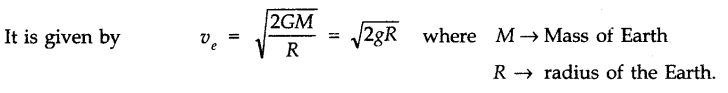

Leave a Reply