Notes For All Chapters Physics Class 11 CBSE
• The kinetic theory was developed in the nineteenth century by Maxwell, Boltzman and others. Kinetic theory explains the behaviour of gases based on the idea that the gas consists of rapidly moving atoms or molecules.
• Ideal Gas
An ideal gas or a perfect gas is that gas which strictly obeys gas laws such as Boyle’s law, Charle’s law, Gay Lussac’s law etc.
An ideal gas has following characteristics:
(i) Molecule of an ideal gas is a point mass with no geometrical dimensions.
(ii) There is no force of attraction or repulsion amongst the molecules of the gas.
• Kinetic Theory and Gas Pressure
The pressure of a gas is the result of continuous bombardment of the gas molecules against the walls of the container. According to the kinetic theory, the pressure P exerted by an ideal gas is given by
• Boyle’s Law
According to this law, the volume (V) of a fixed mass of a gas is inversely proportional to the pressure (P) of the gas, provided temperature of the gas is kept constant.
• Charle’s Law
According to this law, the volume (V) of a given mass of a gas is directly proportional to the
temperature of the gas, provided pressure of the gas remains constant.
• Gay Lussac’s Law (or Pressure Law)
According to this law, the pressure P of a given mass of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature T, provided the volume V of the gas remains constant.
• Equation of State of an Ideal Gas
The relationship between pressure P, volume V and absolute temperature T of a gas is called its equation of state. The equation of state of an ideal gas
PV = nRT
where n is the number of moles of the enclosed gas and R is the molar gas constant which is the same for all gases and its value is
R = 8.315 JK-1 mob-1
• Avagadro’s Law
Equal volumes of all gases under S.T.P. contain the same number of molecules equalling 6.023 x 1023.
• Graham’s Law of Diffusion of Gases
It states that rate of diffusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of the density of the gas.
Hence, denser the gas, the slower is the rate of diffusion.
• Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures
According to this law, the resultant pressure exerted by a mixture of non-interacting gases is equal
to the sum of their individual pressures.
i-e., P = P1 + P2 + ————-Pn
• Mean (or average) speed of molecules of a gas is defined as the arithmetic mean of the speeds of gas molecules.
• Root mean square speed of gas molecules is defined as the square root of the mean of the squares of the speeds of gas molecules.
• Most probable speed of gas molecules is defined as the speed which is possessed by maximum number of molecules in a gas
• Kinetic Interpretation of Temperature
The total average kinetic energy of all the molecules of a gas is proportional to its absolute temperature (T). Thus, the temperature of a gas is a measure of the average kinetic energy ‘IT of the molecules of the gas.
U = 3/2 RT
According to this interpretation of temperature, the average kinetic energy U is zero at T = 0, i.e., the motion of molecules ceases altogether at absolute zero.
• Degrees of Freedom
The total number of independent co-ordinates required to specify the position of a molecule or the number of independent modes of motion possible with any molecule is called degree of freedom.
Mono-, di-, and polyatomic (N) molecules have, 3,5 or (3 N-K) number of degrees of freedom where K is the number of constraints [restrictions associated with the structure].
• Law of Equipartition of Energy
For a dynamic system in thermal equilibrium, the energy of the system is equally distributed amongst the various degrees of freedom and the energy associated with each degree of freedom per molecule is 1/2 kT, where k is Boltzman constant.
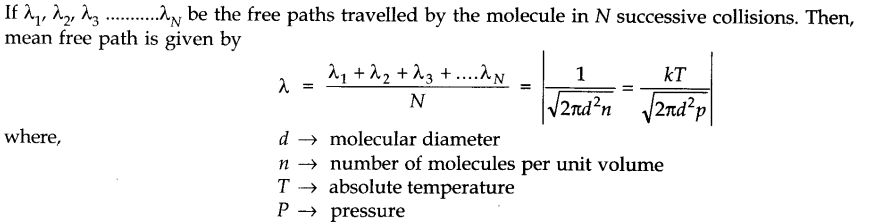
• Mean Free Path
Mean free path of a molecule in a gas is the average distance travelled by the molecule between two successive collisions
(i) Smaller the number of molecules per unit volume of the gas, larger is the mean free path.
(ii) Smaller the diameter, larger is the mean free path.
(iii) Smaller the density, larger is the mean free path. In the case of vacuum, ρ = 0, λ —>∞
(iv) Smaller the pressure of a gas, larger is the mean free path.
(v) Higher the temperature of a gas, larger is the mean free path.
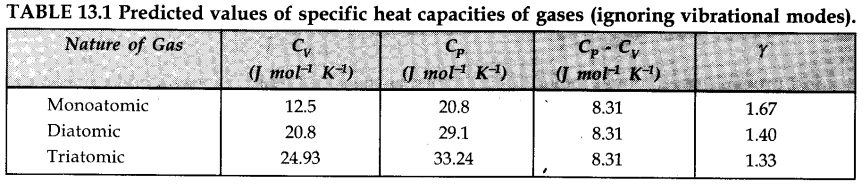
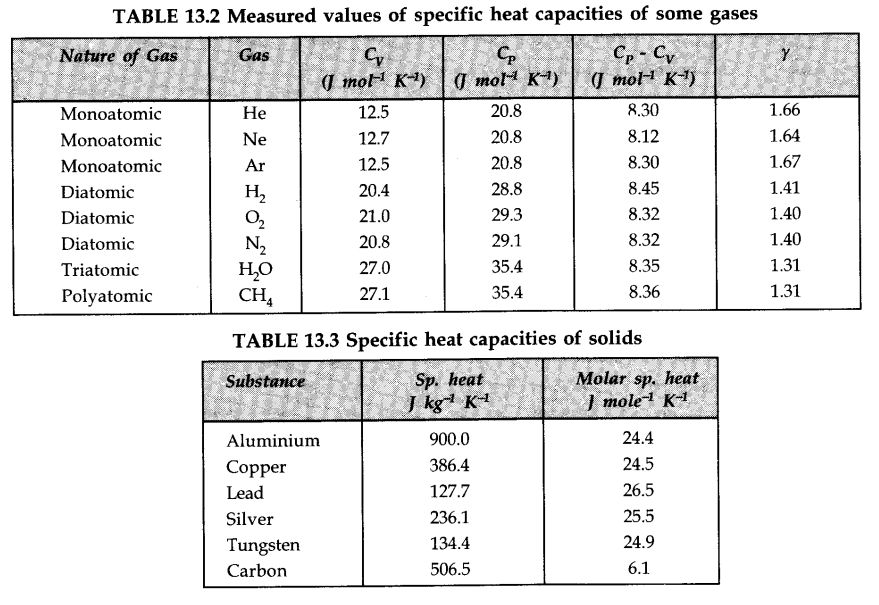
• IMPORTANT TABLES
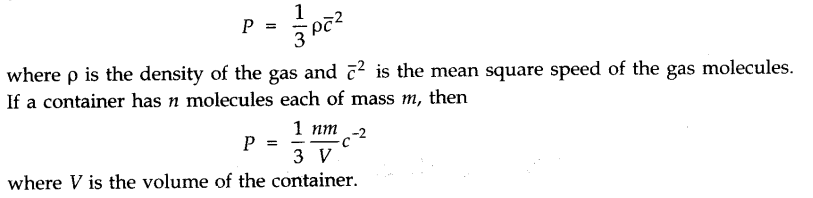
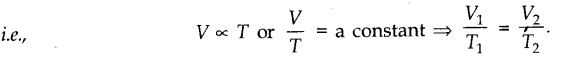
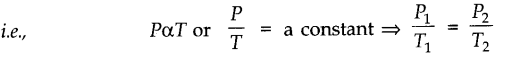
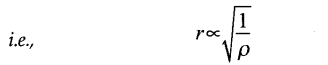
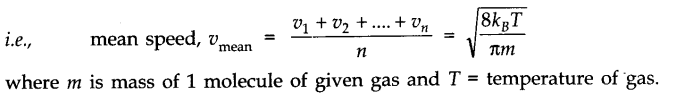
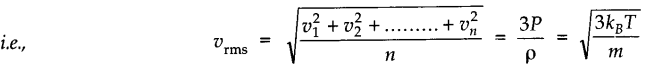


Leave a Reply