Notes For All Chapters Physics Class 11 CBSE
• Motion in a plane is called as motion in two dimensions e.g., projectile motion, circular motion etc. For the analysis of such motion our reference will be made of an origin and two co-ordinate axes X and Y.
• Scalar and Vector Quantities
Scalar Quantities. The physical quantities which are completely specified by their magnitude or size alone are called scalar quantities.
Examples. Length, mass, density, speed, work, etc.
Vector Quantities. Vector quantities are those physical quantities which are characterised by both magnitude and direction.
Examples. Velocity, displacement, acceleration, force, momentum, torque etc.
• Characteristics of Vectors
Following are the characteristics of vectors:
(i) These possess both magnitude and direction.
(ii) These do not obey the ordinary laws of Algebra.
(iii) These change if either magnitude or direction or both change.
(iv) These are represented by bold-faced letters or letters having arrow over them.
• Unit Vector
A unit vector is a vector of unit magnitude and points in a particular direction. It is used to specify the direction only. Unit vector is represented by putting a cap (^) over the quantity.
• Equal Vectors
• Zero Vector
• Negative of a Vector
• Parallel Vectors
• Coplanar Vectors
Vectors are said to be coplanar if they lie in the same plane or they are parallel to the same plane, otherwise they are said to be non-coplanar vectors.
• Displacement Vector
The displacement vector is a vector which gives the position of a point with reference to a point other than the origin of the co-ordinate system.
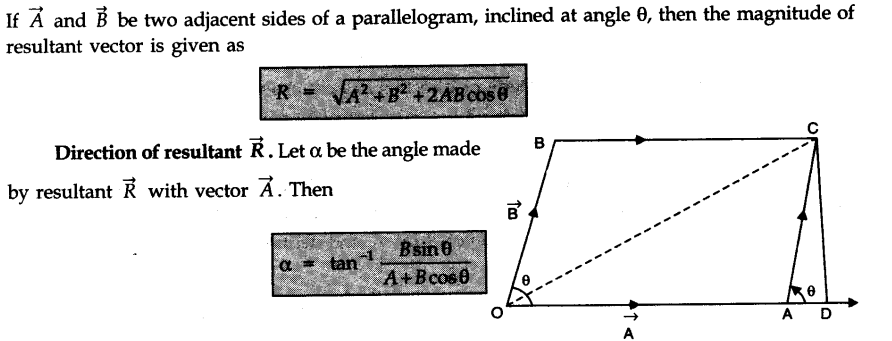
• Parallelogram Law of Vector Addition
If two vectors, acting simultaneously at a point, can be represented both in magnitude and direction by the two adjacent sides of a parallelogram drawn from a point, then the resultant is represented completely both in magnitude and direction by the diagonal of the parallelogram passing through that point.
• Triangle Law of Vector Addition
If two vectors are represented both in magnitude and direction by the two sides of a triangle taken in the same order, then the resultant of these vectors is represented both in magnitude and direction by the third side of the triangle taken in the opposite order.
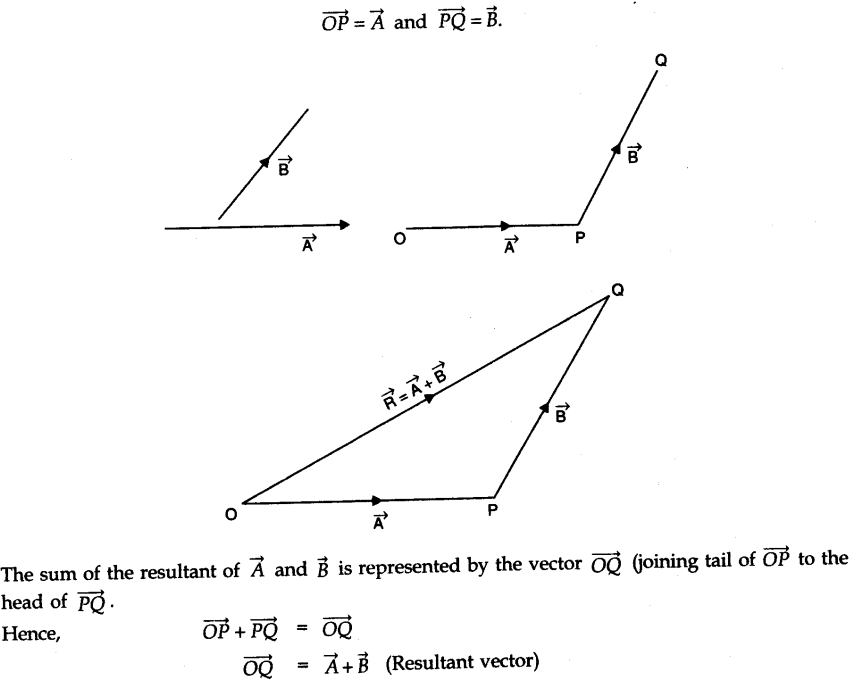
• Polygon Law of Vector Addition
If a number of vectors are represented both in magnitude and direction by the sides of a polygon taken in the same order, then the resultant vector is represented both in magnitude and direction by the closing side of the polygon taken in the opposite order.
• Properties of Vector Addition
Vector addition has following properties:
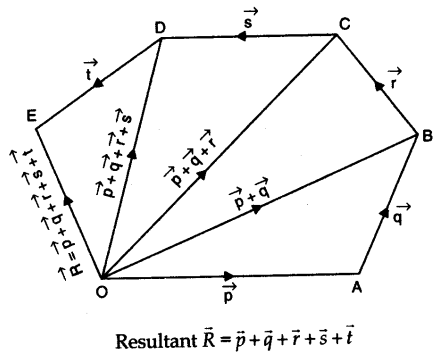
• Resolution of Vectors
It is a process of splitting a single vector into two or more vectors in different directions which together produce the same effect as is produced by the single vector alone.
The vectors into which the given single vector is splitted are called component of vectors. In fact, the resolution of a vector is just opposite to composition of vectors.
If the components of a given vector are perpendicular to each other, then they are called rectangular components.
• Position Vector
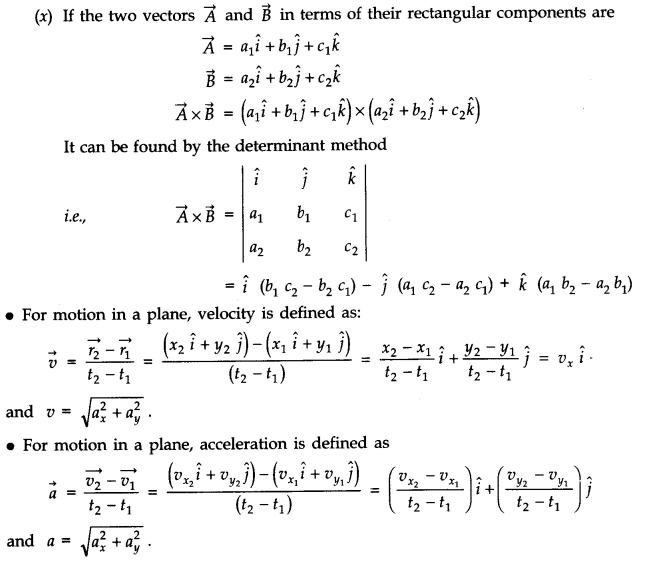
• Multiplication of Vectors
(i) Scalar product (Dot product). Scalar product of two vectors is defined as the product of the magnitude of two vectors with cosine of smaller angle between them.
• Properties of Scalar Product
• Properties of Cross Product
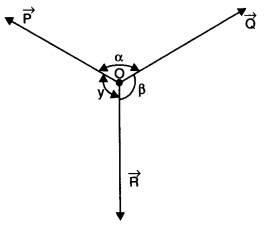
• Lami’s Theorem
Lami’s theorem states, “If a particle under the simultaneous action of three forces is in equilibrium, then each force has a constant ratio with the sine of the angle between the other two forces.”
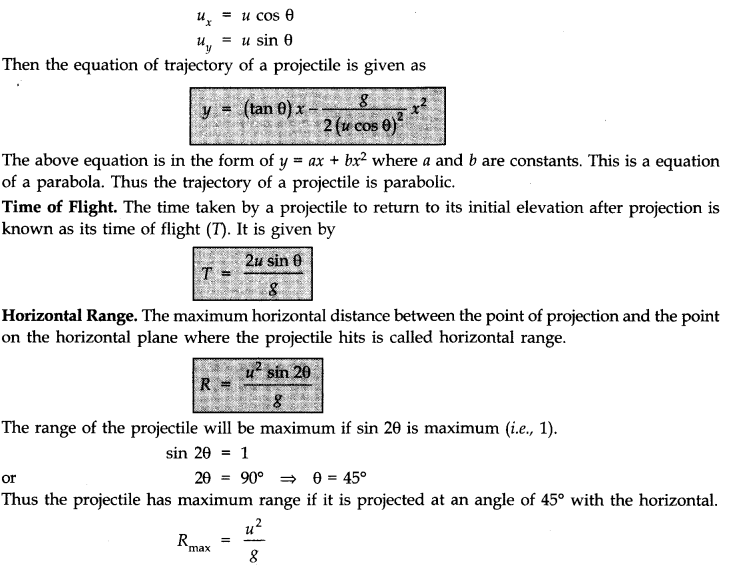
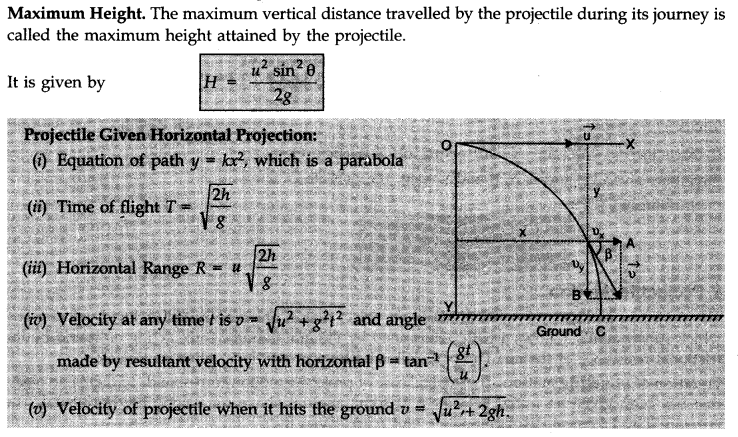
• Projectile Motion
The projectile is a general name given to an object that is given an initial inclined velocity and which subsequently follows a path determined by the gravitational force acting on it and by the frictional resistance of the air. The path followed by a projectile is called its trajectory.
Equation of projectile motion. The general case of projectile motion corresponds to that of an object that has been given an initial velocity u at some angle 8 above (or below) the horizontal. The horizontal and vertical displacements x and y are given by
• Angular Displacement
Angular displacement of the object moving around a circular path is defined as the angle traced out by the radius vector at the centre of the circular path in a given time.
θ (angle) = arc/radius
θ —> the magnitude of angular displacement. It is expressed in radians (rad).
• Angular Velocity
Angular velocity of an object in circular motion is defined as the time rate of change of its angular displacement.
• Angular Acceleration
Angular acceleration of an object in circular motion is defined as the time rate of change of its angular velocity.
• Uniform Circular Motion
When a body moves in a circular path with a constant speed, then the motion of the body is known as uniform circular motion.
The time taken by the object to complete one revolution on its circular path is called time period. For circular motion, the number of revolutions completed per unit time is known as the frequency (v). Unit of frequency is 1 Hertz (1 Hz). It is found that
• Centripetal Acceleration
To maintain a particle in its uniform circular motion a radially inward acceleration should be continuously maintained. It is known as the centripetal acceleration.
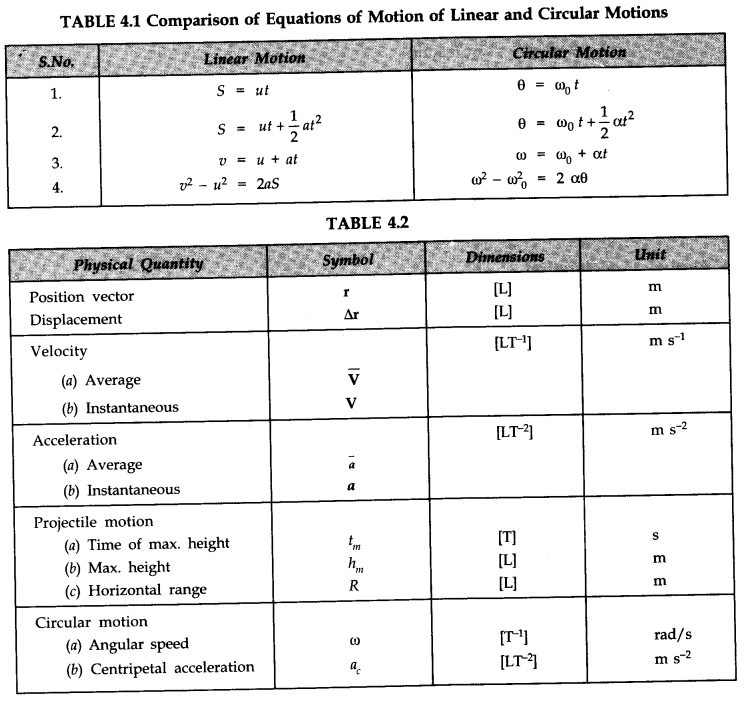
• IMPORTANT TABLES
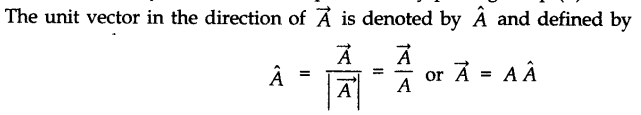
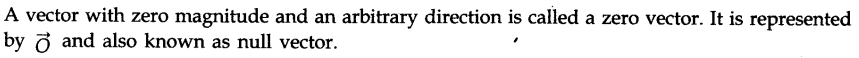
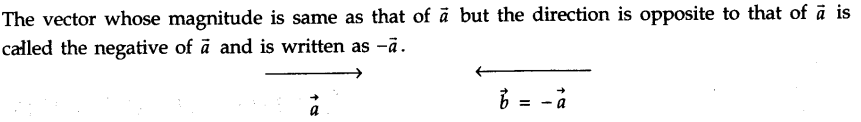

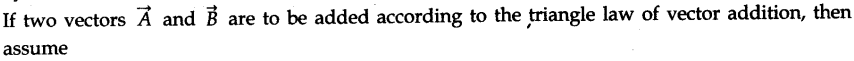





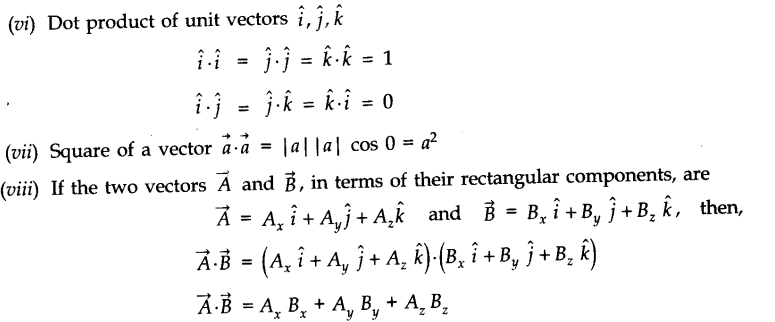
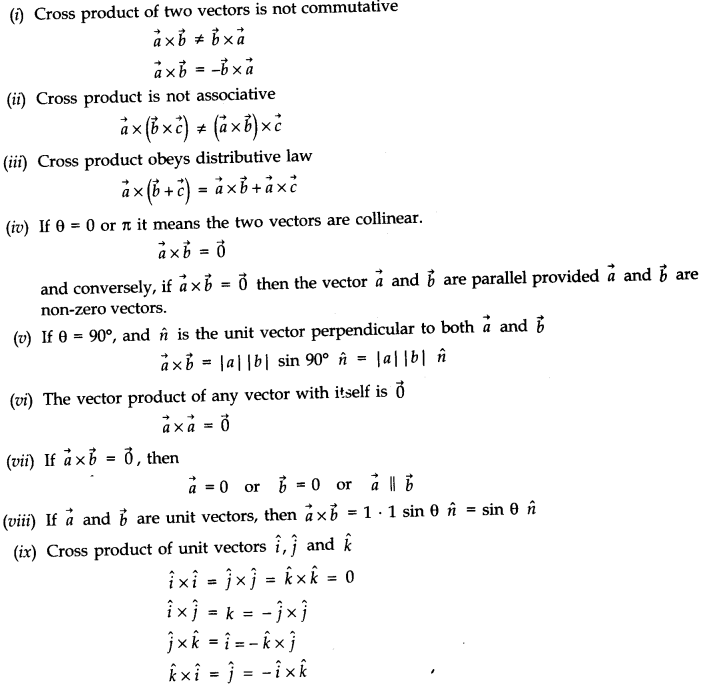
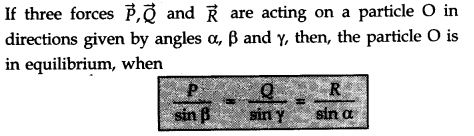
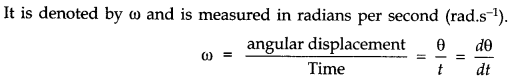
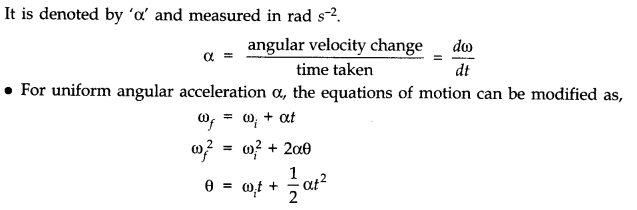
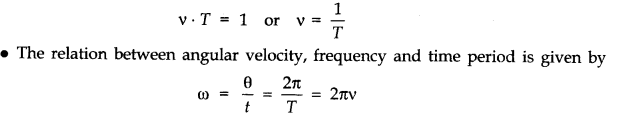
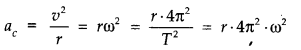

Leave a Reply