Notes For All Chapters Physics Class 11 CBSE
• Periodic Motion
Motions, processes or phenomena, which repeat themselves at regular intervals, are called periodic.
• Oscillatory Motion
The motion of a body is said to be oscillatory motion if it moves to and fro about a fixed point after regular intervals of time. The fixed point about which the body oscillates is called mean position or equilibrium position.
• Simple Harmonic Motion
Simple harmonic motion is a special type of periodic oscillatory motion in which
(i) The particle oscillates on a straight line
(ii) The acceleration of the particle is always directed towards a fixed point on the line.
(iii) The magnitude of acceleration is proportional to the displacement of the particle from the
• Characteristics of SHM
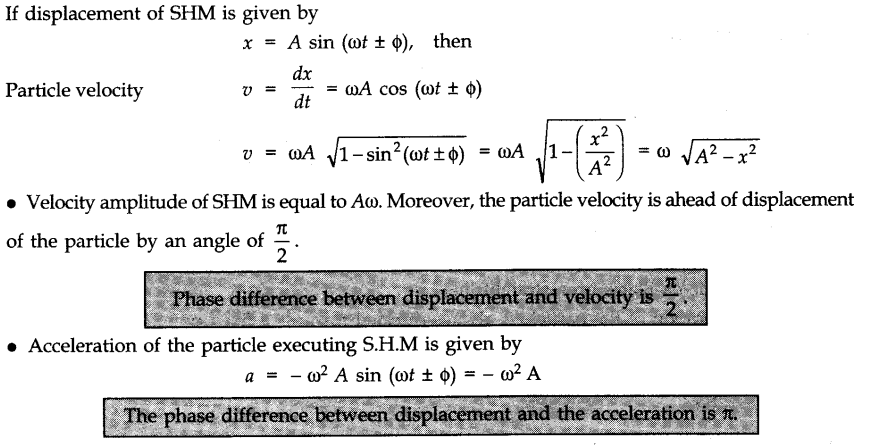
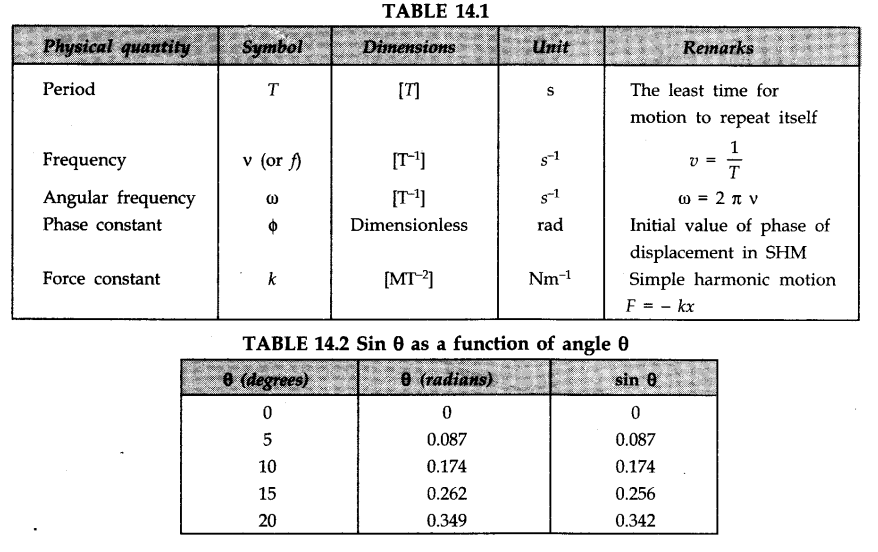
The displacement x in SHM at time t is given by
x = A sin (ωt+ Ф )
where the three constants A, ω and Ф characterize the SHM, i.e., they distinguish one SHM from another. A SHM can also be described by a cosine function as follows:
x = A cos (ωt + δ)
• The displacement of an oscillating particle at any instant is equal to the change in its position vector during that time. The maximum value of displacement in an oscillatory motion on either side of its mean position is called “displacement amplitude” or “simple amplitude”.
Thus, amplitude A = x max.
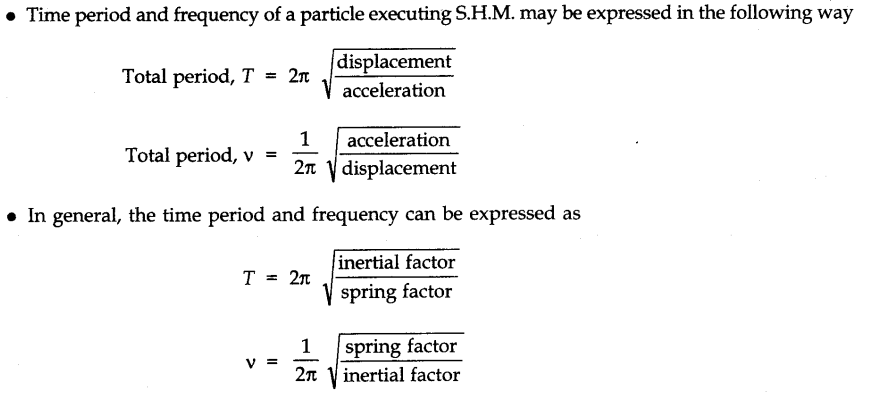
• The time taken by an oscillating particle to complete one full oscillation to and fro about its mean (equilibrium) position is called the “time period” of SHM. It is given by
• Frequency
The number of oscillations in one second is called frequency. It is expressed in sec-1 or Hertz. Frequency and time period are independent of amplitude.
• Phase
The quantity (ωt+ Ф) is called the phase of SHM at time t; it describes the state of motion at that instant. The quantity Ф is the phase at time f = 0 and is called the phase constant or initial phase or epoch of the SHM. The phase constant is the time-independent term in the cosine or sine function.
• The force responsible for maintaining the S.H.M. is called restoring force.
If the displacement (x) from the equilibrium position is small, the restoring force (F) acting on the body is given by
F = -kx
where k is a force constant.
• Energy in S.H.M.
When a body executes SHM, its energy changes between kinetic and potential, but the total energy is always constant. At any displacement x from the equilibrium position:
• Springs in Series
If two springs, having spring constant k1 and k2, are joined in series, the spring constant of the combination is given by
• Springs in Parallel
If two springs, having spring constants k1 and k2, are joined in parallel, the spring constant of the combination is given by
k = k1 + k2
• When one spring is attached to two masses m1 and m2, then
• Simple Pendulum
A simple pendulum is the most common example of bodies executing S.H.M. An ideal simple pendulum consists of a heavy point mass body suspended by a weightless in extensible and perfectly flexible string from a rigid support about which it is free to oscillate.
• The time period of simple pendulum of length ‘l’ is given by
The time period of a simple pendulum depends on
(i) length of the pendulum and
(ii) the acceleration due to gravity (g).
• A second’s pendulum is a pendulum whose time period is. 2s. At a place where g = 9.8 ms-2, the length of a second’s pendulum is found to be 99.3 cm (= 1 m).
• If a liquid of density p oscillates in a vertical U-tube of uniform cross sectional area A, then the time period of oscillation is given by
• If a cylinder of mass m, length L, density of material p and uniform area of cross section A, oscillates vertically in a liquid of density o, then the time period of oscillation is given by
• Undamped and Damped Simple Harmonic Oscillations
Undamped Simple Harmonic oscillations: When a simple harmonic system oscillates with a constant amplitude which does not change with time, its oscillations are called undamped simple harmonic oscillations.
Damped Simple Harmonic oscillations: When a simple harmonic system oscillates with a decreasing amplitude with time, its oscillations are called damped simple harmonic oscillations.
The angular frequency of the damped oscillator is given by
• A system is said to execute free oscillations, if on being displaced or disturbed from its position of equilibrium, it oscillates itself without outside interference.
When a system is compelled to oscillate with a frequency other than its natural frequency, it is said to execute forced oscillations.
The external force which causes forced oscillation, is of sinusoidal nature. It is given as
• Resonance is the phenomenon of setting a body into oscillations with large amplitude under the influence of some external periodic force whose frequency is exactly equal to the natural frequency of the given body. Such oscillations are called the “resonant oscillations”.
• The two or more oscillations linked together in such a way that the exchange of energy takes place between them are called coupled oscillators. The oscillations produced by coupled oscillators are known as coupled oscillations.
• The speed of a mechanic wave depends upon the properties of the medium in which it is travelling. If E is the elastic constant and ρ is the density of the medium then the speed of the wave is given by
• In case of electric magnetic waves, we know that they are the combinations of the oscillation of electric and magnetic fields in perpendicular directions. Their speed of propagation depends upon the permitivity and the permeability of the medium. If μ0 is permeability and ε0 is the permitivity of the medium in vaccum, then
• IMPORTANT TABLES
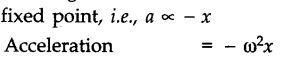

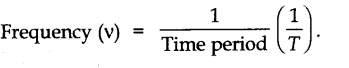
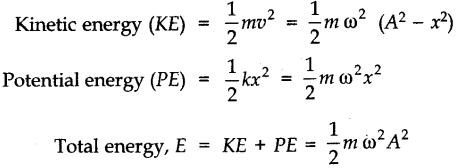
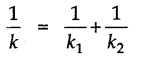
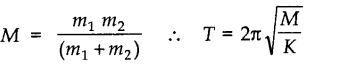
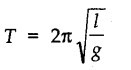
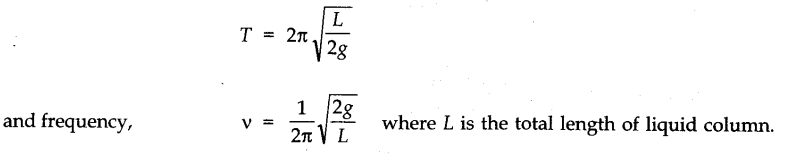
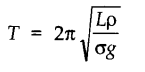

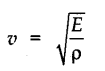
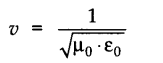

Leave a Reply