Notes For All Chapters Physics Class 11
Science
Science is a systematic and organised attempt to acquire knowledge about the surroundings through observations, experiments and verifications.
Scientific Method
Several inter-related steps are involved in scientific method. Some of the most significant steps are as follows:
1. The systematic observations
2. Reasoning
3. Mathematical modelling
4. Theoretical prediction
Physics
Physics is a fundamental science concerned with understanding the natural phenomena that occur in our universe.
It has many branches such as Mechanics, Electromagnetism, Thermodynamics, Modem Physics, etc. Between 1600 and 1900, three broad areas were developed, which is together called Classical Physics. These three areas of study are classical mechanics, thermodynamics and electromagnetism. But by 1905 it became apparent that classical ideas failed to explain several phenomena. Then some new theories were developed in what is called Modem Physics such as Special Relativity, Quantum Mechanics, etc.
Scope and Excitement of Physics
The scope of Physics is very broad and covers a wide range of magnitude of physical quantities such as length, mass, time, energy, etc.
It deals with the macroscopic world like galaxies and universe as well as microscopic world like nucleus of an atom and fundamental particles like electrons, protons, neutrons etc.
Immense excitement is involved in the study of physics since it explains every naturally occuring phenomena with a set of rules, so that clear understanding can be achieved. The challenge to carry out imaginative new experiments to unlock the secrets of nature, to verify or refute theories, is really exciting.
Physics in Relation to Other Sciences
Physics is a very significant branch of science which plays a crucial role in understanding the developments pertaining to the other branches of science such as Chemistry, Biology etc.
(i) Physics in relation to Mathematics. Study of physical variables led to the idea of differentiation, integration and differential equation. Meaningful interpretation of Mathematics becomes Physics.
(ii) Physics in relation to Chemistry. The concept of X-ray diffraction and radioactivity has helped to distinguish between the various solids and to modify the periodic table.
Understanding the bonding and the chemical structure of substances is easy with the help of the concept of interactions between various particles.
(iii) Physics in relation to Astronomy. Optical telescopes of reflecting and refracting type enabled man to explore the space around. Discoveries like radio telescopes have revolutionised the study of Astronomy.
(iv) Physics in relation to Biology. The conceptual study of pressure and its measurement has helped us to know blood pressure and hence the functioning of heart. Invention of X-rays developed the field of diagnosis. Electron and optical microscopic designs have revolutionised the study of medical science.
(v) Physics in relation to Meteorology. The discoveries regarding the study of pressure variations help us to forecast the weather.
Various other inventions of physics have opened new vistas of study in the field of sciences and social sciences.
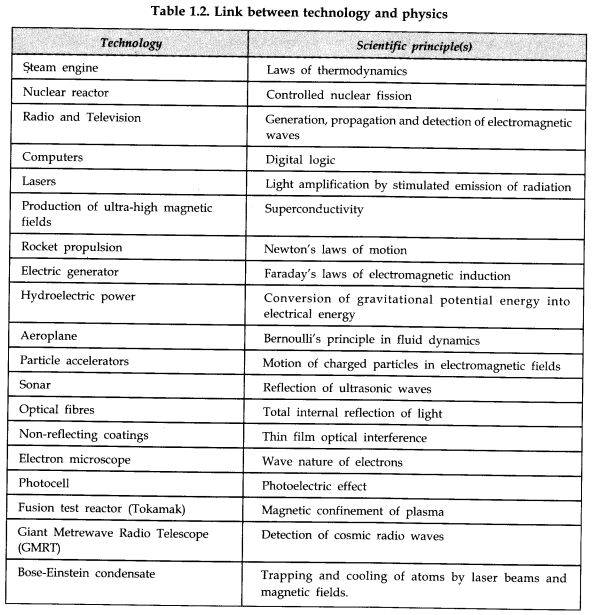
Physics in Relation to Technology and Society
Advancement in physics has led to new technologies and vice-versa. Sometimes technology gives rise to new dimension of physics; at other times physics generates new technology. In fact, the technological development is closely related to the application of science and physics in particular. Physics has a dominant influence on society. It has helped the human being to develop its ideas. Development of digital communication systems, rapid mass transport system, lasers making bloodless surgeries, etc., has made human life easy and pleasant.
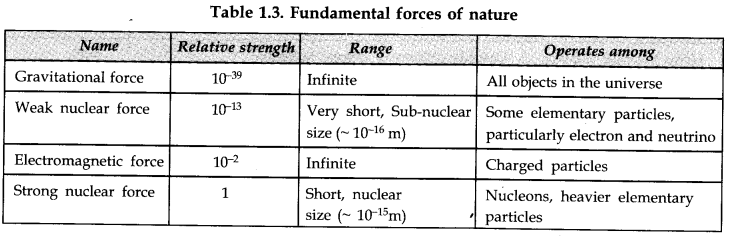
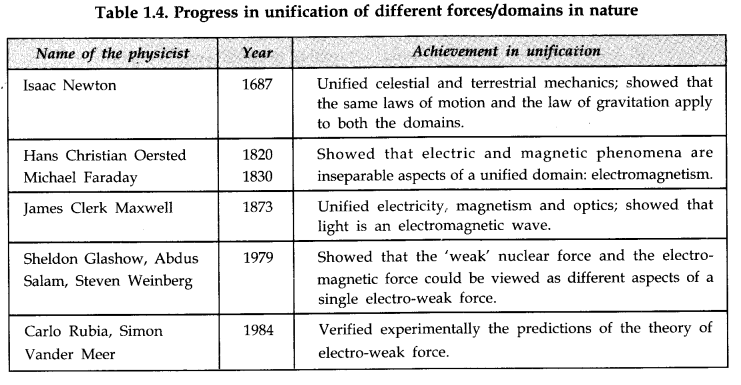
1. There are four fundamental forces in nature that govern the diverse phenomena of the microscopic and macroscopic world. These are the ‘gravitational force’, the ‘electromagnetic force’; the ‘strong nuclear force’, and the ‘weak nuclear force’. Unification of forces is a basic quest in physics. The electromagnetic and the weak nuclear forces have now been unified and are seen as aspects of a single ‘electro-weak’ force. Attempts are being made to unify electro-weak and the strong force.
2. Conservation of energy, momentum, angular momentum, charge, etc., are considered to be the fundamental laws in physics. Conservation laws have a deep connection with symmetries of nature. Symmetries of space and time, and other types of symmetries play a central role in modem theories of fundamental forces in nature.
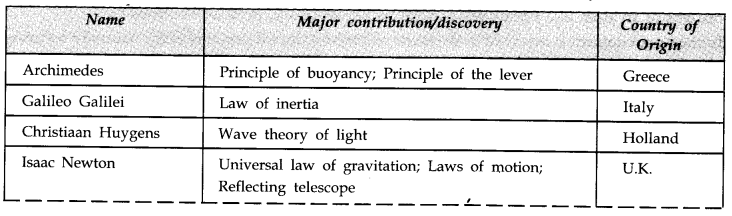
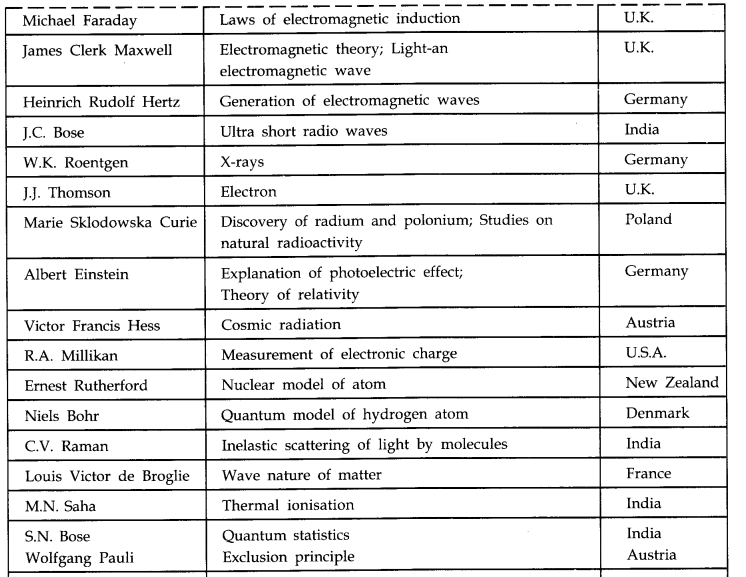
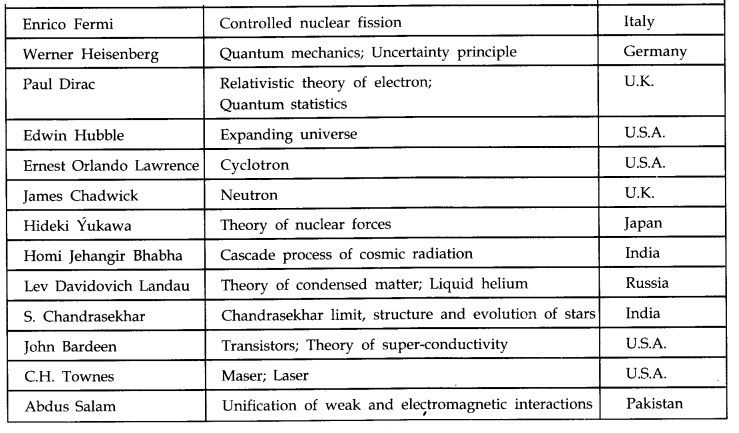
IMPORTANT TABLES
Table 1.1 Some Physicists from Different Countries of the World and their Major Contributions

Leave a Reply