Notes For All Chapters Physics Class 11 CBSE
• A rigid body is a body with a perfectly definite and unchanging shape. The distances between all pairs of particles of such a body do not change.
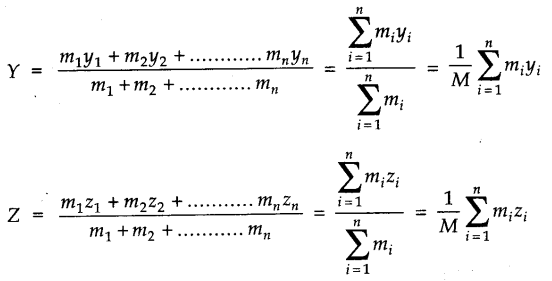
• Centre of Mass
For a system of particles, the centre of mass is defined as that point where the entire mass of the system is imagined to be concentrated, for consideration of its translational motion.
If all the external forces acting on the body/system of bodies were to be applied at the centre of mass, the state of rest/ motion of the body/system of bodies shall remain unaffected.
• The centre of mass of a body or a system is its balancing point. The centre of mass of a two- particle system always lies on the line joining the two particles and is somewhere in between the particles.
• Motion of centre of Mass
The centre of mass of a system of particles moves as if the entire mass of the system were concentrated at the centre of mass and all the external forces were applied at that point. Velocity of centre of mass of a system of two particles, m1 and m2 with velocity v1 and v2 is given
by,
• If no external force acts on the body, then the centre of mass will have constant momentum. Its velocity is constant and acceleration is zero, i.e., MVcm = constant.
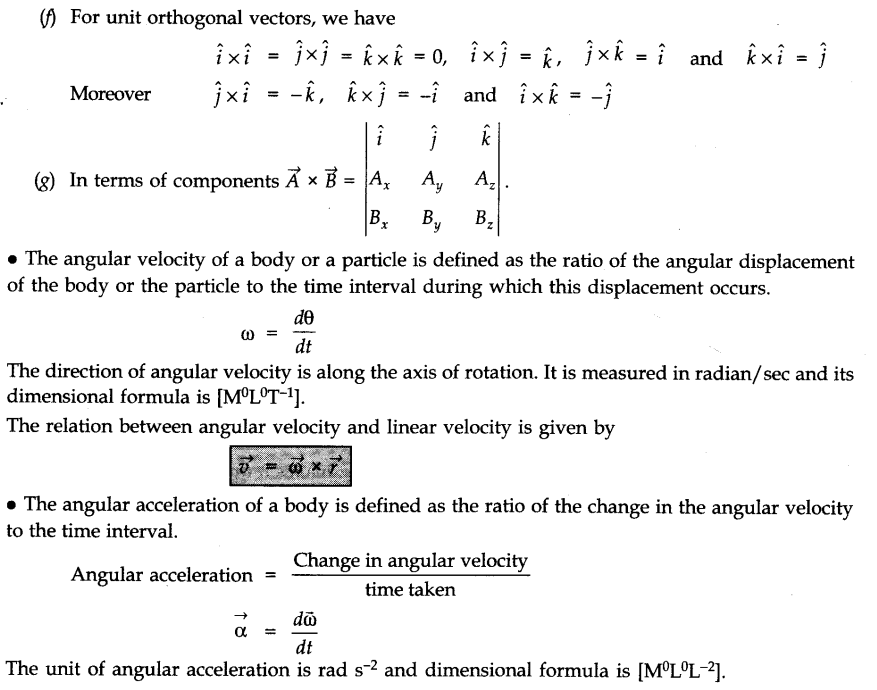
• Vector Product or Cross Product of two vectors
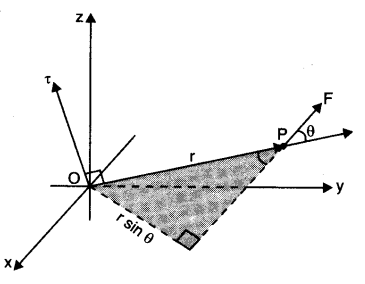
• Torque
Torque is the moment of force. Torque acting on a particle is defined as the product of the magnitude of the force acting on the particle and the perpendicular distance of the application of force from the axis of rotation of the particle.
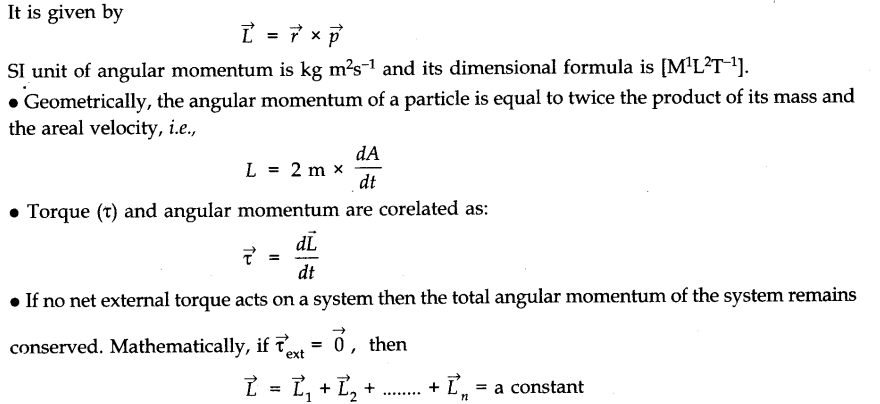
• Angular Momentum
The angular momentum (or moment of momentum) about an axis of rotation is a vector quantity, whose magnitude is equal to the product of the magnitude of momentum and the perpendicular distance of the line of action of momentum from the axis of rotation and its direction is perpendicular to the plane containing the momentum and the perpendicular distance.
• Axis of Rotation
A rigid body is said to be rotating if every point mass that makes it up, describes a circular path of a different radius but the same angular speed. The circular paths of all the point masses have a common centre. A line passing through this common centre is the axis of rotation.
• A rigid body is said to be in equilibrium if under the action of forces/torques, the body remains in its position of rest or of uniform motion.
For translational equilibrium, the vector sum of all the forces acting on a body must be zero. For rotational equilibrium, the vector sum of torques of all the forces acting on that body about the reference point must be zero. For complete equilibrium, both these conditions must be fulfilled.
• Couple
Two equal and opposite forces acting on a body but having different lines of action, form a couple. The net force due to a couple is zero, but they exert a torque and produce rotational motion.
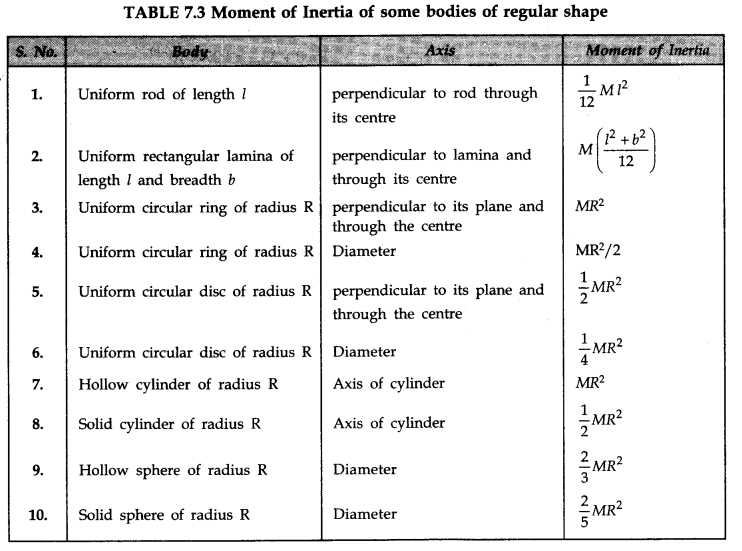
• Moment of Inertia
The rotational inertia of a rigid body is referred to as its moment of inertia.
The moment of inertia of a body about an axis is defined as the sum of the products of the masses of the particles constituting the body and the square of their respective perpendicular distance from the axis.
It is given by .
• Radius of Gyration
The distance of a point in a body from the axis of rotation, at which if whole of the mass of the body were supposed to be concentrated, its moment of inertia about the axis of rotation would be the same as that determined by the actual distribution of mass of the body is called radius of gyration.
If we consider that the whole mass of the body is concentrated at a distance K from the axis of rotation, then moment of inertia I can be expressed as I = MK2
• Theorem of Parallel Axes
According to this theorem, the moment of inertia I of a body about any axis is equal to its moment of inertia about a parallel axis through centre of mass, Icm, plus Ma2 where M is the mass of the body and V is the perpendicular distance between the axes, i.e.,
I = Icm + Ma2
• Theorem of Perpendicular Axes
According to this theorem, the moment of inertia I of the body about a perpendicular axis is equal to the sum of moments of inertia of the body about two axes at right angles to each other in the plane of the body and intersecting at a point where the perpendicular axis passes, i.e.,
• Rolling Motion
The combination of rotational motion and the translational motion of a rigid body is known as rolling motion.
• Law of Conservation of Angular Momentum
According to the law of conservation of angular momentum, if there is no external couple acting, the total angular momentum of a rigid body or a system of particles is conserved.
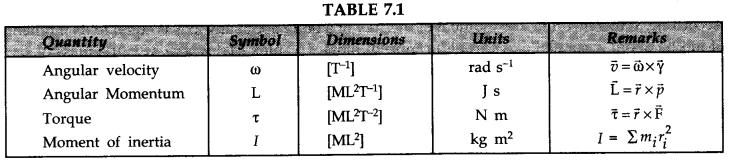
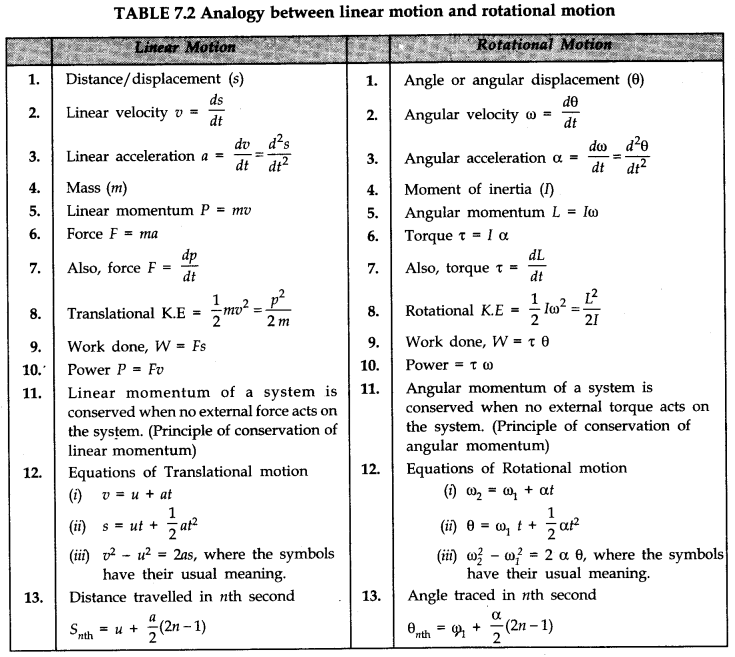
• IMPORTANT TABLES

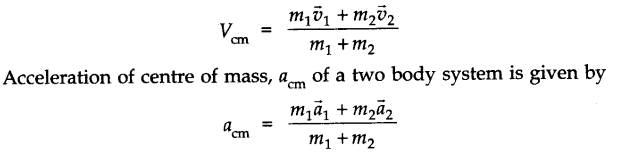



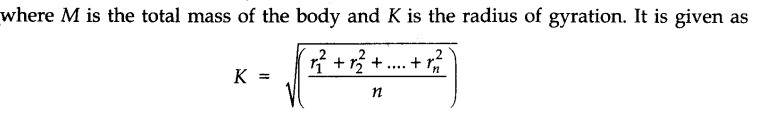


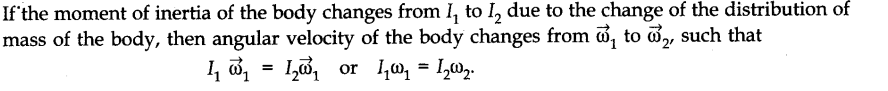

Leave a Reply