Notes For All Chapters Science Class 6
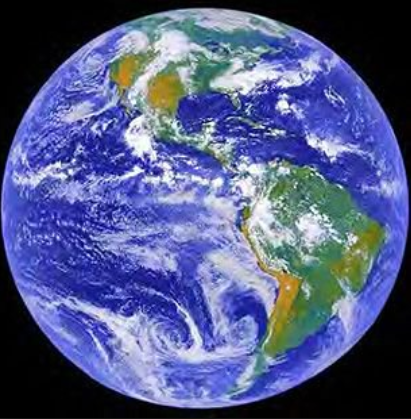
Introduction: It is common knowledge that water is important on our Earth and without water, life as we know it would cease to exist. While Earth has an abundant reservoir of water, covering three-fourths of its surface, Freshwater is a mere 2.6% of the total water. Water is said to be a renewable resource but the rate at which humans and animals are using water, fresh water might be a scarce resource in the recent future. Our body is also made up of 70% water and we use water for a number of reasons from cooking to cleaning and of course drinking it. A lot of experts predict that the next World War will be fought over water!
Figure 1 Two-thirds of Earth’s surface covered with water
Where does water come from?
People living in different regions have different sources of the water that they use. While some draw it from wells, ponds and lakes directly, others like many of us receive water through taps via a network of pipes connected to these lakes, ponds and rivers.
Water Cycle
To know how these rivers get their water from we need to study a little about the water cycle and the processes of evaporation and condensation.
Evaporation: The process of conversion of water into its gaseous state i.e. vapours is known as evaporation.
Condensation: The process of conversion of vapours into water is referred to as condensation.
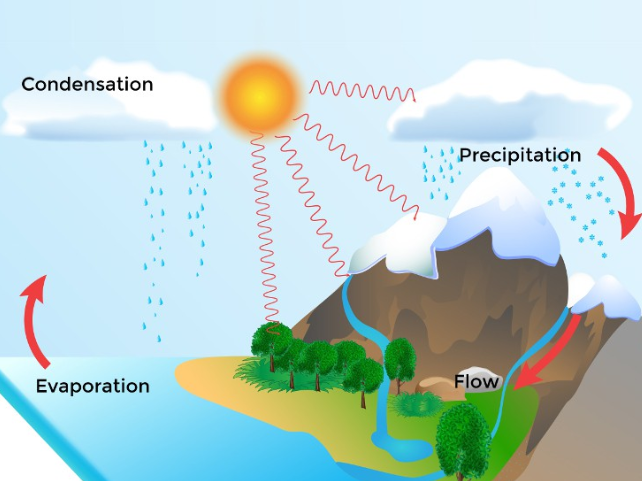
Water cycle can be defined as the process through which water gets evaporated from open surfaces like oceans and seas, gets condensed as it rises in the cool atmosphere and ultimately pours down as rain (precipitation) back into oceans, lakes, rivers and ponds.
Figure 2 Water cycle
Transpiration: The process of evaporation of water from the surface of the leaves into the atmosphere is defined as the process of transpiration. In this manner, plants also contribute to the water cycle.
It is through the process of water cycle that we are able to make use of the ocean water. Ocean water is saline in nature and hence cannot be used directly. When it gets evaporated, it leaves behind the salts and forms clouds.
As the warm air from these surfaces rises into the cold air of the atmosphere, saturation and condensation occur to form tiny droplets of water which result in cloud formation.
These clouds then lead to rainfall and snow which deposit in lakes, wells and ponds is then used by us to satisfy our needs. Apart of this rainwater gets absorbed by the soil, some of it gets evaporated while the rest seeps in the ground and becomes another source of water for us in the form of groundwater. Handpumps, wells and even lakes draw water from groundwater. The water cycle is a continuous process.
Excess v/s deficient rainfall
Intensity and duration of rain vary in different regions across the country. While rainfall is very important for irrigation and the continuous availability of water, excess rainfall can pose a number of problems. Due to excess rainfall, the water level of rivers and oceans rises which can potentially spread and submerge nearby cities and villages which poses a grave danger to both life and property. These are known as floods.
Figure 3 Floods posing danger to property and life
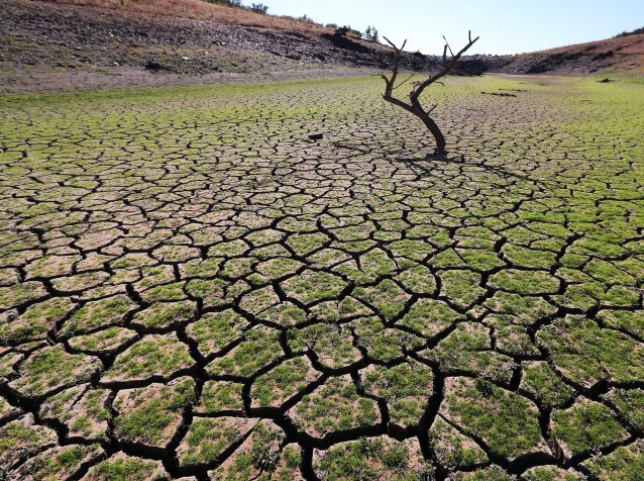
Similarly, deficient rainfall can also prove to be life-threatening. A lot of farmers in India continue to depend on rainfall to irrigate their fields. In case of deficient rain, soil and wells still continue to lose water through transpiration and evaporation and if it doesn’t rain for a prolonged period, fields can dry up because even the groundwater does not get replenished. These are known as droughts.
Figure 4 Dried fields as a result of droughts
Conservation of water
There are a number of reasons why water conservation needs to be a priority for everyone. Here are some of them:
(i) Mostly all water is in the oceans in saline form and can’t be used directly
(ii) While the total water on Earth does not change, but the water available for us to use diminishes with overuse
(iii) When the groundwater goes below drastically, it cannot be accessed anymore
(iv) Water is required in industries and for production of food
(v) The population growth is exponential but the water sources are only depleting
Figure 5 A few tips to help save water
Rainwater Harvesting
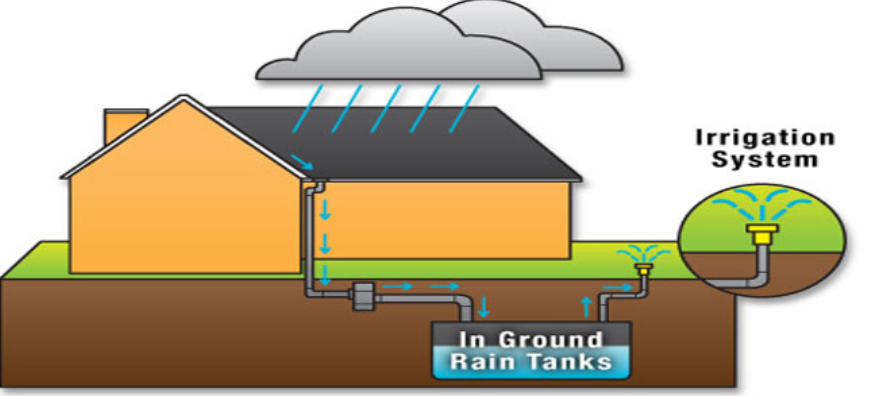
Rainwater does not always fall on soil or water sources; in fact, much of it falls on rooftops of houses and concrete roads and thus does not become a part of groundwater. Hence, a very important method has been devised to harvest rainwater so that it can be stored for future use:
Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting – In this method, rainwater that falls on rooftops is allowed to pass in a storage tank through pipes. This water might be dirty and hence not fit for direct use; hence it can be allowed to seep directly into the ground with the help of pipes.
Figure 6 Rainwater harvesting




Leave a Reply