Notes For All Chapters – Science Curiosity Class 6
Measurement of Length and Motion
How do we Measure?
- In ancient times, people measured lengths using body parts (e.g., handspan, foot).
- However, body-based measurements are not consistent, as body sizes vary.
Standard Units of Measurement
- To avoid confusion, standard units were introduced globally (SI units).
SI unit of length: metre (m).
- 1 metre = 100 centimetres (cm).
- 1 cm = 10 millimetres (mm).
- For larger distances: 1 kilometre (km) = 1000 metres.
Correct Way of Measuring Length
- Use the appropriate scale for the object (e.g., a 15 cm scale for small objects, measuring tape for larger ones).
Key points:
- Place the scale correctly along the object.
- Your eye must be positioned directly above the scale.
- If the scale is broken, start from another mark and subtract the readings.
Measuring Curved Lines
- Curved lines can be measured using a thread. Measure the thread’s length with a ruler.
Describing Position
- A reference point is needed to describe the position of an object.
- Example: Kilometre stones show the distance from a city.
Motion
- An object is in motion if its position changes with time relative to a reference point. Otherwise, it is at rest.
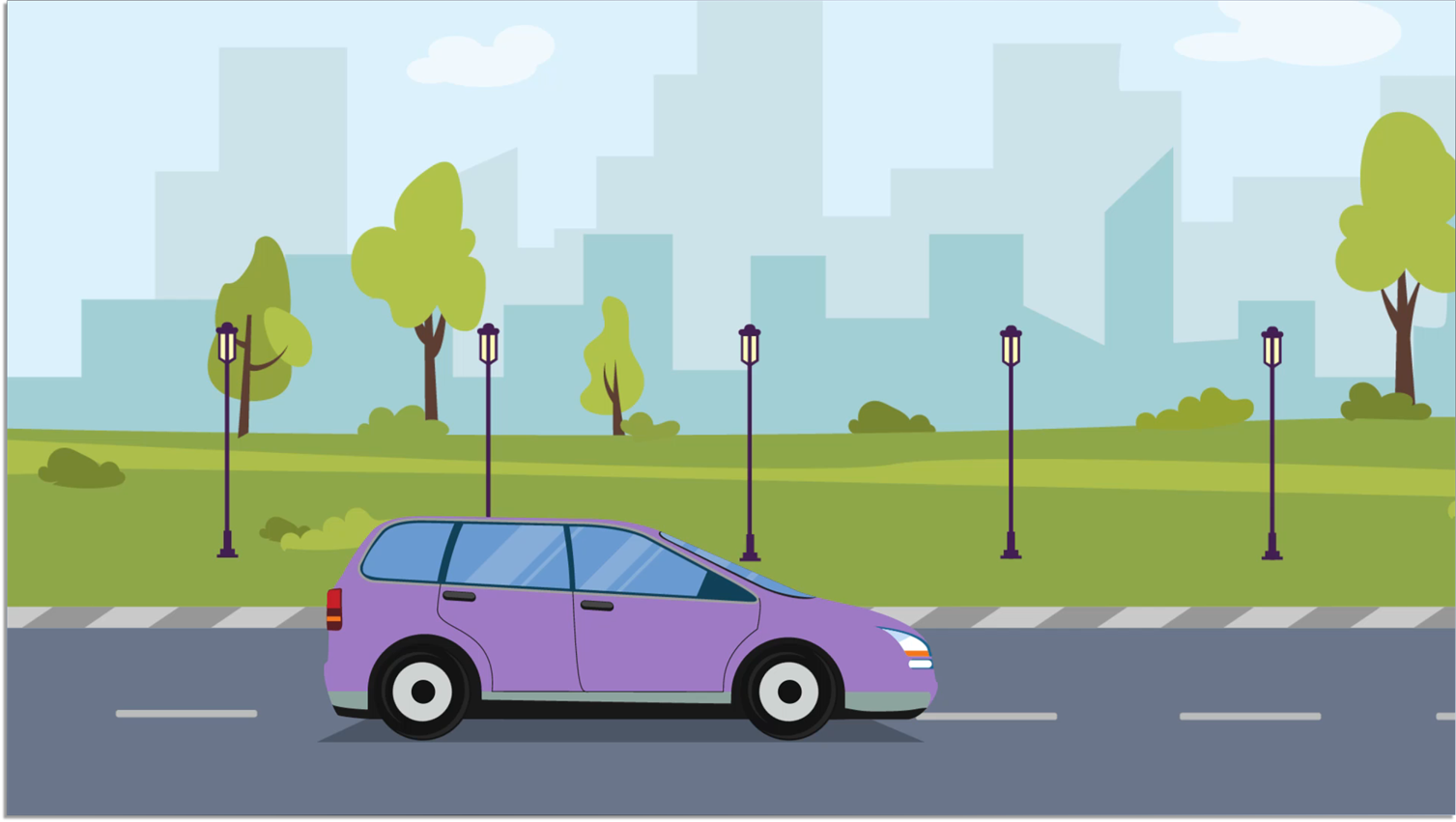
- Example: A car moving on a road is in motion.
Types of Motion
- Linear Motion: Movement along a straight path (e.g., car moving on a straight road).
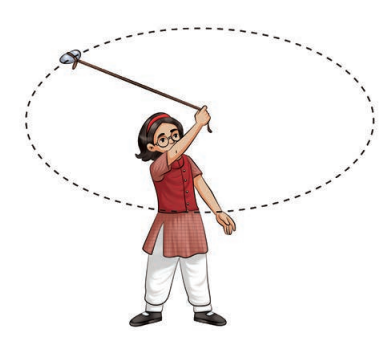
- Circular Motion: Movement along a circular path (e.g., a merry-go-round).
- Oscillatory Motion: Movement to and fro around a fixed point (e.g., a swing).
Key Formulas
- 1 km = 1000 m
- 1 m = 100 cm
- 1 cm = 10 mm
Practical Activities
- Measure everyday objects (e.g., pencil, notebook) using appropriate scales.
- Identify linear, circular, and oscillatory motions in your surroundings (e.g., swing, clock hands).




Very good
Nice
nice