Solutions For All Chapters Maths Class 6
Ex 10.3 Class 6 Maths Question 1.
Find the areas of the rectangles whose sides are:
(a) 3 cm and 4 cm
(b) 12 m and 21 m
(c) 2 km and 3 km
(d) 2 m and 70 cm
Solution:
(a) Length of the rectangle = 3 cm
Breadth of the rectangle = 4 cm
∴ Area of the rectangle = length x breadth = 3 cm x 4 cm
= 12 cm² or 12 sq cm
(b) Length of the rectangle = 12 m and breadth = 21 m
∴ Area of the rectangle = length x breadth = 12 m x 21 m
= 252 m² or 252 sq m
(c) Length of the rectangle = 2 km and breadth 3 km
∴ Area of the rectangle = length x breadth = 2 km x 3 km
= 6 km² or 6 sq km
(d) Length of the rectangle = 2 m
and breadth = 70 cm or 0.70 m
∴ Area of the rectangle = length x breadth = 2 m x 0.70 m
= 1.40 m² or 1.40 sq m
Ex 10.3 Class 6 Maths Question 2.
Find the areas of the squares whose sides are:
(a) 10 cm
(b) 14 cm
(c) 5 m
Solution:
(a) Side of the square = 10 cm
∴ Area of the square = Side x Side = 10 cm x 10 cm = 100 cm² or 100 sq cm
(b) Side of the square = 14 cm
∴ Area of the square = Side x Side = 14 cm x 14 cm = 196 cm² or 196 sq cm
(c) Side of the square = 5 m
∴ Area of the square = Side x Side = 5 m x 5 m = 25 m² or 25 sq m
Ex 10.3 Class 6 Maths Question 3.
The length and breadth of three rectangles are as given below:
(a) 9 m and 6 m
(b) 17 m and 3 m
(c) 4 m and 14 m
Which one has the largest area and which one has the smallest?
Solution:
(a) Length of the rectangle = 9 m
and breadth = 6 m
∴ Area of the rectangle = length x breadth
= 9 m x 6 m
= 54 m² or 54 sq m
(b) Length of the rectangle = 17 m
and breadth = 3m
∴ Area of the rectangle
= length x breadth = 17 m x 3 m 51 m² or 51 sq m
(c) Length of the rectangle = 4 m
and breadth = 14 m
Area of the rectangle = length x breadth
= 4 m x 14 m
= 56 m² or 56 sq m
Rectangle (c) has the largest area, i.e., 56 sq m and Rectangle (b) has the smallest area, i.e., 51 sq m.
Ex 10.3 Class 6 Maths Question 4.
The area of a rectangular garden 50 m long is 300 sq m. Find the width of the garden.
Solution:
Length of the rectangular garden = 50 m
Area of the rectangular garden = 300 sq m
∴ Width = Area ÷ Length
= 300 sq m ÷ 50 m = 6 m
Hence width of the garden = 6 m.
Ex 10.3 Class 6 Maths Question 5.
What is the cost of tiling a rectangular plot of land 500 m long and 200 m wide at the rate of ₹8 per hundred sq m?
Solution:
Length of the rectangular plot = 500 m
and the breadth = 200 m
∴ Area of the plot = length x breadth = 500 m x 200 m = 100000 sq m
Now rate of tiling the plot = ₹8 per 100 sq m
Cost of tiling the garden = ₹( 8/100 x 100000 ) = ₹8000
Hence the required cost = ₹8000
Ex 10.3 Class 6 Maths Question 6.
A table-top measures 2 m by 1 m 50 cm. What is its area in square metres?
Solution:
Length of the table-top = 2 m
and its breadth = 1 m 50 cm or 1.50 m
∴ Area of the table-top = length x breadth
= 2 m x 1.50 m
= 3 m² or 3 sq m
Hence, the area of table-top = 3 sq m.
Ex 10.3 Class 6 Maths Question 7.
A room is 4 m long and 3 m 50 cm wide. How many square metres of carpet is needed to cover the floor of the room?
Solution:
Length of the room = 4 m
and its breadth = 3 m 50 cm = 3.5 m
Area of the room = length x breadth
= 4 m x 3.5 m = 14 sq m
Hence, the area of the carpet needed = 14 sq m
Ex 10.3 Class 6 Maths Question 8.
A floor is 5 m long and 4 m wide. A square carpet of sides 3 m is laid on the floor. Find the area of the floor that is not carpeted.
Solution:
Length of the floor = 5 m
and its breadth = 4 m
∴ Area of the floor = length x breadth
= 5m x 4m = 20sqm
Side of the carpet = 3m
∴ Area of the square carpet = side x side = 3m x 3m = 9 sqm
∴ Area of the floor which is not carpeted = 20 sq m – 9 sq m
= 11 sq m.
Ex 10.3 Class 6 Maths Question 9.
Five square flower beds each of side 1 m are dug on a piece of land 5 m long and 4 m wide. What is the area of the remaining part of the land?
Solution:
Side of the square flower bed = 1 m.
∴ Area of 1 square flower bed = 1m x 1m = 1sqm.
∴ Area of 5 square flower beds = 1 sq m x 5 = 5 sq m.
Now length of the land = 5 m
and its breadth = 4 m
∴ Area of the land = length x breadth =5m x 4m = 20 sq m
∴ Area of the remaining part of the land = 20 sq m – 5 sq m
= 15 sq m.
Ex 10.3 Class 6 Maths Question 10.
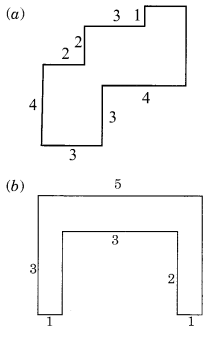
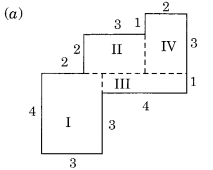
By splitting the following figures into rectangles, find their areas (The measures are given in centimetres).
Solution:
Splitting the given figure into the rectangles I, II, III and IV, we have
Area of the rectangle I = length x breadth
= 4 cm x 3 cm = 12 sq cm
Area of the rectangle II = length x breadth
= 3 cm x 2 cm = 6 sq cm.
Area of the rectangle III = length x breadth
= 4 cm x 1 cm = 4 sq cm
Area of the rectangle IV = length x breadth
= 3 cm x 2 cm = 6 sq cm
∴ Total area of the whole figure
= 12 sq cm + 6 sq cm + 4 sq cm + 6 sq cm
= 28 sq cm.
(b) Splitting the given figure into the rectangles I, II and III, we get
Area of the rectangle I
= 12 cm x 2 cm = 24 sq cm
Area of the rectangle II
= 8 cm x 2 cm = 16 sq cm
Area of rectangle III
= 3 cm x 1 cm = 3 sq cm
∴ Total area of the given figure = 3 sq cm + 3 sq cm + 3 sq cm = 9 sq cm.
Ex 10.3 Class 6 Maths Question 11.
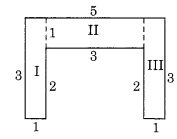
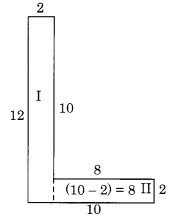
Split the following shapes into rectangles and find their areas (The measures are given in centimetres).
Solution:
(a) Splitting the given figure into the rectangles I and II, we get
Area of the rectangle I
= 12 cm x 2 cm = 24 sq cm
Area of the rectangle II
= 8 cm x 2 cm = 16 sq cm
∴ Total area of the whole figure = 24 sq cm + 16 sq cm = 40 sq cm.
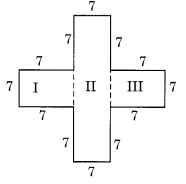
(b) Splitting the given figure into the rectangles I, II and III, we get
Area of the rectangle I
= 7 cm x 7 cm = 49 sq cm
Area of the rectangle II
= 21 cm x 7 cm = 147 sq cm
Area of the rectangle III
= 7 cm x 7 cm = 49 sq cm
∴ Total area of the whole figure
= 49 sq cm + 147 sq cm + 49 sq cm
= 245 sq cm.
Ex 10.3 Class 6 Maths Question 12.
How many tiles whose length and breadth are 12 cm and 5 cm respectively will be needed to fit in a rectangular region whose length and breadth are respectively:
(a) 100 cm and 144 cm
(b) 70 cm and 36 cm
Solution:
Length of one tile = 12 cm
Breadth of the tile = 5 cm
∴ Area of 1 tile = length x breadth = 12 cm x 5 cm = 60 sq cm
(a) Length of the rectangular region = 144 cm
Breadth of the region = 100 cm
∴ Area of the rectangular region = length x breadth = 144 cm x 100 cm
= 14400 sq cm
∴ Number of tiles needed to cover the whole rectangular region
= 14400 sq cm ÷ 60 sq cm
= 240 tiles
(b) Length of the rectangular region = 70 cm
Breadth of the region = 36 cm
∴ Area of the rectangular region = length x breadth = 70 cm x 36 cm = 2520 sq cm
∴ Number of tiles needed to cover the whole rectangular region
= 2520 sq cm ÷ 60 sq cm
= 42 tiles.


Leave a Reply