Solutions For All Chapters Maths Class 6
NCERT Solutions For Class 6 Maths Practical Geometry Exercise 14.6
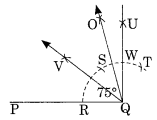
Ex 14.6 Class 6 Maths Question 1.
Draw ∠POQ of measure 75° and find its line of symmetry.
Solution:
Step I : Draw a line segment P̅Q̅ .
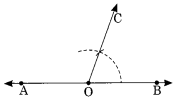
Step II : With centre Q and suitable radius, draw an arc to cut PQ at R.
Step III : With centre R and radius of the same length, mark S and T on the former arc.
Step IV : With centres S and T and with the same radius, draw two arcs which meet each other at U.
Step V: Join QU such that ∠PQU = 90°.
Step VI : With centres S and W, draw two arcs of the same radius which meet each other at Q.
Step VII: Join Q and O such that ∠PQO = 75°.
Step VIII: Bisect ∠PQO with QV.
Thus, OV is the line of symmetry of ∠PQO.
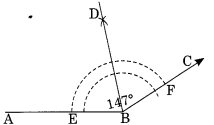
Ex 14.6 Class 6 Maths Question 2.
Draw an angle of measure 147° and construct its bisector.
Solution:
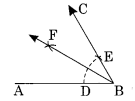
Step I : Draw ∠ABC = 147° with the help of protractor.
Step II : With centres B and radius of proper length, draw an arc which meets AB and AC at E and F respectively.
Step III : With centres E and F and the radius more that half of the length of arc EF, draw two arcs which meet each other at D.
Step IV : Join B and D.
Thus, BD is the bisector of ∠ABC.
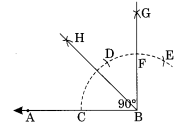
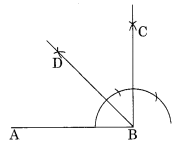
Ex 14.6 Class 6 Maths Question 3.
Draw a right angle and construct its bisector.
Solution:
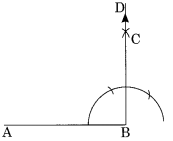
Step I: Draw a line segment AB.
Step II : With centre B and proper radius draw an arc to meet AB at C.
Step III : With centre C and same radius, mark two marks D and E on the former arc.
Step IV : With centres D and E and the same radius, draw two arcs which meet each other at G.
Step V : Join B and G such that ∠ABG = 90°
Step VI : Draw BH as the bisector of ∠ABG such that ∠ABH = 45°.
Thus ∠ABG is the right angle and BH is the bisector of ∠ABG.
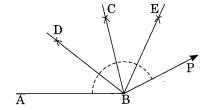
Ex 14.6 Class 6 Maths Question 4.
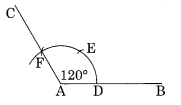
Draw an angle of 153° and divide it into four equal parts.
Solution:
Step I : Draw ∠ABP = 153° with the help of protractor.
Step II : Draw BC as the bisector of ∠ABP which dividers ∠ABP into two equal parts.
Step III : Draw BD and BE as the bisector of ∠ABC and ∠CBP respectively.
Thus, the bisectors BD, BC and BE divide the ∠ABP into four equal parts.
Ex 14.6 Class 6 Maths Question 5.
Construct with ruler and compasses, angles of the following measures:
(a) 60°
(b) 30°
(c) 90°
(d) 120°
(e) 45°
(f) 135°
Solution:
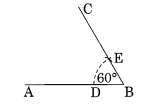
(a) Angle of 60°
Step I: Draw a line segment A̅B̅ .
Step II : With centre B and proper radius draw an arc.
Step III : With centre D and radius of the- same length mark a point E on the former arc.
Step IV : Join B to E and product to C. Thus ∠ABC is the required angle of measure 60°.
(b) Step I: Draw ∠ABC = 60° as we have done in section (a).
Step II: Draw BF as the bisector of ∠ABC.
Thus ∠ABF = 60/2 = 30°.
(c) Angle of 90°
In the given figure,
∠ABC = 90°(Refer to solution 3)
(d) Angle of 120°.
Step I: Draw A̅B̅
Step II : With centre A and radius of proper length, draw an arc.
Step III : With centre D and the same radius, draw two mark E and F on former arc.
Step IV : Join A to F and produce to C. Thus ∠CAB = 120°
(e) Angle of 45s, i.e., 90/2 = 45°
In the figure ∠ABD = 45° (Refer to solution 3)
(f) An angle of 135°
Since 135° = 90° + 45°
= 90° + (90/2)°
In this figure ∠ABC = 135°
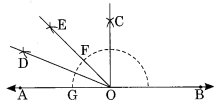
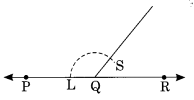
Ex 14.6 Class 6 Maths Question 6.
Draw an angle of measure 45° and bisect it.
Solution:
Step I : Draw a line AB and take any point O on it.
Step II: Construct ∠AOE = 45° at O.
Step III: With centre O and proper radius, draw an arc GF.
Step IV : With centres G and F and proper radius, draw two arcs which intersect each other at D.
Step V : Join O to D.
Thus ∠AOE = 45° and OD is its bisector.
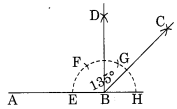
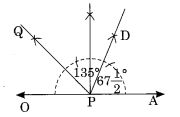
Ex 14.6 Class 6 Maths Question 7.
Draw an angle of measure 135° and bisect it.
Solution:
Steps I: Draw a line OA and take any point P on it.
Step II: Construct ∠APQ = 135°.
Step III : Draw PD as the bisector of angle APQ.
Thus ∠APQ = = 67
.
Ex 14.6 Class 6 Maths Question 8.
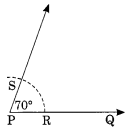
Draw an angle of 70°. Make a copy of it using only a straight edge and compasses.
Solution:
Step I : Draw a line AB and take any point 0 on it.
Step II : Draw ∠COB = 70° using protractor.
Step III: Draw a ray
Step IV: With centre O and proper radius, draw an arc which meets and
at E and F respectively.
Step V : With the same radius and centre at P, draw an arc meeting at R.
Step VI: With centre R and keeping and radius equal to EF, draw an arc intersecting the former arc at S.
Step VII : Join P and S and produce it. Thus, QPS is the copy of AOB = 70°.
Ex 14.6 Class 6 Maths Question 9.
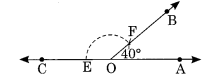
Draw an angle of 40°. Copy its supplementary angle.
Solution:
Step I: Construct ∠AOB = 40° using protractor.
∠COF is the supplementary angle of ∠AOB.
Step II : Draw a ray and take any point Q on it.
Step III : With centre O and proper radius, draw an arc which intersects and
at E and F respectively.
Step IV : With centre Q and same radius, draw an arc which intersects at L.
Step V: With centre L and radius equal to EF, draw an arc which intersects the former arc at S.
Step VI : Join Q and S and produce.
Thus, ∠PQS is the copy of the supplementary angle COB.

Leave a Reply