Notes For All Chapters – Maths Class 6 Ganita Prakash
1. Introduction to Symmetry:
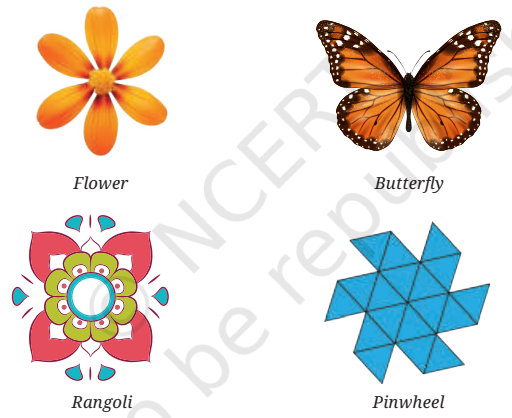
- Symmetry refers to a figure or object where parts are repeated in a definite pattern. Examples include butterflies, flowers, pinwheels, and rangoli designs.
- Objects without a repetitive pattern, like clouds, are not symmetrical.
2. Line of Symmetry:
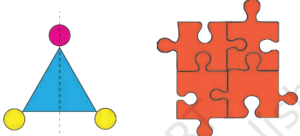
- A line of symmetry divides a figure into two parts that perfectly overlap when folded along that line.
- Example: A triangle can have a vertical line of symmetry, while a puzzle piece may not align when folded.
3. Multiple Lines of Symmetry:
- Figures can have more than one line of symmetry. For example:
- A square has four lines of symmetry: vertical, horizontal, and along both diagonals.
- A rectangle has only two lines of symmetry: vertical and horizontal.
- Reflection: Symmetry can be described as a reflection where one part of the figure mirrors the other.
4. Generating Symmetrical Shapes:
- Ink Blot Technique: Fold a paper, drop ink on one side, and fold again to create symmetrical patterns.
- Paper Cutting: Fold and cut paper to create symmetric designs when unfolded. This technique is used for decorative purposes like festive decorations.
5. Symmetry in Everyday Objects:
- Objects such as the Taj Mahal or the Gopuram display symmetry. Identify lines of symmetry in such structures.
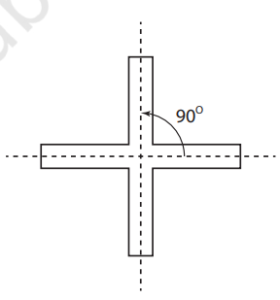
6. Rotational Symmetry:
- A figure has rotational symmetry if it looks the same after being rotated by a certain angle.
- The centre of rotation is the fixed point around which the figure rotates.
- Example: A square has four angles of symmetry: 90°, 180°, 270°, and 360°
7. Angles of Symmetry:
- The angle of symmetry is the smallest angle through which a figure can be rotated to look exactly the same. For example:
- A windmill has angles of symmetry at 90°, 180°, 270°, and 360°.
- A hexagon with equal sides has six angles of symmetry.
8. Symmetry in Radial Arms:
- Figures with radial arms (like a fan) can have multiple angles of symmetry. For example:
- A figure with 3 radial arms has angles of 120°, 240°, and 360°.
9. Symmetry of Circles:
- A circle has infinite angles of symmetry, as it can be rotated by any angle and still coincide with its original position.
- Every diameter of a circle acts as a line of symmetry.
10. Summary:
- Line of symmetry divides a figure into two identical parts.
- Rotational symmetry occurs when a figure looks the same after being rotated by a certain angle.
- Figures may have both lines of symmetry and angles of symmetry, but not necessarily both.
- Circle: The most symmetrical shape, with infinite rotational and reflectional symmetries.




Leave a Reply